Mischa ransomware / virus (Improved Instructions) - Jul 2017 update
Mischa virus Removal Guide
What is Mischa ransomware virus?
Mischa ransomware: Petya's evil little brother
Mischa ransomware is a computer virus, affectionally addressed by its creators as a “little brother” of the infamous Petya virus[1] which recently became even more dangerous by employing a new tactic for extorting money from the infected computer users. It installs the already mentioned Mischa virus if the infiltration of the initial ransomware is unsuccessful, this way, protecting itself against failure.
If you are not yet familiar with the mechanics of the ransomware viruses, you should know that these programs infiltrate the users’ computer by deception and encrypt the containing data using an algorithm which is, to this day, impossible to crack.
Finally, the victim receives a note, in which he/she finds an indicated sum of money the ransomware developers demand in exchange of the files. It is not recommended to follow any of these instructions as you may end up with no files and robbed of your money as well. Instead, you should remove the virus from your computer immediately. Sophisticated anti-malware tools, such as FortectIntego, may help you in the process.
Recently, the creators of Mischa and Petya viruses initiated a Janus Cybercrime Solutions campaign which offers the regular users to become affiliates in ransomware distribution. After issuing a registration fee, the user is granted the name of an official distributor and can start making money. The share affiliates receive is calculated according to the payment volume they manage to generate in a week.
The larger the volume, the more you earn. Though taking part in such shady businesses is, obviously, very dangerous and illegal, it is likely that some evil-minded individuals will sign up. Thus, these infections will become even more dangerous. We encourage you to take all measures possible to protect your system before it is too late.

