Petya virus (Updated) - Bonus: Decryption Steps
Petya virus Removal Guide
What is Petya virus?
Petya – a dangerous ransomware virus that launched first worldwide attack in 2016
Petya is a file-encrypting virus that was first discovered in 2016. Since then, this ransomware[1] has been updated a couple of times. Among variants of malware are PetrWrap, GoldenEye, Mamba virus, Mischa, Diskcoder.D, or Bad Rabbit. The crypto-virus launched massive worldwide campaigns and affected organizations and companies in Ukraine, Russia, Spain, Denmark, etc. The purpose of this malware is the same as any other cyber threat that belongs to the same category – to encrypt files and make victims pay the ransom.
| Summary of the virus | |
|---|---|
| Name | Petya |
| Alternative names | NotPetya |
| Type | Ransomware |
| Release date | 2016 |
| Versions | PetrWrap, GoldenEye, Mamba, Mischa, BadRabbit |
| Encryption algorithm | RSA-4096 and AES-256 |
| File extension | .encrypted |
| Ransom note | YOUR_FILES_ARE_ENCRYPTED.HTML, YOUR_FILES_ARE_ENCRYPTED.TXT |
| Distribution | Malicious spam emails |
| Targeted countries | Ukraine, Russia, UK, Spain, Denmark, the Netherlands, India, etc. |
| Decryption | The original version of the virus is not decryptable; however, some of the variants can be recovered for free |
| To remove malware, install SpyHunter 5Combo Cleaner and run a full system scan. To fix up corrupted Windows system files, we recommend FortectIntego repair tool | |
The rise of the strain started similarly to WannaCry – the outbreak was spotted out of nowhere and continued spreading rapidly. Some anti-virus tools identify the threat as NotPetya and Nyetya ransomware. However, it is already known that it spreads via malicious spam emails and uses RDP attacks to compromise computers.
When the original version of malware emerged, it possessed a “kill disk” feature. In other words, even it encrypted files, it did not manage the proper communication with Command and Control servers to monitor victim identification numbers.
Likewise, ExPetr/NotPetya/Petna messed with the ID process[2]. What is more, one of the email domains associated with the perpetrators was canceled. In short, due to these factors, data recovery becomes impossible as a victim computer is not assigned a specific code that would help retrieve the matching decrypter.[3]
The malware simply generates random numbers and characters instead of a specific key. In other words, IT specialists call the malware to be a data wiper, though technically, it just makes the data recovery is futile. Lastly, due to the scale of inflicted damage, experts speculate that the threat used a mixture of exploits: PSExec, WMI, and Eternal Blue, to target SMB and local networks.[4]. Thus, there is no point in remitting the payment as affected users will not recover their data.
The ransomware has already infected several banks, power suppliers, the companies “Rosneft,” “Maersk, “Saint – Gobain” and other companies.[5] Ukraine software company MeDoc has been accused of releasing the virus.[6] Though the company denied such allegations, some IT experts claim to have evidence revealing that the firm was the initial source.
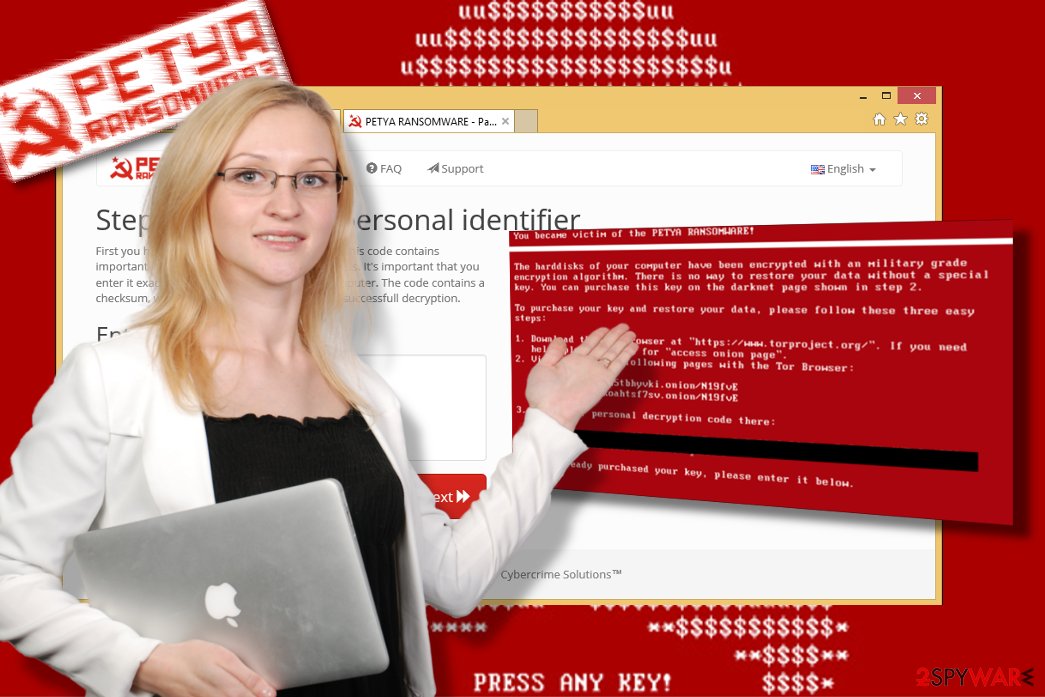
The operation of ransomware
Unlike the other ransomware programs, this malware immediately restarts the computer. When it boots it again, a message shows up on the screen saying:
DO NOT TURN OFF YOUR PC!
IF YOU ABORT THIS PROCESS, YOU COULD DESTROY ALL OF YOUR DATA!
PLEASE ENSURE THAT YOUR POWER CABLE IS PLUGGED IN!
