How to remove a Trojan horse
Trojan – a type of malware that uses ancient Greek war tactics to break into your computer
A Trojan (or a Trojan horse) is a malicious computer program that uses deception in order to infect the host machine and start running malicious processes on it to steal, damage, modify or delete various data. Just like in ancient Greece the war veteran Odysseus compiled a plan on how to enter the city of Troy and take it over, the main payload of this type of malware is disguised as seemingly legitimately-looking application. Usually, hackers behind Trojans use some type of social engineering[1] in order to make unsuspecting victims click on the malicious file.
The infection starts as soon as the obfuscated executable is opened, but users rarely notice any changes to their systems, usually for weeks, months, or even years. After a while, however, users might notice the impact that Trojan horse did overtime: programs start crashing, internet connection slows down, frequent Blue Screen of Death occurrences and other signs indicate that the computer is far from being healthy.
Trojans are often compared to (or called) viruses or worms, and this categorization is mainly misleading.[2] The latter two have many similarities between each other: viruses need to infect files on the computer to spread, while worms do so without attaching themselves to anything. However, a Trojan horse has to be executed by the user, so it does not propagate automatically.
Trojans are one of the most widespread malware types and can affect all platforms, including Windows, Linux, Macs,[3] Android, and iOS devices. While most of the malware is downloaded by visiting shady websites or clicking on phishing links, some of the trojanized apps were even found in official sources like Google Play.[4]

Trojan types and classification
Trojans are flexible malicious programs and can save a variety of purposes for the threat actors behind them. Usually, such programs are used for stealing sensitive information, spreading other malware, or simply disrupting computer's performance. Also, hackers can use them for getting an unauthorized remote access to a compromised computer, infecting files, and damaging the system.
Based on these attributes, Trojans are categorized as follows:
Banker Trojan
Banker Trojan is possibly one of the most prevalent Trojan types out there.[5] Malicious applications are designed to steal financial information from infected users. There are also several ways that they do it: from imitating the original bank login page or application to stealing the plain text information from the login screens with the help of keylogging functionality.
Backdoor
Backdoors are a type of Trojans that are capable of bypassing normal authentication or security measures. Once installed, the backdoor provides malicious actors with the possibility of gaining elevated privileges on the network or the computer and controlling it remotely. Backdoors are also often used to combine multiple infected machines into a botnet that can be used for DDoS attacks,[6] malspam, etc.

Rootkit
Rootkits are one of the most severe and hard-to-get-rid-of infections in the wild.[7] The purpose of this malware is to harbor the malicious activities performed off the infected machine and prevent them from being detected by security solutions. Rootkits are often injected with the help of privilege escalation vulnerabilities with the help of a phished login credentials.
Trojan downloader and Trojan dropper
Both of these types are designed to run in the background, and allow the update process of the Trojan to be executed, equipping it with new features. Additionally, Trojan droppers can also contact remote command and control servers to download and install additional Trojans, adware, or other malware.
Remote Access Trojan (RAT)
Remote Access Trojans incorporate backdoor functionality to escalate the privileges within the host system. The impact of the RAT on the system might be excruciating: hackers can format drivers, alter system files, take screenshots/use video camera to record video, stealing credit card information, etc.

Trojan distribution methods
As previously mentioned, Trojans are usually hidden within malicious files that need to executed by victims. Nevertheless, some Trojans might abuse the software vulnerabilities[8] and get installed automatically. Below you will find main methods on how Trojans are delivered to victims' computers.
Email attachments
Many trojans are distributed with the help of spam e-mails. Cybercriminals often employ bots to send out phishing messages to a large (usually random) group of people. The contents of the email may greatly vary in quality, as some phishing emails are very poorly constructed: littered with spelling/grammar errors, poor formatting, etc. However, some of them use email spoofing and polish the message to perfection, making many victims click on the malicious attachment or the hyperlink.
Instant messaging (IM) applications
Trojan delivery via instant messaging apps dates back to mIRC and ICQ times, when users were tricked into downloading a malicious payload and installing it unintentionally. Nowadays, social engineering skills are put to most social media and some popular chatting apps like Discord, WhatsApp, or Skype. IM programs and social media are the two platforms that social engineering is widely applied and users can get easily tricked by clicking on the (disguised) link and instantly install the Trojan on their systems.
Vulnerabilities
Some Trojans can get into the system using a web browser or other vulnerabilities. Their authors run insecure web sites filled with malicious code or distribute unsafe advertising pop-ups. Whenever the user visits such a site or clicks on such a pop-up, harmful scripts instantly install the Trojan. The user cannot notice anything suspicious, as a threat does not display any setup wizards, dialogs, or warnings.
Backdoors
Trojans sometimes get installed by other parasites like viruses, worms, backdoors or even spyware. They get into the system without user knowledge and consent and affect everybody who uses a compromised computer. Some threats can be manually installed by malicious computer users who have sufficient privileges for the software installation. Very few Trojans can spread by exploiting remote systems with certain security vulnerabilities.
Fake installers and software cracks
Some Trojans are already integrated into application installers. In most of the cases, users infect their machines when they download pirated software or software cracks[9] via dangerous sources like Torrents. These on-itself dangerous sites often host malware, but the will of having free software that is otherwise not often surpasses the will to protect the computer from malware. Additionally, hackers might create fake websites (copies of legitimate ones) and lead users to fake installs that once executed load up the malicious code on the computer.