How does this ransomware act on the infected computer?
Since the mechanics of Petya virus are much more complicated, and it requires to gain an administrative privilege to initiate its malicious processes, the rather simple way Mischa infiltrates the system is a convenient backup plan for the Petya virus.
Unlike Petya, which needs administrative privileges to modify the master boot record (MBR), Mischa is simply installed on the computer and immediately starts scanning it for files. This virus, as well as the majority of other ransomware, targets documents, videos, images, archives but may easily infect applications, i.e. the .exe files, as well.
Once the encryption is completed, an additional 4-digit extension is then added to the infected documents and applications. From this point on, the files on the computer are not accessible anymore.
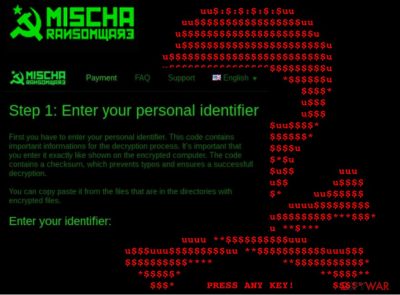
As soon as the users realize that they have lost access to their data, the ransomware drops documents labeled as YOUR_FILES_ARE_ENCRYPTED.HTML and YOUR_FILES_ARE_ENCRYPTED.TXT to every folder of the corrupted device. In these documents, the ransomware developers state their conditions. At the moment, the victims are asked to pay 1.93 Bitcoins (which is equal around $875 USD) for the decryption key.
However, there is no guarantee that the sum will not be increased. Next in the ransom note are the links to TOR network websites, through which the victim must transfer payment. The user is given a special code which he/she has to submit upon paying the ransom. Unfortunately, there is no way to decrypt the locked files without paying. But transferring money to some obscure cyber criminals’ account is not the best idea either.
The best option, in this case, is to remove Mischa virus from the infected computer and recover files from a backup. You can also try to restoring them using special data recovery tools.
Mischa returns in GoldenEye ransomware combo
GoldenEye is a ransomware duo including Petya and Mischa virus. Once run, the virus saves itself in %APPDATA% folder under the name of the random system application. It automatically launches and starts encrypting victim's files.
The malware attempts to bypass UAC and to launch the second attack using Petya ransomware.
The virus easily bypasses UAC if it is set to default or lower. In case it is set to max, the UAC window keeps appearing repeatedly until the victim allows the program to make changes to the computer.
During the data encryption process, Mischa creates a YOUR_FILES_ARE_ENCRYPTED.txt file with instructions on how to access darknet page with instructions on how to recover encrypted data. The virus corrupts each file with a new key or an initialization vector. Research suggests that the ransomware employs AES in CBC mode encryption algorithm.
The low-level part (in case the victim doesn't allow the program to make changes via UAC) uses Petya ransomware, which performs Master File Table encryption. The ransomware then displays a yellow blinking screen with a skull on it. The GoldenEye ransomware was later distributed via an affiliate scheme, although before it has been circulated via phishing emails mostly.
Mischa not involved in the latest global cyberattack
The cyber attack that took place on June 27-28 in 2017[2] has wreaked havoc on thousands of computers worldwide, primarily in Ukraine. Most affected countries were UK, Germany[3], France, and many others.
Presumptions that it was Petya ransomware were denied because it was actually a modified version of the virus. In fact, the developers of the real Petya/GoldenEye/Mischa viruses verified that the ransomware used in the cyber attack wasn't Petya.
Therefore, the infamous virus quickly dubbed as NotPetya or ExPetr. However, it shortly became clear that the ransomware used in June 2017 cyber attack wasn't even a ransomware – it worked as a wiper that destroys files and leaves no possibility to recover them.
It turned out that NotPetya was generated random code shown as victim's ID. It means that even cyber criminals cannot get any decryption information from such string; therefore they can't help victims even if they decide to pay the ransom. Apparently, if you became a victim, do not pay up. It won't help you to restore files no matter what.
The good thing is, after the global NotPetya attack, the developer of Petya/Mischa/GoldenEye released the master decryption key, allowing victims to retrieve their files for free. To recover files encrypted by this ransomware, use instructions provided below the article. Before you attempt to use the decrypter, take care of Mischa removal first.
How can Mischa infect your computer?
Usually, the malicious Petya-Mischa bundle travels via deceptive emails, which feature a link to an online cloud containing a PDF file of a supposed job application. In reality, there is no job application and by clicking the indicated link, the user simply downloads the executive virus file on the computer.
Once downloaded the file will look like a regular PDF document. If the user opens this file, a malicious script activates the virus, and the virus installation begins. First, the executive file will try to install Petya. If for some reason, that fails, Mischa ransomware will then be installed on the computer.
A way to avoid having your computer infected with a ransomware virus is by obtaining a reputable antivirus software, which will provide you with some extra protection against these viruses. Also, you should be especially careful with your email as well.
Stay away from the “Spam” catalog as most of the malicious emails usually end up there. You should always pay attention to the received emails, and look for clues such as grammar and spelling mistakes, insisting tone and similar suspicious characteristics. Most importantly, you should keep a backup of your files in some external storage drive and update it regularly.
However, we have to warn you not to leave the drive plugged in at all times because the Mischa virus can easily infiltrate and encrypt the files in your external drive as well.
Removing Mischa ransomware from the system
To make your PC function normally again, the only option you have is to remove Mischa virus from your computer. Unfortunately, the virus removal will not return your files, but if you want to keep using your device normally again, you must clear it of all the malicious components.
For that, you should use sophisticated and acknowledged antivirus utilities. But remember, this ransomware attempts to stop security programs from running, so your antivirus may struggle to remove the threat. In this case, you can try decontaminating the virus manually by closely following Mischa removal instructions provided below. Just do not forget to scan your computer after you remove the virus to make sure no malicious residue files are left on your PC!
Getting rid of Mischa virus. Follow these steps
Manual removal using Safe Mode
Removing Mischa can be hard. We strongly suggest you to reboot your PC into Safe Mode with Networking to initiate the removal process. Otherwise, you might not be able to run your security programs at all. Remember – do not attempt to remove the virus manually unless you are a professional malware analyst.
Important! →
Manual removal guide might be too complicated for regular computer users. It requires advanced IT knowledge to be performed correctly (if vital system files are removed or damaged, it might result in full Windows compromise), and it also might take hours to complete. Therefore, we highly advise using the automatic method provided above instead.
Step 1. Access Safe Mode with Networking
Manual malware removal should be best performed in the Safe Mode environment.
Windows 7 / Vista / XP
- Click Start > Shutdown > Restart > OK.
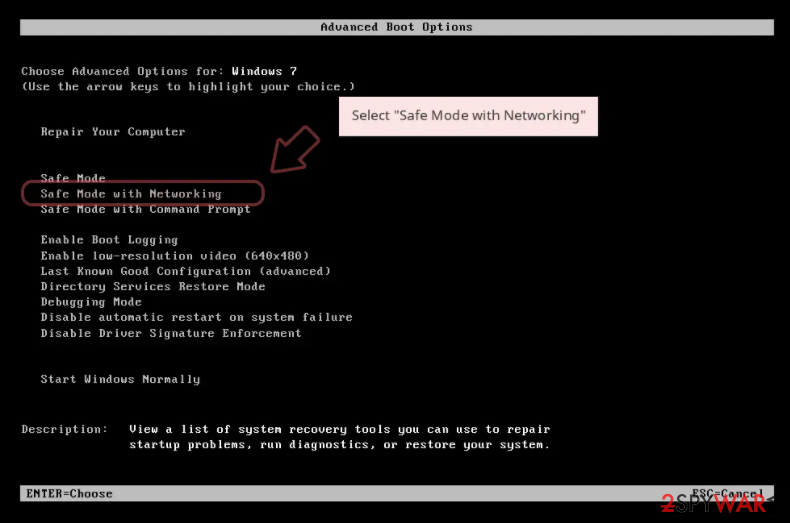
- When your computer becomes active, start pressing F8 button (if that does not work, try F2, F12, Del, etc. – it all depends on your motherboard model) multiple times until you see the Advanced Boot Options window.
- Select Safe Mode with Networking from the list.

