How to remove a browser hijacker
Browser hijacker – a group of software used to corrupt web browsers and initiate shady marketing campaigns
Browser hijacker is a potentially unwanted program (PUP), usually a web browser add-on or plugin, which causes modifications in web browser’s settings. Such programs start their activity from changing a start page, a default search engine, and a new tab page. As soon as browser hijacker finishes these alterations, it gets the ability to redirect people to predetermined websites that are trying to increase their popularity. By promoting required websites and helping them increase their visitor traffic, the developers of browser hijackers earn the money. Unfortunately, but there is no guarantee that all of such websites are legitimate and harmless.
Almost of each of browser hijackers is capable of collecting information about people’s browsing habits. Such programs can know what search terms you use, what sites you visit the most, what files you upload, what information you enter and similar data, which is considered non-personally identifiable information (Non-PII). However, fraudulent versions of browser hijackers can try to collect personally identifiable information and reveal it to unrelated parties. It can be said that all programs categorized as hijackers are released for commercial reasons. If you want to protect your privacy and improve your PC’s security, you should remove browser hijacker type program from the system.
Effect on the system and computer's performance
Once the browser hijacker enters its target PC system, it typically causes these activities:
- Modifications on each of web browsers. When infected with the browser hijacker, you can expect to discover an unknown home page, the default search engine, and the new tab page. Besides, browser hijackers can also add or remove entries in your bookmark list and fill it with unknown or even unwanted bookmarks. It initiates these system changes without users’ approval.
- Redirects to unknown domains. Browser hijackers are mostly used for redirecting people to predetermined websites and promoting them in this way. This effect is achieved by showing altered search results and sometimes even blocking reputable websites. Beware that there is no guarantee that each of such websites is harmless, so redirects can seriously decrease your computer’s security.
- Collection of personally non-identifiable information. Similarly to adware-type programs, browser hijackers can try to record information, which is related to people’s activity on the web. According to the developers of such programs, they mostly collect data about people’s activity on the web, like visited websites, information that is added there, computer’s IP address, its location, browser’s type, etc. However, fraudulent people may use such software for collecting login data, contact information, and other confidential details.
- Preventing the removal from the system. Typically, browser hijackers provide no uninstall option for preventing their removal. They can also rely on browser helper objects that may cause their reappearance on your browser after rebooting the affected PC system.
- Causing problems related to the system's stability and performance. Most browser hijackers slow down the web browser and computer’s performance because some of them are poorly developed. When infected with such a version of browser hijacker, you can also notice instability issues, errors, and overall performance problems on your computer.

Browser hijacker distribution methods
Four major ways have been exploited in the distribution of browser hijacker:
Freeware, shareware, or ad-supported programs. Beware that there are lots of different download managers, video streaming programs, video recording programs, and similar free programs that have been bundled with suspicious browser add-ons or toolbars. Even reliable products can be set to trick people into changing their default browser settings.
Misleading official websites. You can be convinced to download a misleading program, which is considered a browser hijacker, manually. Please, double-check search engines, toolbars, browser add-ons, and extensions before installing them on your computer. You can always google their name and see what other people think about them.
Adware-type programs. These potentially unwanted programs have also been used for spreading browser hijackers as optional components. First of all, we do not recommend downloading adware to the system. Also, if you think that intrusive ads are not a bad thing, you should monitor the installation of such software because you can easily install the browser hijacker on your PC.
Fake pop-up ads. Some part of browser hijackers have been spreading around with the help of fake ads that report about missing updates. If a pop-up notification is claiming that your Java, Flash Player, or FLV Player is out of date, you should ignore it because there might be that it is used just for distributing the unsafe program. Once the victim clicks such a pop-up ad, a harmful script installs a browser hijacker or similar PUP.

The most typical browser hijackers
delta-homes.com: Thousands of people have been affected by this malicious browser hijacker. It has been actively spread in a bundle with both, legitimate and malicious programs, so there is no surprise that there are so many users who have discovered it on their computers without approving its installation. The latest versions of the Delta Homes virus can be removed only with the help of updated anti-spyware.
mysearch: Another clear example of browser hijacker. No matter how attractive it looks, ads that are displayed thru it can be dangerous. Mysearch can be removed either manually or automatically. However, 2spyware researchers recommend using the second removal option. Otherwise, you cannot be sure that all additional components, including browser helper objects, are removed from your computer.