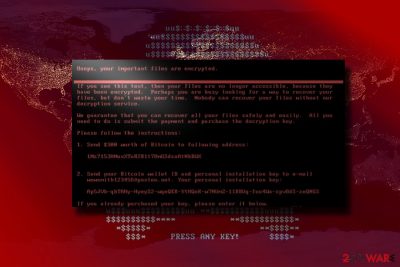
Even though it may look like a system error, in fact, at a given moment, the virus is silently carrying out file encryption in the system’s background. If the user tries to reboot the system or the file encryption is executed, a flashing red skeleton appears on the screen along with the text “PRESS ANY KEY!”. After pressing the key, a new window with a ransom note appears.
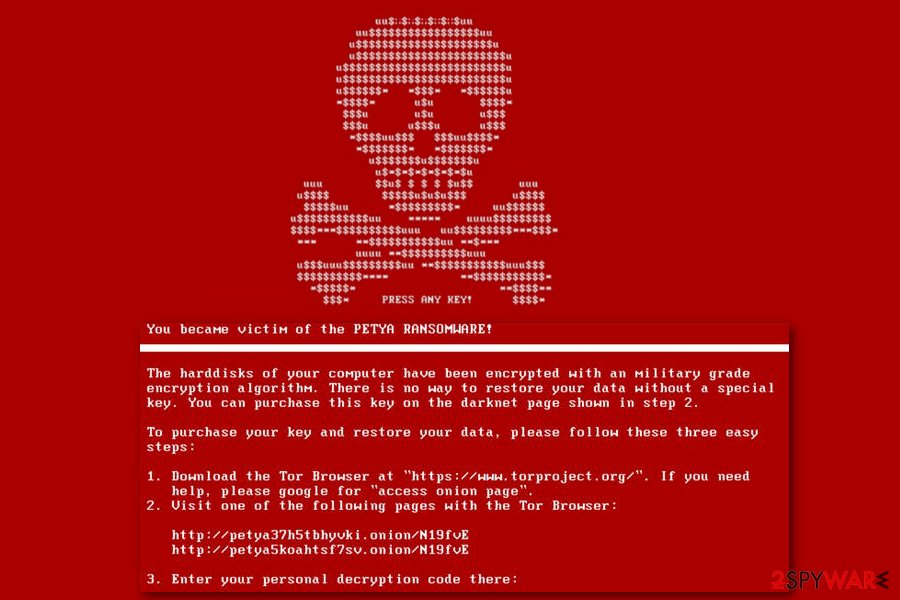
At the beginning of its functionality, the victim was typically asked to pay 0,9 BitCoin, which equaled around $400. However, now it requires $300 in Bitcoin. Therefore, different companies, which have numerous computers, can be required a different amount of ransom.
The ransomware encrypts files with very complex RSA-4096 and AES-256 [7] algorithms, even used for military purposes. Such code is impossible to decrypt without a private key. Of course, typically to other ransomware programs like Locky virus, CryptoWall virus, and CryptoLocker, this private key is stored on some remote server, which can only be accessed by paying a ransom to the virus creators.
Data encryption is not the only task for ransomware
Once this virus is in the system, it will try to overwrite the Windows boot files or the so-called master boot record [8] required to load your operating system. You will not be able to remove the virus from your computer unless you restore your MBR settings.
Even if you manage to fix these settings and delete the virus from your system, unfortunately, your files will remain locked because virus removal does not decrypt the encrypted documents but merely deletes the infectious files. Of course, this procedure is essential if you want to continue using your computer. We advise using sophisticated and reputable antivirus tools like SpyHunter 5Combo Cleaner to take care of virus removal.
Security experts have just announced about the ransomware decryption key, which can help you decrypt your files with the special algorithm. To get a chance to use this algorithm, you need to visit this website. However, the decryption of your files shouldn't be your only headache.
You should also make sure that you remove the ransomware from your computer before starting the second encryption of your files. If you find any trouble while performing the removal, check the detailed guide on the second page of this post.
Bad Rabbit ransomware
The recent reports state that the latest version of Petya ransomware hit Kyiv Metro and Odesa International Airport on the 24th of October. Even though the majority of attacks were reported in Russia (66%) and Ukraine (12.2%), other countries such as Bulgaria, Turkey, and Japan[9] suffered from Bad Rabbit ransomware too.
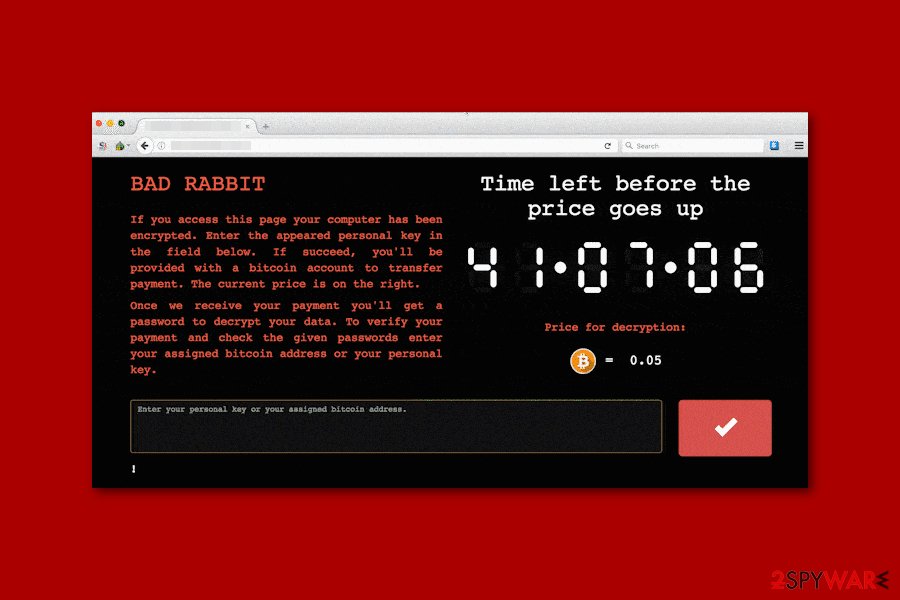
Malware spreads via fake Flash update that is available on corrupted websites. The Bad Rabbit virus is executed from the install_flash_player.exe that is installed to the Win32/Filecoder.D directory. Additionally, malware scans an internal network for open Windows' Server Message Block (SMB) shares. The same infiltration strategy was used by WannaCry, and there’s no doubt that it was more than successful. However, this version of malware does not exploit the EthernalBlue vulnerability.
The virus performs full drive encryption using the DiskCryptor and a combination of RSA-2048 and AES-128-CBC cryptography. To the targeted files, it also appends a .encrypted file extension. Apart from taking files hostage, the malware also uses the Mimikatz tool to collect credentials, including usernames and passwords.