Windows 10 / Windows 8
- Right-click on Start button and select Settings.

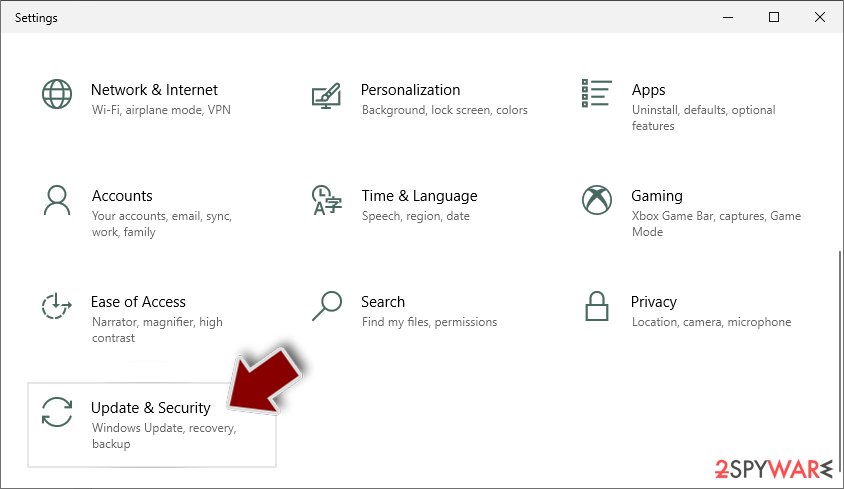
- Scroll down to pick Update & Security.

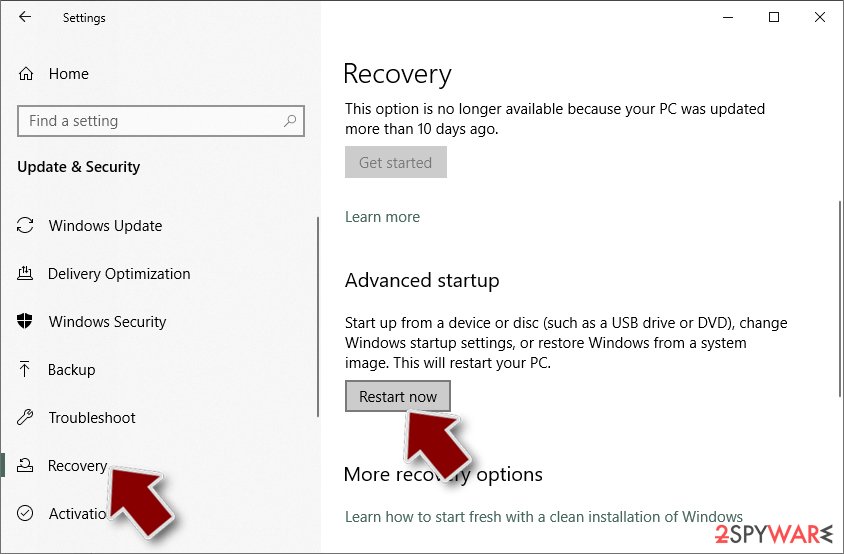
- On the left side of the window, pick Recovery.
- Now scroll down to find Advanced Startup section.
- Click Restart now.