Chromium virus: You should be careful with a wide group of browser hijackers created using Chromium code. Any Chromium hijackers that are set to hijack web browsers without users' approval can track your search sessions and then redirect you to sponsored places. Additionally, they can be set to track you behind your back and collect information that is considered non-personal. You can never guess what kind of data is collected with the help of this program and what parties are capable of using it for their needs.
What to do if you think that your computer is infected
You can remove browser hijackers with the help of automatic removal and manual removal methods. Here is more about both of them:
Automatic removal: The easiest way to prevent infiltration of a browser hijacker is to install a reputable anti-spyware. The same can be said about the removal of such potentially unwanted software. You should think about the manual removal of browser hijacker only if you are a tech-savvy person and an experienced PC user. Such programs are typically spread in a bundle with different components that can hardly be found in typical locations, like Task Manager.
Manual removal: 2spyware team is always trying to test each of the examples of browser hijackers. However, on rare occasions, even the most accurate removal steps fail to help. That is because their developers periodically update browser hijackers and similar PUPs. If you feel that you are advanced enough to find each component of the browser hijacker, you are more than welcome to use manual removal guides that are provided on every browser hijacker’s description.
How to remove browser hijacker from Chrome?
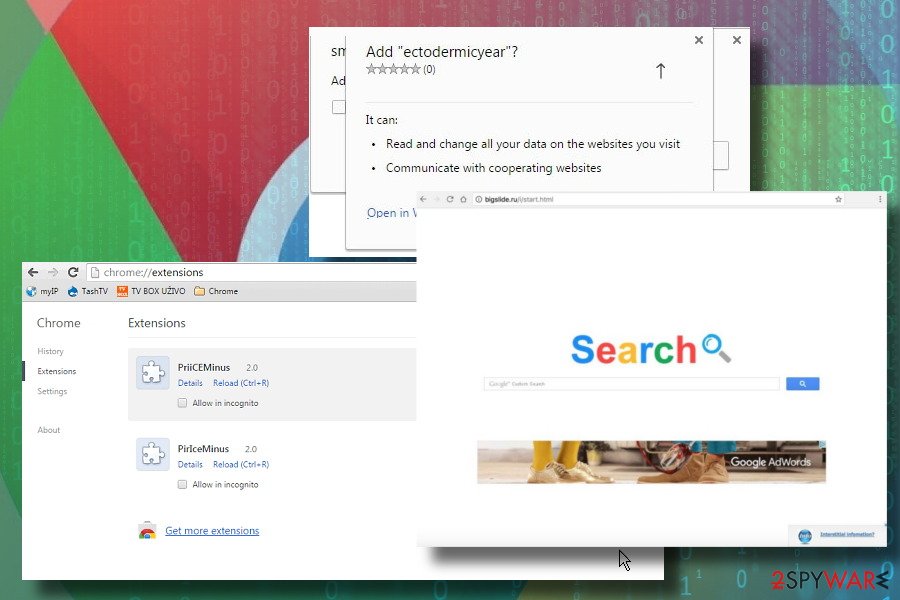
Google Chrome hits the top among the most popular web browsers on the market. In 2017, it exceeded 1 billion on the mobile market and currently has 57,36% of web browser's market share. Thus, there's no surprise why developers of browser hijackers keep developing extensions targeting Chrome. While some of the hijackers are not aggressive, usually it's sufficient to merely set Google as a default start page and search engine. No additional procedures to get rid of them are needed.
However, most of the hijacks compromise web browser's settings in a more profound sense, i.e., multiple extensions are dropped, cookies installed, shortcuts redirecting to suspicious websites injected, and similar. In this case, it's necessary to reset Google Chrome's settings. In some rare cases, browser hijackers appear to be too aggressive to be rooted out without a professional malware removal tool. Therefore, if changing Chrome's settings manually and performing a full reset did not work, you should run a scan with a professional anti-virus and then repeat the procedure with restore settings.
How to remove browser hijacker from Firefox?