Following data encryption, malware delivers a ransom note that redirects to the payment website. Victims are asked to transfer 0.05 Bitcoins in order to get a decryption password. People have 41 hours until the size of the ransom increases. However, paying the ransom is not recommended.
Authors of malware launched new ransomware campaign in June 2017
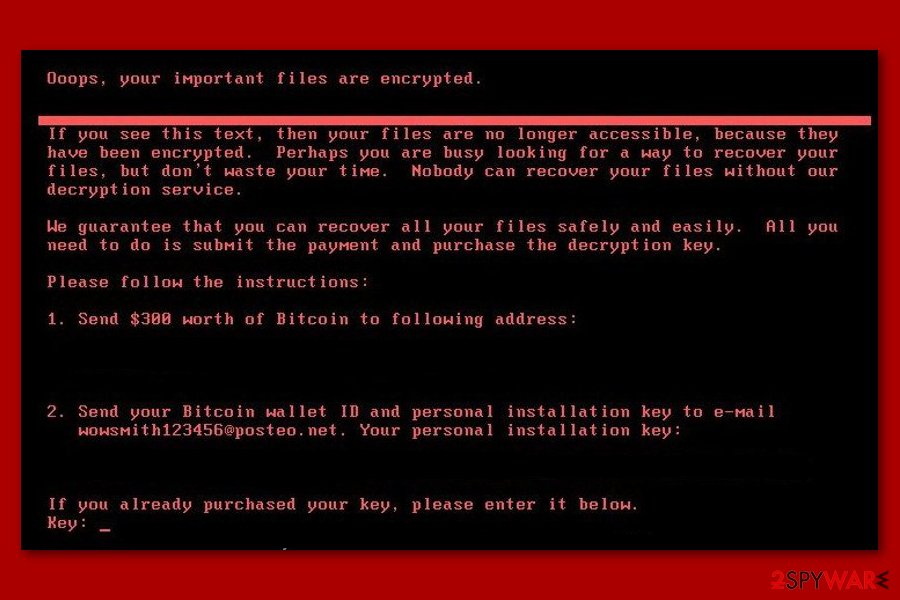
In June 2016, cybercriminals updated their creation. Then they used the wowsmith123456@posteo.net email address to collect ransoms. It requires paying $300 in Bitcoin in exchange for recovering the connection to victims' data. Ukraine, UK, Spain, Denmark, the Netherlands, India, and other countries have already approved the attack.
The ransomware does not encrypt victim's files one by one – this is clear evidence showing that the virus was recently updated. Instead, it reboots the computer first and then encrypts the MFT (master file table) of the hard drive. The MBR (master boot record) stops operating what causes failure when trying to seize the needed information about files, like their names, sizes, and location.
You can still get infected with the ransomware virus after downloading a fake office document, so be sure to be careful with unknown emails. However, The Hacker News has reported that the virus DOES use the same Windows SMBv1 vulnerability which was used by the WannaCry infection.[10] To protect yourself, make sure you install SpyHunter 5Combo Cleaner, Malwarebytes, or another reputable security software on the system.
UPDATE: According to IT expert Lawrence Abrams, there is a solution preventing the attack – netizens should create a text file entitled as perfc and place in in C:Windows folder.[11] It seems that ransomware removes itself if it detects such a file on the system.
UPDATE July 2017: After a long wait, malware analysts finally release a decryptor for the virus, and it promises to decrypt files that have been processed by the ransomware's malicious code. The Petya Decryptor comes in two basic forms: a CD version and a Windows executable file. We should note that this tool is merely designed to extract the individual decryption key. At the same time, the data recovery can be performed using the decryption software, including Mischa and GoldenEye decrypters. More detailed instructions on how to use these tools are provided in the instruction section of our article.
Unfortunately, the decryptor is still powerless against hybrid ransomware versions.
Petya virus victim list
| Victims | |
| M.E.Doc servers | The attack originates in Ukraine. It started spreading on 18 June (or earlier) as an update for a popular M.E.Doc accounting software package. |
| The National Bank of Ukraine | Later, the National Bank of Ukraine announces about the “external cyber attack.” It warns financial institutions to be extra careful with the malware attack. |
| Oshchadbank state bank | After one hour, Oshchadbank state bank reports about the limited functionality services for its clients because of ransomware virus. |
| Cabinet of Ministers of Ukraine | The members of the Ministry of Ukraine start tweeting of their computers locked by ransomware. |
| Maersk | Next, the virus moves on and infects container transportation giant Maersk in Netherlands and Denmark. The company stops all container operations. |
| Rosneft | Russian oil giant Rosneft confirms attacks on the same day. |
| DLA Piper | DLA Piper, a global business law firm, reports about malware attack. The company takes down its servers. |