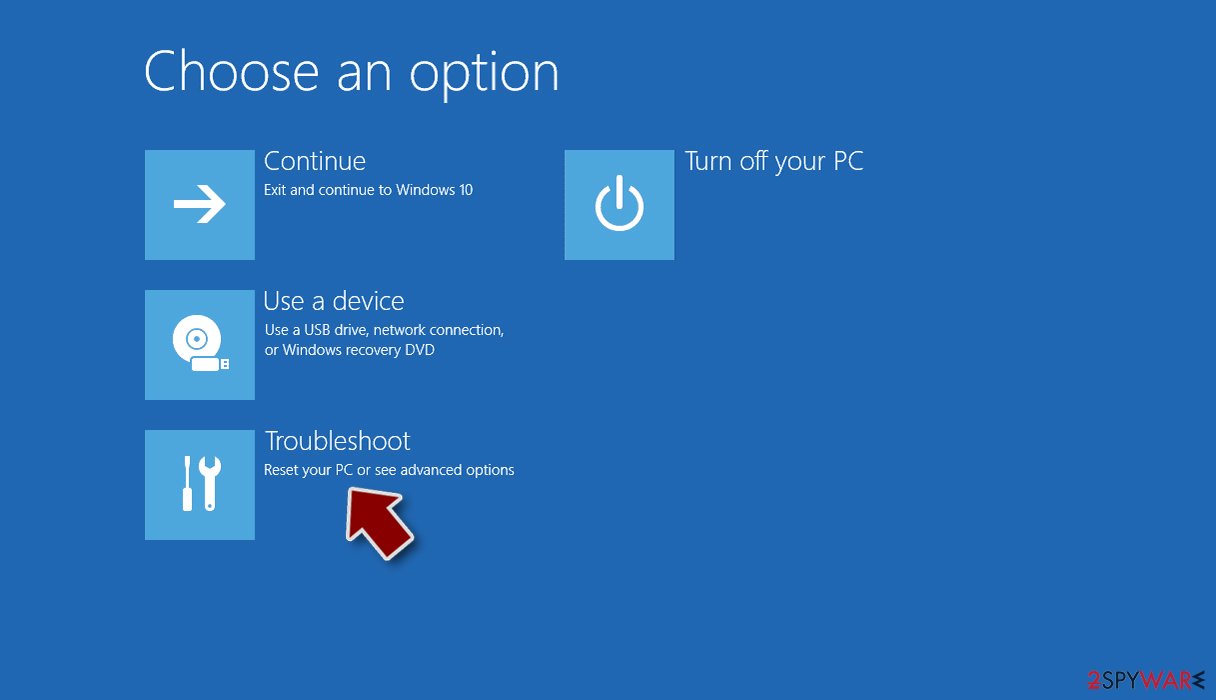
- Select Troubleshoot.

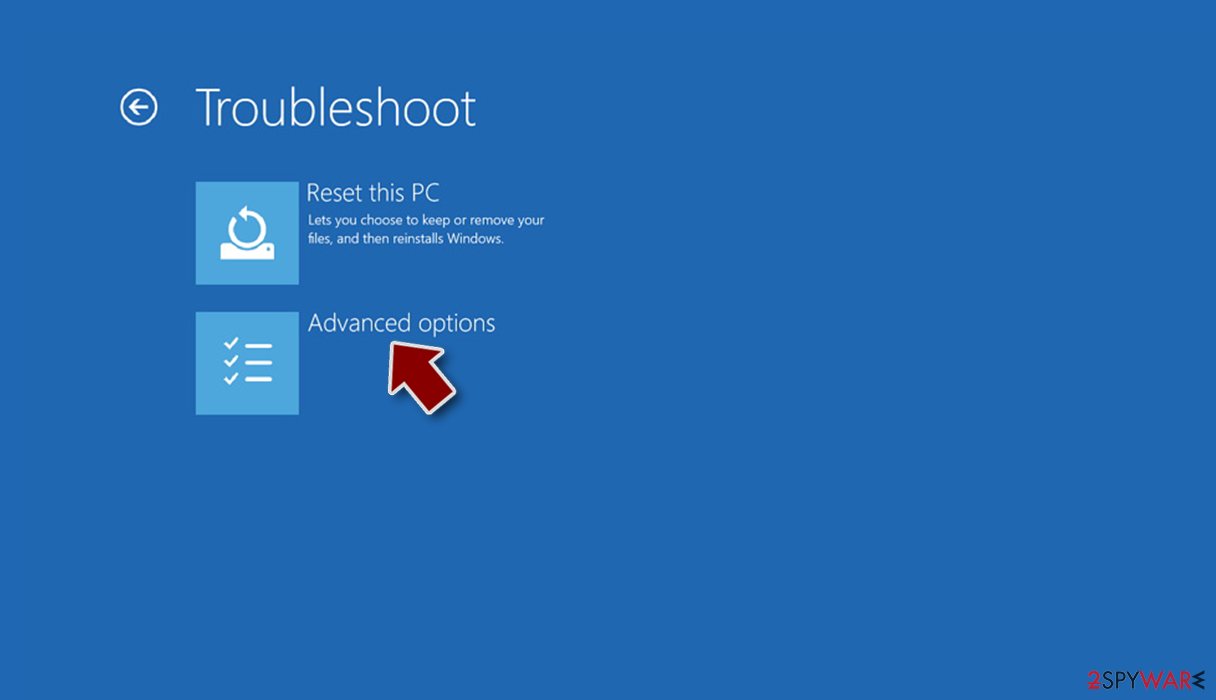
- Go to Advanced options.