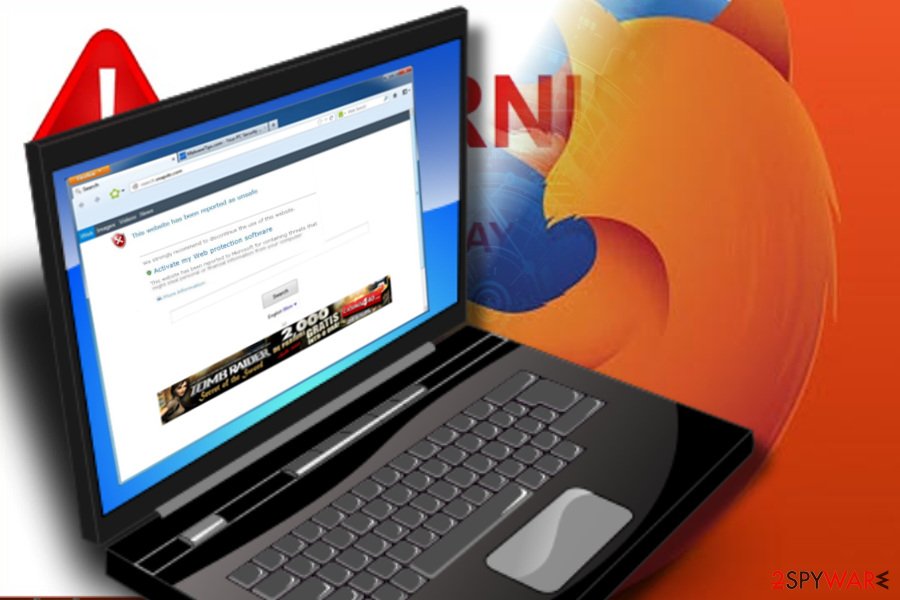
Firefox has always been a step back from Google. However, it's one of the most popular web browsers in the world and takes 5.45% of the market share. Despite the fact that Firefox's team has been and still is working hard to improve its security, the browser still isn't immune to the browser's hijack.
There are many Firefox redirect viruses that once installed replace the start page, search engine, a new tab page, and other settings and force its users to visit unwanted websites. However, there's a handful of changes that a browser hijacker can initiate on the system, but ordinary Internet users can hardly notice, including DNS settings, search results, tracking cookies, extensions, and similar.
Firefox does have a built-in phishing and malware protection feature, but if it failed to block browser hijacker, it would not help in removing it as well. Usually, malware removal from Firefox encompasses two phases. The first phase – malware elimination from the system. Often, it requires invoking a professional anti-virus program. The second phase – removal of malicious Firefox extensions. The latter can be initiated by restoring the default Firefox settings.
How to remove browser hijacker from IE?
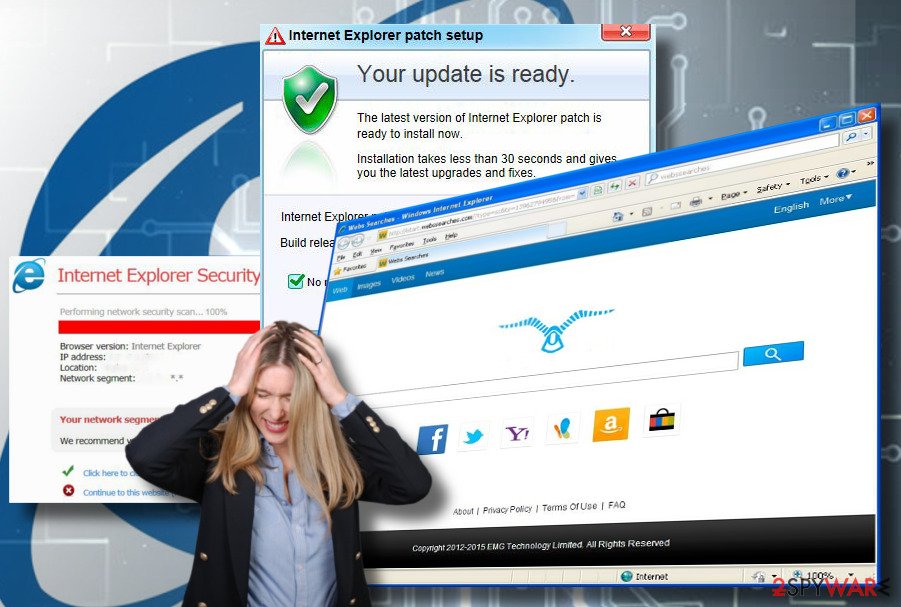
Internet Explorer (IE) should officially be dead. However, a minority of Windows users keep using it due to compatibility reasons. As an old browser, IE supports applications developed at the end of 20th century and the very beginning of 21st century. However, in comparison to the newer web browsers, IE is exceptionally vulnerable to cyber-attacks, and browser hijacking is not an exception.