| Mondelez | Mondelez offices report about the ransomware attack on 27, June. The attacks disabled its servers. |
| WPP | A popular marketing company in UK, WPP, reports about a suspected cyber attack. |
| Kiev Metro | Kiev Metro was reported to suffer from Bad Rabbit attack on 24th of October. |
| Odessa International Airport | Odessa International Airport also reported that they were hit by ransomware on the same day in October. |
Unfortunately, the number of victims is still growing. Not all of them have reported about problems related to this malware strain. However, it is believed that there are several thousand companies infected with this ransomware.
The list of ransomware variants
This ransomware has been growing ever since it hit the Internet in 2016 – the developers of malware have already released these supplementary ransomware versions:
Mischa ransomware was spotted in May 2016. It is known to be a part of Janus Cybercrime Solutions campaign[12] which allows wannabe hackers to join the affiliate network of malware. However, to become one of its distributors, you need to pay a registration fee.
Depending on the volume of the ransom payment, the users can earn up to 85% of the revenue share for spreading the virus around the Internet. If you even consider becoming an affiliate of such a nasty company, keep in mind that its creators hold nothing sacred and can easily take advantage of you as well, so be very careful.
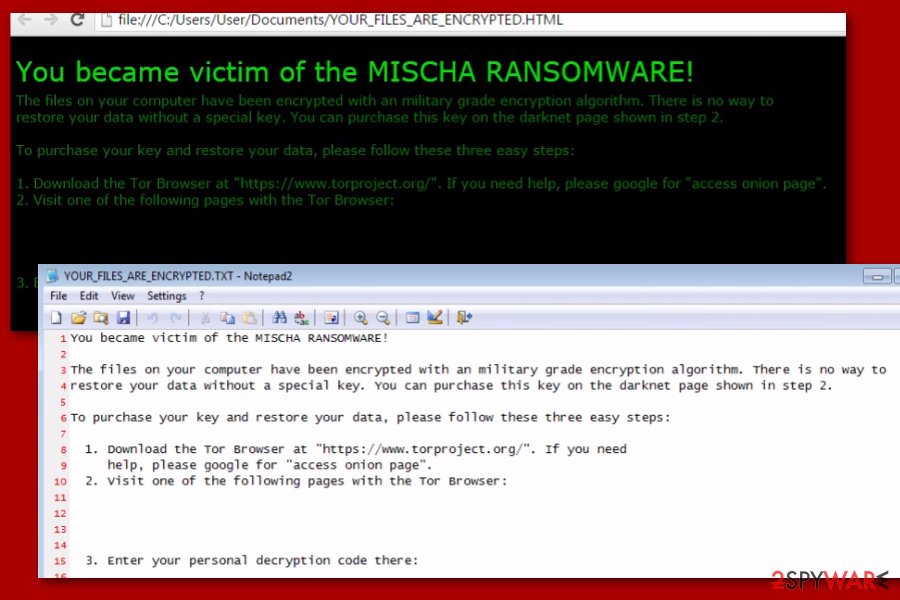
Petrwrap ransomware does not belong to Janus Cybercrime Solutions campaign, which is considered as an affiliate network of the ransomware. It is a separate virus that is based on the altered ECDH algorithm letting its developers generate private and public keys outside the RaaS system.
The malware has been using a vulnerable RDP network and the PsExec tool to infiltrate target PC systems and launch the virus. Nevertheless, it is also possible to get the malware after downloading an infected email attachment.
GoldenEye ransomware virus is very similar to Petya. To show the victim his or her loss, it appends specific file extensions to the target files. The virus also bypasses User Account Control (UAC) to implement a low-level attack and drop the ransomware on the system. If the UAC is set to the maximum, the victim is asked to allow the malicious program to make changes on the computer repeatedly. The “Yes” will execute the malware.
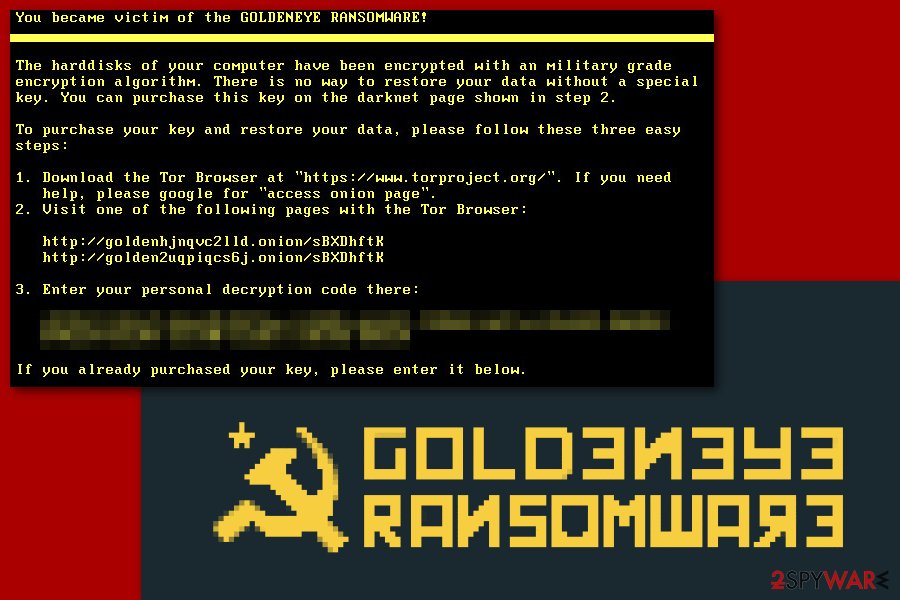
Mamba ransomware itself is extremely dangerous and may infect practically any PC, but its primary targets are the computers of German companies. This malicious program enters the victims’ computers stealthily and carries out its malicious activities without the computer owner even suspecting the computer might be under threat.
In this version, hackers finally managed to apply a Salsa20 encryption algorithm eliminating the previous vulnerabilities of the malware. Otherwise, the virus functions similarly to its previous version, spreading in the form of a corrupted PDF file. The virus developers have been mainly using spam emails and fake software updates to spread the threat.
Bad Rabbit ransomware virus is also known as Diskcoder.D. It was discovered on October 2017 when it hit organizations in Russia and Ukraine. Malware uses a combination of AES and RSA encryption ciphers and appends .encrypted file extensions. This version of malware spreads via fake Flash updates and can exploit SMB vulnerabilities. Additionally, it can not only encrypt files and demand to pay 0.05 Bitcoins but steal credentials.