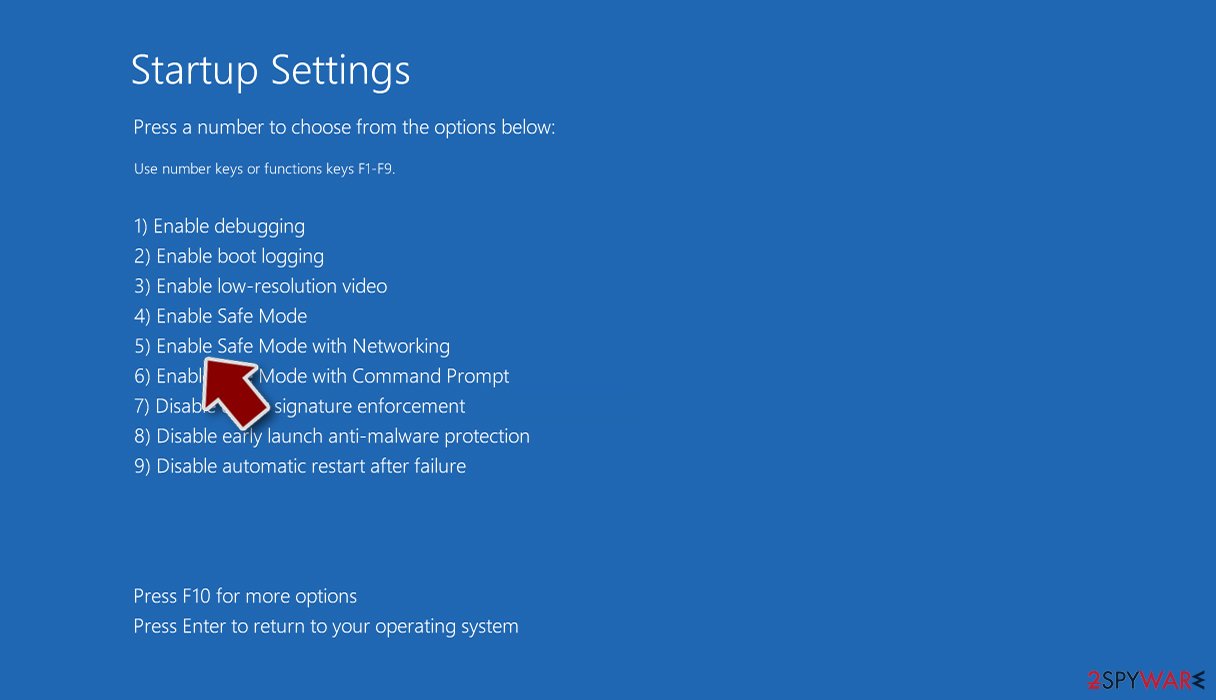
- Select Startup Settings.

- Press Restart.
- Now press 5 or click 5) Enable Safe Mode with Networking.

Step 2. Shut down suspicious processes
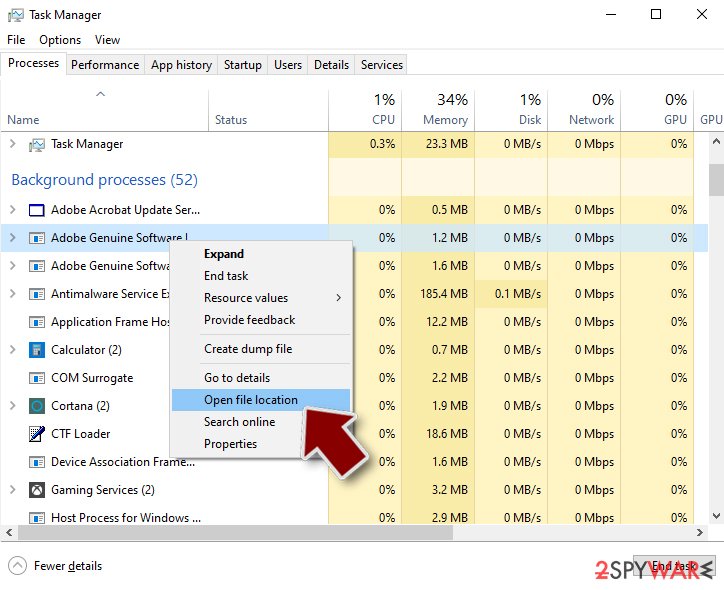
Windows Task Manager is a useful tool that shows all the processes running in the background. If malware is running a process, you need to shut it down:
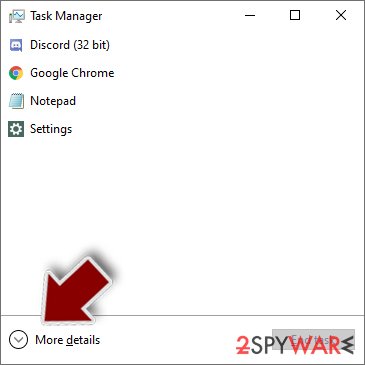
- Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc on your keyboard to open Windows Task Manager.
- Click on More details.