If your Windows PC running IE has been hijacked, we would not only recommend you to remove malware and hijacker from the web browser. We encourage you to switch to the newer Windows OS version and start using a more secure web browser, be it Chrome, Edge or Firefox.
Nevertheless, the removal of browser hijackers from IE is not a complicated procedure. The most important thing is to learn what kind of malware infiltrated the system so that all constituent parts would be revealed. A reputable anti-virus program can facilitate the manual malware removal procedure, but it won't restore the previous IE settings. You will have to do that manually by enabling a Reset Internet Explorer Setting option.
How to remove browser hijacker from Microsoft Edge?

Microsoft Edge is a newcomer in the web browser market as it has only been launched in 2015, along with Windows 10 OS release. Many researchers have been conducted regarding Edge's security and, in most of the cases, it turns out to be more secure if compared to Google Chrome or Mozilla Firefox. Unfortunately, the improved security system, including advanced SmartScreen, does not protect this web browser from browser hijackers.
Unwanted web browser extensions that hijack Edge typically manifest on the system after the installation of freeware. Thus, if your start page, search provider, and other customized settings have been compromised, most probably you will have to render a reliable security software and scan your PC with it. However, malware removal won't reset the altered settings. You will have to restore the changes manually by resetting Microsoft Edge default settings. If If you need help, you can follow the Edge reset instructions.
How to remove browser hijacker from Safari?
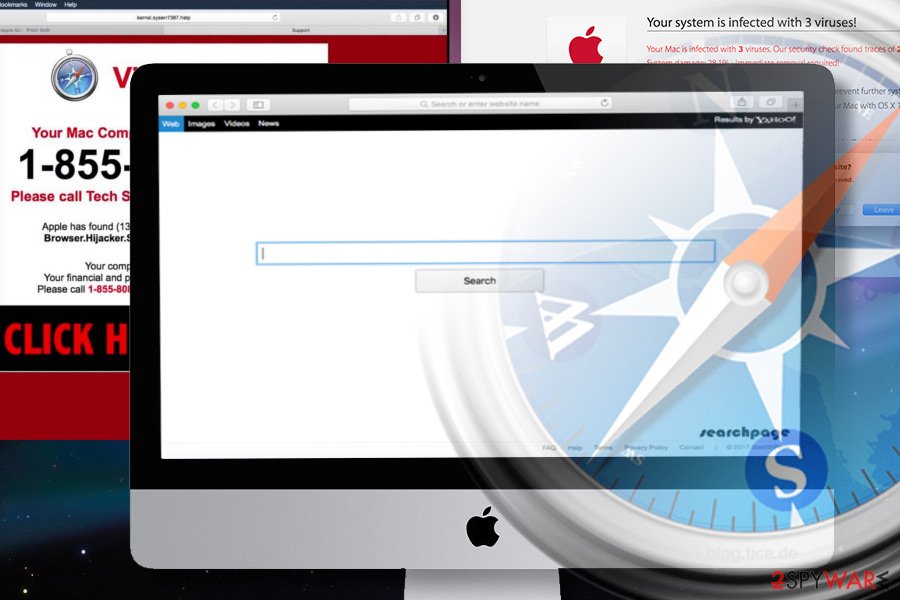
Safari has been considered the most secure web browser for many years. However, since 2015 the situation changed significantly when Mac OS X devices become a target for advertisers, scammers, and other unfair third-parties that seek to gain profit by any means.
As for now, Safari is the second most widely used web browser after Google and is targeted by hundreds of different malware types, a part of which replaces Safari's start page and search engine to redirect to sponsored websites. Luckily, we can help our visitors to remove any malware from it in an easy way.
2spyware team has submitted a tutorial that explains how to reset Safari settings. However, before addressing unwanted components within the browser, we highly recommend scanning the system with an anti-virus to get rid of all PUPs that might have transferred the hijacker to your device.
Latest browser hijackers added to the database
Kill Weatherly browser hijacker
Remove Qtr Search browser hijacker
What is Smartdownloader.site browser hijacker
Information updated: 2021-01-11