Top 5 facts about cryptominers
×
It all starts with knowledge
Get the latest security news, full analysis of the newest computer threats, and easy-to-use prevention tips. Subscribe to 2-spyware.com newsletter!
Files
- 000.exe virus 17/12/21
- Sitool.exe virus 22/10/21
- wscntfy.exe 20/05/21
- fsg_4104.exe 12/05/21
- mmtask2.exe 12/05/21
- NvMcTray.dll 11/05/21
- iehelper.dll 11/05/21
- gui.exe 07/05/21
Software
- Restoro 10/03/23
- eTrust Pestpatrol 30/04/21
- OSHI Defender 27/04/21
- Defender Pro Ultimate Security Suite 27/04/21
- Ad Aware Pro 27/04/21
- VIPRE Antivirus and Antispyware 27/04/21
- MASTR SCAN 27/04/21
- ParetoLogic Anti Spyware 27/04/21
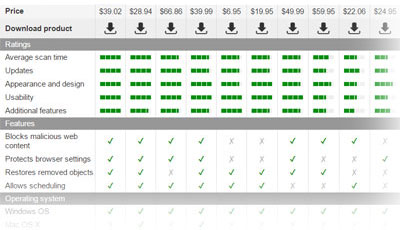
Compare