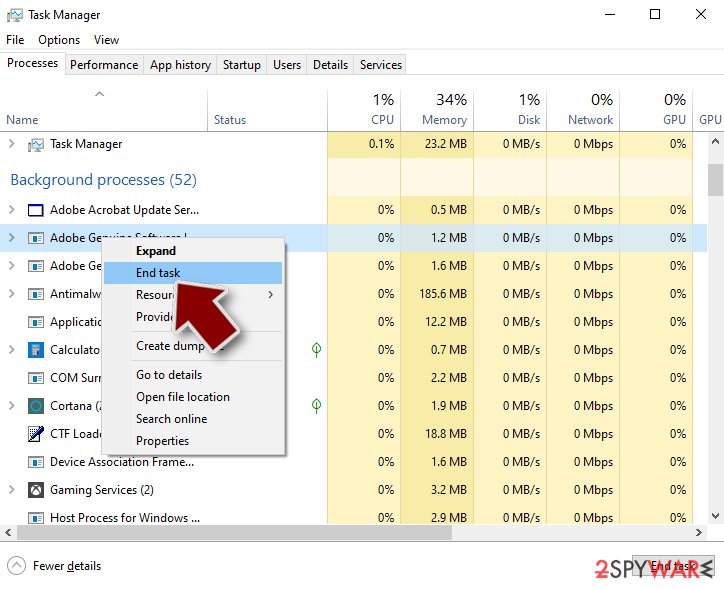
- Scroll down to Background processes section, and look for anything suspicious.
- Right-click and select Open file location.

- Go back to the process, right-click and pick End Task.

- Delete the contents of the malicious folder.
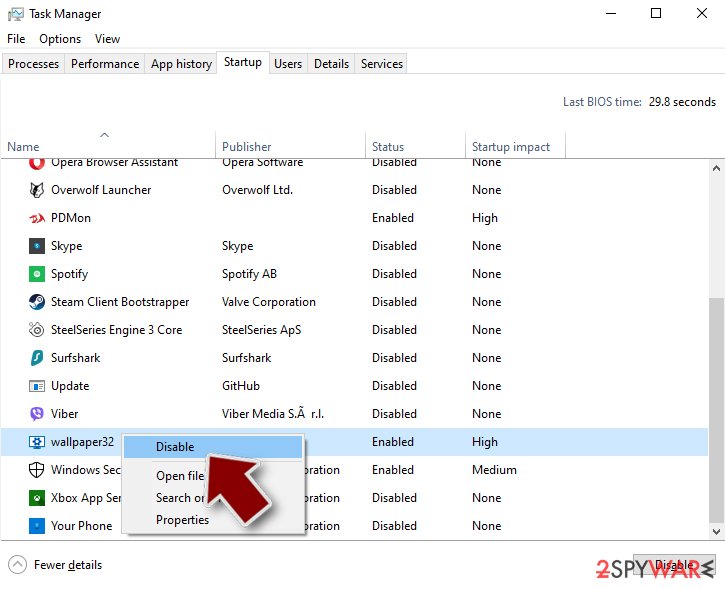
Step 3. Check program Startup
- Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc on your keyboard to open Windows Task Manager.
- Go to Startup tab.
- Right-click on the suspicious program and pick Disable.