Malware mostly spreads via malicious spam emails
Petya virus is usually distributed through spam emails, which contain a Dropbox download link to a file called “application folder-gepackt.exe” attached to them. The virus activates when the mentioned file is downloaded and opened. However, the latest version of this virus uses the CVE-2017-0199 Office RTF vulnerability to infiltrate a computer.
As you already know how this virus spreads, you might already have an idea how to protect your computer from this virus attack. Of course, you need to be careful about opening emails that are received from suspicious and unknown sources, feature supposedly relevant information which does not relate to your expected correspondence[13].
You should also be sure to download MS17-010 and other Microsoft patches to fix SMB vulnerability. It is believed to be one of the ransomware sources at the moment. Finally, make sure you equip your system with reputable antivirus software and keep it up to date.
To protect your files from being encrypted, it is always recommended to backup them from time to time. In this case, you should make sure that your important pieces of data are stored in three physical places, such as the cloud, some external drive, etc.
Petya removal guide and data recovery possibilities
As we already mentioned, uninstalling the ransomware from your computer is essential for the safety of your future files. Also, restoring data from external drives can only be carried out when the virus and all its related parts are fully eliminated from the PC. Otherwise, it may infiltrate and lock the files in these external platforms as well.
You cannot remove it from your computer through the simple uninstall procedure because such option is not feasible with this malicious program. This means that you will have to delete the virus automatically. Automatic malware removal should be carried out using some trusted antivirus software, which will detect and delete this virus from your computer. For this tasks, we recommend FortectIntego, SpyHunter 5Combo Cleaner or Malwarebytes.
If you are encountering some troubles removing this virus automatically or it blocks your antivirus from running, you can always check our detailed virus removal instructions provided at the end of this article.
Getting rid of Petya virus. Follow these steps
Manual removal using Safe Mode
To remove ransomware from Windows with the help of Safe Mode, keep in mind that this is a complex cyber infection. Don't expect it to give up your computer easily. To help you launch your anti-virus easier, use the following instructions:
Important! →
Manual removal guide might be too complicated for regular computer users. It requires advanced IT knowledge to be performed correctly (if vital system files are removed or damaged, it might result in full Windows compromise), and it also might take hours to complete. Therefore, we highly advise using the automatic method provided above instead.
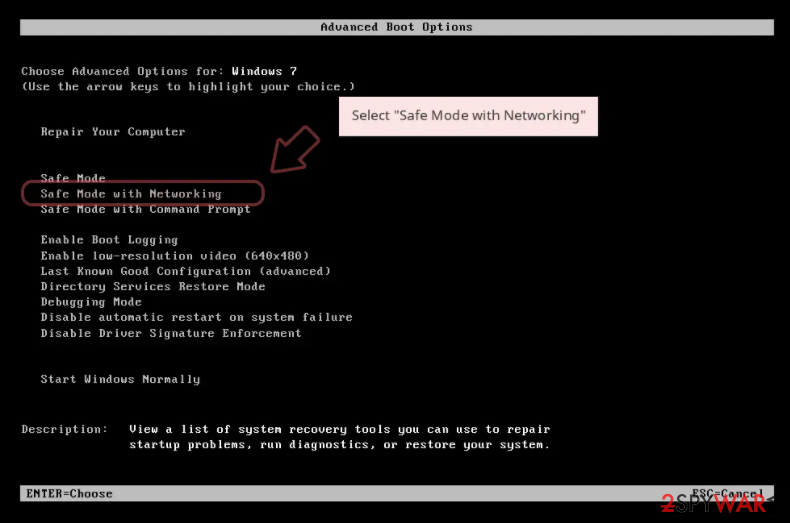
Step 1. Access Safe Mode with Networking
Manual malware removal should be best performed in the Safe Mode environment.
Windows 7 / Vista / XP
- Click Start > Shutdown > Restart > OK.
- When your computer becomes active, start pressing F8 button (if that does not work, try F2, F12, Del, etc. – it all depends on your motherboard model) multiple times until you see the Advanced Boot Options window.
- Select Safe Mode with Networking from the list.

Windows 10 / Windows 8
- Right-click on Start button and select Settings.

- Scroll down to pick Update & Security.

- On the left side of the window, pick Recovery.
- Now scroll down to find Advanced Startup section.
- Click Restart now.

- Select Troubleshoot.

- Go to Advanced options.

- Select Startup Settings.

- Press Restart.
- Now press 5 or click 5) Enable Safe Mode with Networking.

Step 2. Shut down suspicious processes
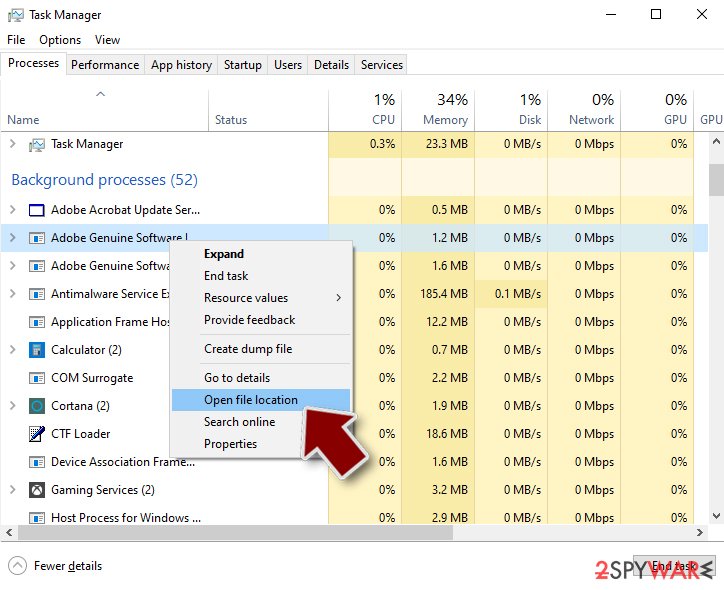
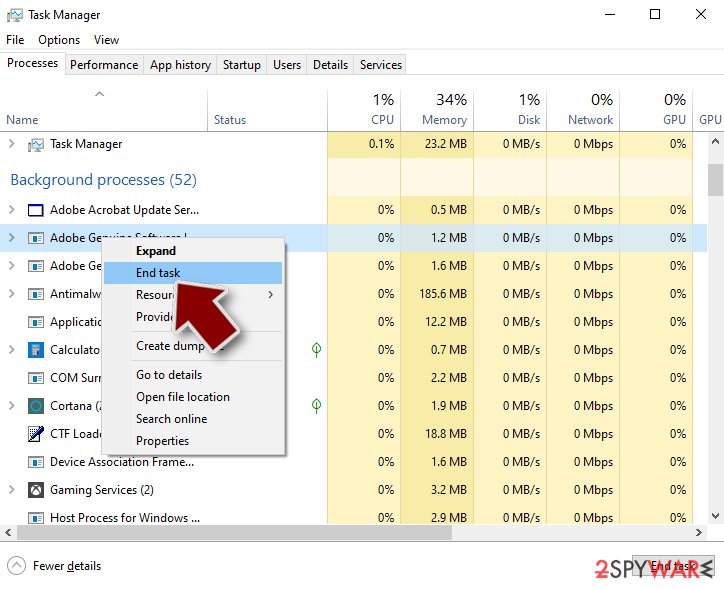
Windows Task Manager is a useful tool that shows all the processes running in the background. If malware is running a process, you need to shut it down:
- Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc on your keyboard to open Windows Task Manager.
- Click on More details.

- Scroll down to Background processes section, and look for anything suspicious.
- Right-click and select Open file location.

- Go back to the process, right-click and pick End Task.

- Delete the contents of the malicious folder.
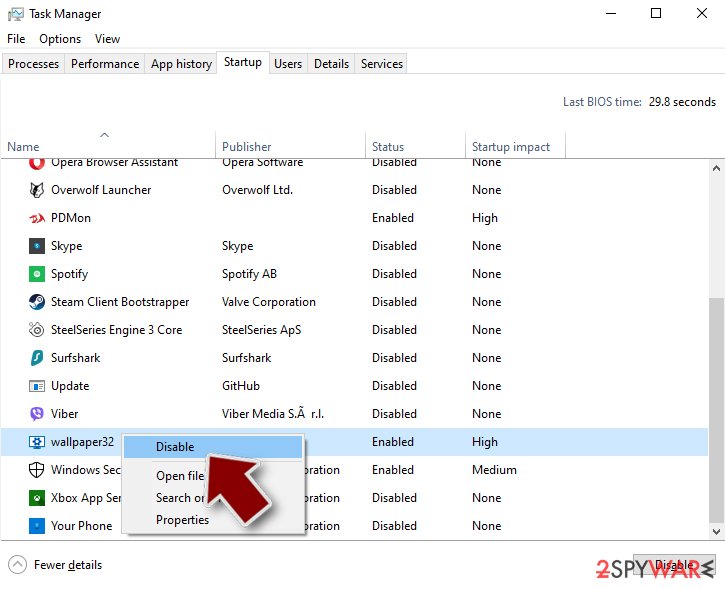
Step 3. Check program Startup
- Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc on your keyboard to open Windows Task Manager.
- Go to Startup tab.
- Right-click on the suspicious program and pick Disable.

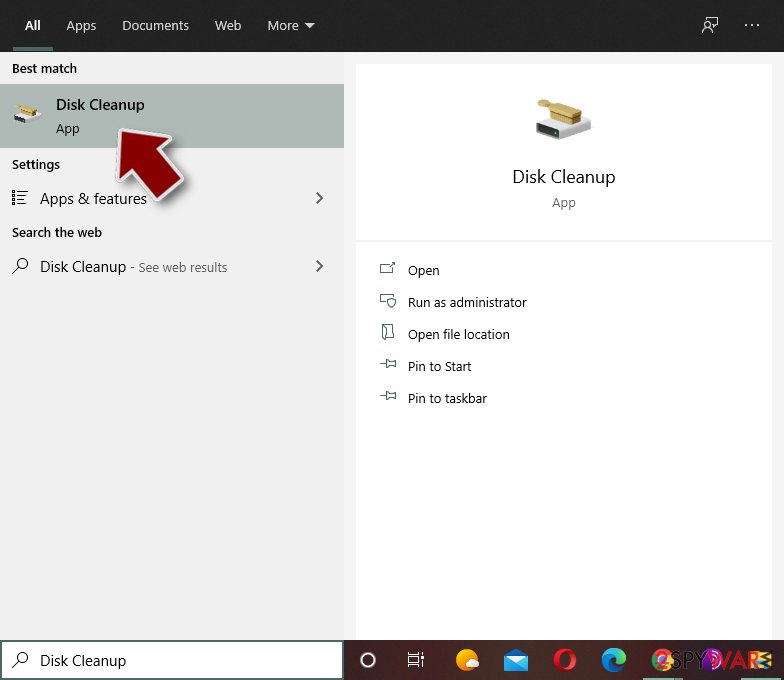
Step 4. Delete virus files
Malware-related files can be found in various places within your computer. Here are instructions that could help you find them:
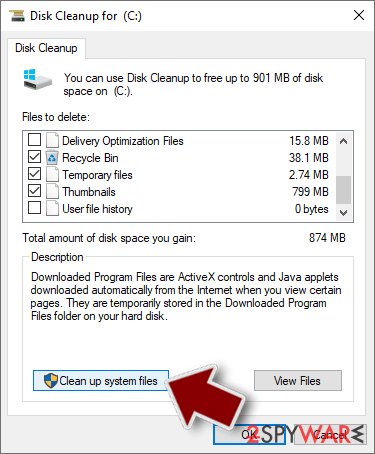
- Type in Disk Cleanup in Windows search and press Enter.