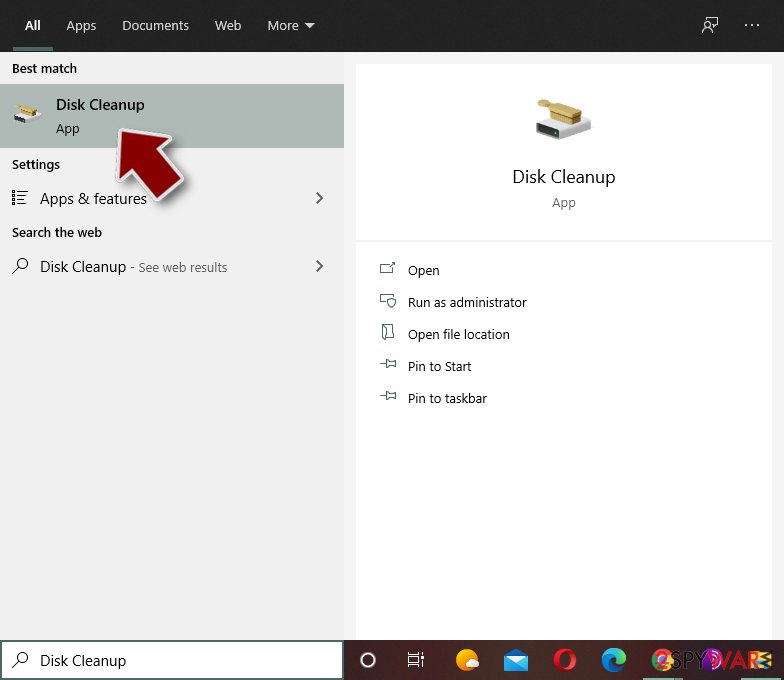
Step 4. Delete virus files
Malware-related files can be found in various places within your computer. Here are instructions that could help you find them:
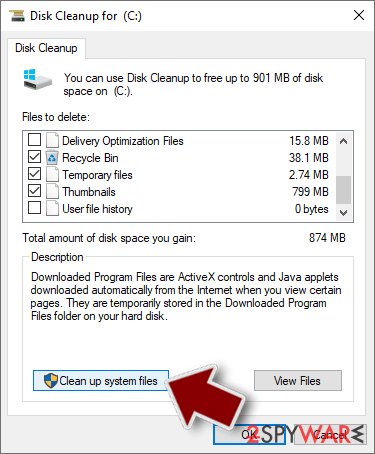
- Type in Disk Cleanup in Windows search and press Enter.

- Select the drive you want to clean (C: is your main drive by default and is likely to be the one that has malicious files in).
- Scroll through the Files to delete list and select the following:
Temporary Internet Files
Downloads
Recycle Bin
Temporary files - Pick Clean up system files.

- You can also look for other malicious files hidden in the following folders (type these entries in Windows Search and press Enter):
%AppData%
%LocalAppData%
%ProgramData%
%WinDir%
After you are finished, reboot the PC in normal mode.
Remove Mischa using System Restore
If the first option didn't help with Mischa removal, try this one.
-
Step 1: Reboot your computer to Safe Mode with Command Prompt
Windows 7 / Vista / XP- Click Start → Shutdown → Restart → OK.
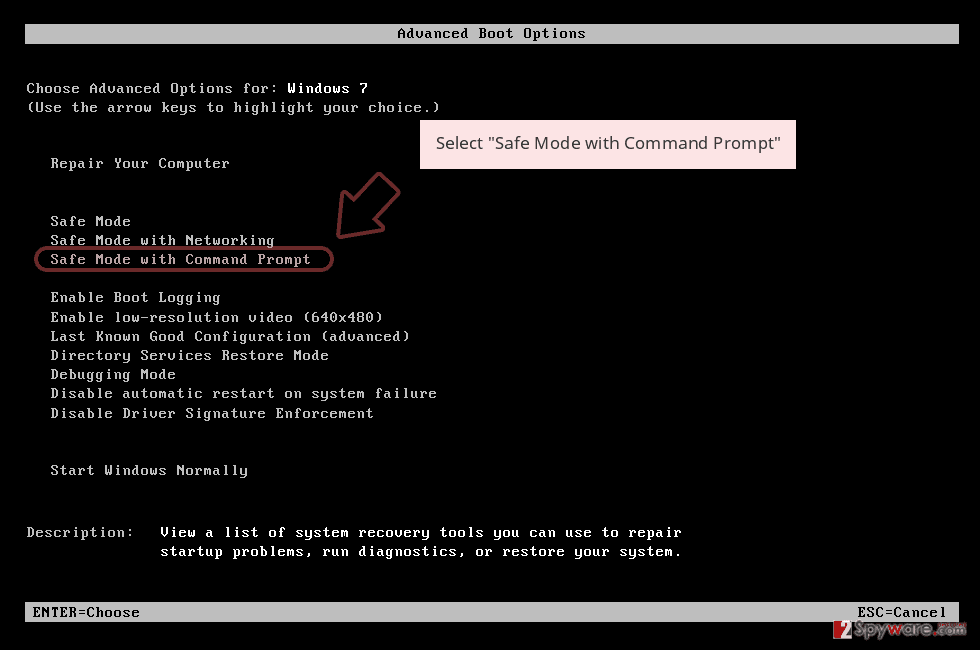
- When your computer becomes active, start pressing F8 multiple times until you see the Advanced Boot Options window.
-
Select Command Prompt from the list

Windows 10 / Windows 8- Press the Power button at the Windows login screen. Now press and hold Shift, which is on your keyboard, and click Restart..
- Now select Troubleshoot → Advanced options → Startup Settings and finally press Restart.
-
Once your computer becomes active, select Enable Safe Mode with Command Prompt in Startup Settings window.