- Select the drive you want to clean (C: is your main drive by default and is likely to be the one that has malicious files in).
- Scroll through the Files to delete list and select the following:
Temporary Internet Files
Downloads
Recycle Bin
Temporary files - Pick Clean up system files.

- You can also look for other malicious files hidden in the following folders (type these entries in Windows Search and press Enter):
%AppData%
%LocalAppData%
%ProgramData%
%WinDir%
After you are finished, reboot the PC in normal mode.
Remove Petya using System Restore
To get rid of the malware with the help of System Restore, use the following steps. Keep in mind that it is one of the nastiest features of most ransomware which will try to prevent its removal from the infected device.
-
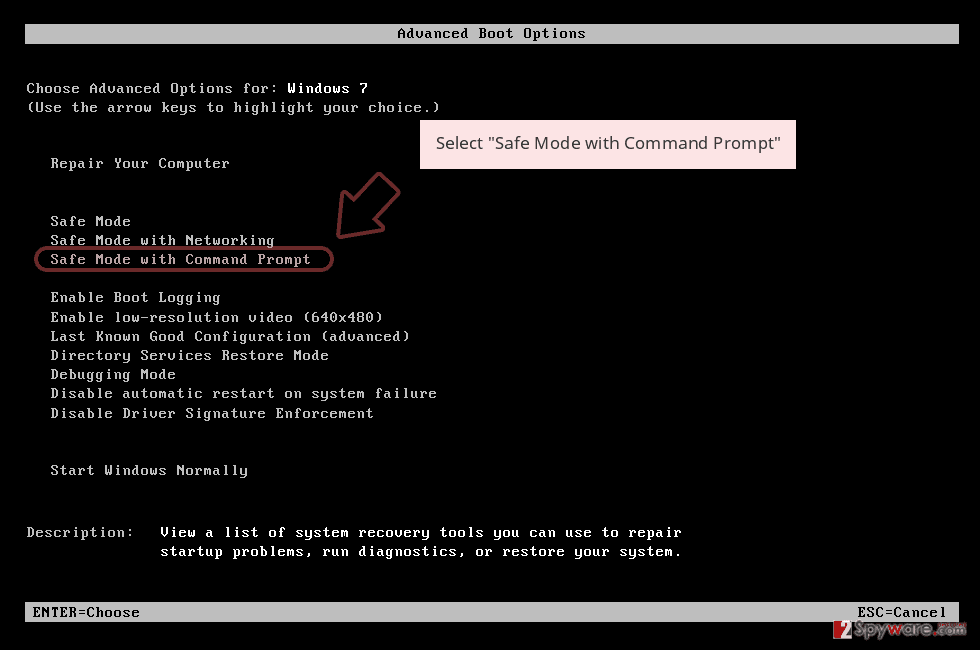
Step 1: Reboot your computer to Safe Mode with Command Prompt
Windows 7 / Vista / XP- Click Start → Shutdown → Restart → OK.
- When your computer becomes active, start pressing F8 multiple times until you see the Advanced Boot Options window.
-
Select Command Prompt from the list

Windows 10 / Windows 8- Press the Power button at the Windows login screen. Now press and hold Shift, which is on your keyboard, and click Restart..
- Now select Troubleshoot → Advanced options → Startup Settings and finally press Restart.
-
Once your computer becomes active, select Enable Safe Mode with Command Prompt in Startup Settings window.

-
Step 2: Restore your system files and settings
-
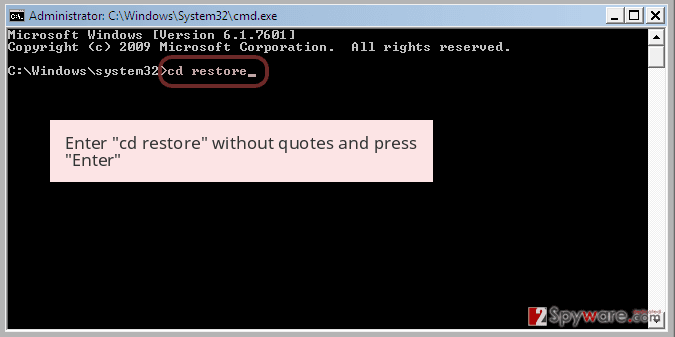
Once the Command Prompt window shows up, enter cd restore and click Enter.

-
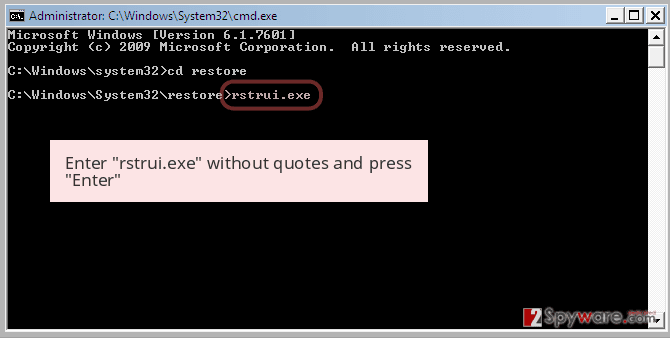
Now type rstrui.exe and press Enter again..

-
When a new window shows up, click Next and select your restore point that is prior the infiltration of Petya. After doing that, click Next.


-
Now click Yes to start system restore.

-
Once the Command Prompt window shows up, enter cd restore and click Enter.
Bonus: Recover your data
Guide which is presented above is supposed to help you remove Petya from your computer. To recover your encrypted files, we recommend using a detailed guide prepared by 2-spyware.com security experts.If your files are encrypted by Petya, you can use several methods to restore them:
What is the use of Data Recovery Pro?
Data Recovery Pro is probably the quickest solution to data decryption. It does not require any extra preparation or skill and is relatively effective when it comes to the file recovery process. Here is how to use it:
- Download Data Recovery Pro;
- Follow the steps of Data Recovery Setup and install the program on your computer;
- Launch it and scan your computer for files encrypted by Petya ransomware;
- Restore them.
Rescue your important files with Windows Previous Versions feature
Windows Previous Versions is one of the data recovery options Windows operating system offers as an in-built feature. Keep in mind that this recovery technique only works when the System Restore function is enabled. Do not hesitate to give it a try:
- Find an encrypted file you need to restore and right-click on it;
- Select “Properties” and go to “Previous versions” tab;
- Here, check each of available copies of the file in “Folder versions”. You should select the version you want to recover and click “Restore”.
ShadowExplorer to help decrypt encrypted files
Unfortunately, malware deletes Volume Shadow Copies of the files it encrypts so it is impossible to use ShadowExplorer for their recovery.
- Download Shadow Explorer (http://shadowexplorer.com/);
- Follow a Shadow Explorer Setup Wizard and install this application on your computer;
- Launch the program and go through the drop down menu on the top left corner to select the disk of your encrypted data. Check what folders are there;
- Right-click on the folder you want to restore and select “Export”. You can also select where you want it to be stored.
A decrypter for Mischa and Goldeneye versions now available
If files on your device have been encrypted by Goldeneye or Mischa versions, the first thing you should do is download the personal key extraction software and generate the decryption key. To make this work, follow this process:
1. Find out what your Victim ID is. It may be included in the ransom note or you may find it attached at the end of every encrypted document.
2. Copy the ID in a .txt file and then run the previously downloaded tool to generate the key.
3. Save the extracted key
When you are done with the key extraction, you can then proceed to the next data recovery step:
4. Obtain Mischa or Goldeneye decryption software
5. Select file you want to decrypt (we recommend making a copy of the files you want to decrypt in order to avoid decryption errors and the potential loss of data).
6. Submit the saved recovery key in the areas provided and click “Decrypt”.
7. If the outcome of the decryption is successful, continue the decryption of the rest of your computer files by supplying the decryptor with the extensions the virus has appended to the encrypted files.
Finally, you should always think about the protection of crypto-ransomwares. In order to protect your computer from Petya and other ransomwares, use a reputable anti-spyware, such as FortectIntego, SpyHunter 5Combo Cleaner or Malwarebytes
How to prevent from getting ransomware
Stream videos without limitations, no matter where you are
There are multiple parties that could find out almost anything about you by checking your online activity. While this is highly unlikely, advertisers and tech companies are constantly tracking you online. The first step to privacy should be a secure browser that focuses on tracker reduction to a minimum.
Even if you employ a secure browser, you will not be able to access websites that are restricted due to local government laws or other reasons. In other words, you may not be able to stream Disney+ or US-based Netflix in some countries. To bypass these restrictions, you can employ a powerful Private Internet Access VPN, which provides dedicated servers for torrenting and streaming, not slowing you down in the process.
Data backups are important – recover your lost files
Ransomware is one of the biggest threats to personal data. Once it is executed on a machine, it launches a sophisticated encryption algorithm that locks all your files, although it does not destroy them. The most common misconception is that anti-malware software can return files to their previous states. This is not true, however, and data remains locked after the malicious payload is deleted.
While regular data backups are the only secure method to recover your files after a ransomware attack, tools such as Data Recovery Pro can also be effective and restore at least some of your lost data.
- ^ Ransomware. Wikipedia. The free encyclopedia.
- ^ Catalin Cimpanu. Surprise! NotPetya Is a Cyber-Weapon. It's Not Ransomware. BleepingComputer. IT News, Reviews and Tech support.
- ^ Anton Ivanov, Orkhan Mamedov. ExPetr/Petya/NotPetya is a Wiper, Not Ransomware. SecureList. Information about viruses, hackers, and spam.
- ^ Petya-esque ransomware is spreading across the world. MalwarebytesLabs. The Security Blog from Malwarebytes.
- ^ Graham Cluley. Global ransomware outbreak happening right now. Graham Cluley blog.
- ^ Thomas Fox-Brewster. Is This Ukrainian Company The Source Of The 'NotPetya' Ransomware Explosion?. Forbes. Lifestyle, Entertainment, Finance, Business, Security.
- ^ AES vs RSA. Toolbox. IT Communities - Share Knowledge at Toolbox.com.
- ^ Pieter Arntz. Meet the Master Boot Record. Malwarebytes labs. The Security Blog From Malwarebytes.
- ^ Marc-Etienne M.Léveillé. Bad Rabbit: Not-Petya is back with improved ransomware. WeLiveSecurity. IT security site covering the latest news, research, cyber threats and malware discoveries.
- ^ Swati Khandelwal. Petya Ransomware Spreading Rapidly Worldwide, Just Like WannaCry. The hacker news. Security in a serious way.
- ^ Catalin Cimpanu. Vaccine, not Killswitch, Found for Petya (NotPetya) Ransomware Outbreak. BleepingComputer. News, Reviews and Tech Support.
- ^ Jim Walter. Petya and Mischa for all Part II: they’re here…. Cylance. Protect your endpoints against advanced malware with the world's first antivirus built on artificial intelligence and machine learning.
- ^ Email and web scams: How to help protect yourself. Microsoft support page.