-
Step 2: Restore your system files and settings
-
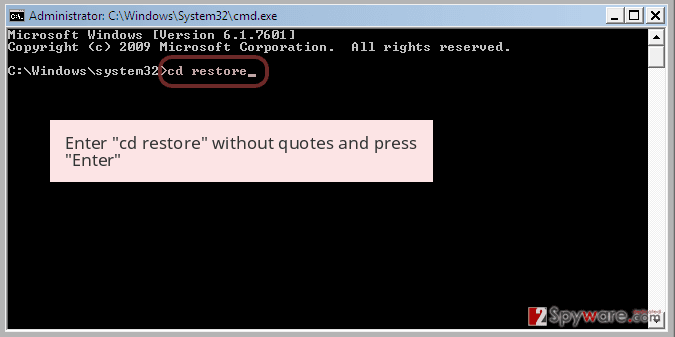
Once the Command Prompt window shows up, enter cd restore and click Enter.

-
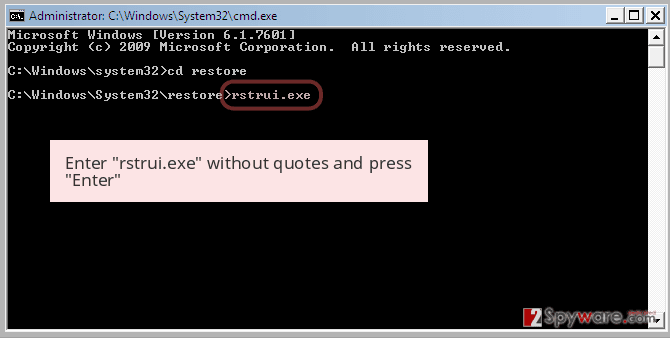
Now type rstrui.exe and press Enter again..

-
When a new window shows up, click Next and select your restore point that is prior the infiltration of Mischa. After doing that, click Next.


-
Now click Yes to start system restore.

-
Once the Command Prompt window shows up, enter cd restore and click Enter.
Bonus: Recover your data
Guide which is presented above is supposed to help you remove Mischa from your computer. To recover your encrypted files, we recommend using a detailed guide prepared by 2-spyware.com security experts.Lately, the developer of Petya and Mischa viruses, known as “Janus,” released a master decryption key. Soon enough malware analysts created a free decryption tool that helps to recover files encrypted by Mischa/Petya/GoldenEye. You can find its download link down below.
If your files are encrypted by Mischa, you can use several methods to restore them:
Use Mischa Decryptor
- To recover your files, open the ransom note and copy your victim's ID. Create a Notebook (.txt) file and, paste and save the victim's ID here.
- Download this decrypter to decrypt the key. Copy the decrypted version of the key and then download one of the programs you need:
- Use the instructions provided in the Decryptor to restore your files.
Finally, you should always think about the protection of crypto-ransomwares. In order to protect your computer from Mischa and other ransomwares, use a reputable anti-spyware, such as FortectIntego, SpyHunter 5Combo Cleaner or Malwarebytes
How to prevent from getting ransomware
Stream videos without limitations, no matter where you are
There are multiple parties that could find out almost anything about you by checking your online activity. While this is highly unlikely, advertisers and tech companies are constantly tracking you online. The first step to privacy should be a secure browser that focuses on tracker reduction to a minimum.
Even if you employ a secure browser, you will not be able to access websites that are restricted due to local government laws or other reasons. In other words, you may not be able to stream Disney+ or US-based Netflix in some countries. To bypass these restrictions, you can employ a powerful Private Internet Access VPN, which provides dedicated servers for torrenting and streaming, not slowing you down in the process.
Data backups are important – recover your lost files
Ransomware is one of the biggest threats to personal data. Once it is executed on a machine, it launches a sophisticated encryption algorithm that locks all your files, although it does not destroy them. The most common misconception is that anti-malware software can return files to their previous states. This is not true, however, and data remains locked after the malicious payload is deleted.
While regular data backups are the only secure method to recover your files after a ransomware attack, tools such as Data Recovery Pro can also be effective and restore at least some of your lost data.
- ^ Inside Petya and Mischa ransomware. Avast blog. Threat Research, IT Security Tips.
- ^ Olivia Solon, Alex Hern. 'Petya' ransomware attack: what is it and how can it be stopped?. The Guardian - Technology. Latest Technology News, Comment and Analysis.
- ^ DieViren. DieViren. Virus Removal Guides, IT Security Tips.