The malicious code of Trojan is capable of performing a variety of activities on the host machine behind users' backs
Trojans are very versatile and can be employed for multiple malicious tasks on the infected machine. In most of the cases, the malware performs several tasks at the time, all while disguising its background activities. Trojans can perform the following actions on the host machine:
- Infecting, corrupting and overwriting files, essential system components, and installed applications. They can also destroy the entire system by erasing critical files or formatting hard drives.
- Stealing financial data, such as credit card numbers, login names, passwords, valuable personal documents, and another user sensitive information.
- Tracking the user and each of the keystrokes he or she enters on a keyboard. Trojan horse can also take screenshots and initiate other activity for stealing specific information.
- Sending all gathered data to a predefined e-mail address, uploading it to a predetermined FTP server, transferring it through a background Internet connection to a remote host or communicating with the authors of malware via Command & Control server.
- Installing a backdoor or activating its own component to let a remote attacker take over a compromised computer.
- Dropping other dangerous parasites.
- Performing Denial of Service (DoS) or other network attacks against certain remote hosts or sending out an excessive amount of e-mail messages in order to flood predefined computers.
- Installing a hidden FTP server that can be used by malicious actors for various illegal purposes.
- Terminating antivirus, anti-spyware and other security-related software. Trojan horse can also disable essential system services and prevent standard system tools from running.
- Blocking user's access to reputable websites and security-related resources.
- Displaying undesirable commercial advertisements and pop-ups.
- Degrading Internet connection and computer speed. It can also decrease system security and cause instability.

Most prominent Trojans released over the years
There are thousands of different Trojans. The following examples illustrate how harmful these threats can be.
Zeus Trojan
Zeus malware, also known as Zbot, is possibly one of the most notorious banking Trojans out there. First spotted in July 2007, the virus managed to infect hundreds of thousands of computers worldwide, affecting such organizations like NASA, BusinessWeek, Bank of America, Amazon,[10] and others.
ZeuS usually infected victims via the drive-by downloads or phishing websites/emails and focused on grabbing forms, as well as stealing login credentials with the help of the keylogging feature. Thanks to the leaked source cone in late 2010 and dozens of arrests related to the threat, the malware became more manageable and the infection rate seized.
Nevertheless, tech support scammers adopted the name of the Trojan due to its immense popularity, making thousands of people believe that their personal information is in great danger and giving money away for the fake support services coming from bad people in the scam call centers.[11]
Trojan.Cryptolocker
Trojan.Cryptolocker is a Trojan which has been used for spreading very dangerous viruses called Cryptolocker and Cryptowall. It is believed that this Trojan can also be used for the distribution of other malware, such as rogue anti-spyware programs, backdoors, and similar threats.
It spreads around with the help of fake security message claiming that the computer is infected with a possible virus. When the user clicks such a message, the Trojan enters the system and quietly installs ransomware. Also, it blocks the system and causes a fake warning message on the victim's desktop. You can also download this threat to your computer as a useful email attachment or a pop-up ad that offers to update your Java or Flash Player.
Trojan.ZeroAccess
Trojan.ZeroAccess is another extremely dangerous Trojan horse, which is also known as max++. Note that there are many versions of this malware and that they all have the same goal – to steal people's personal information while establishing a wide botnet.[12] ZeroAccess and all its variants record every keystroke of the victim and can also make continuous screenshots. This Trojan usually sneaks into the system from various Internet resources such as insecure web pages or peer-to-peer networks and starts its work without wasting its time.
12Trojan.Win32.Krepper.ab
12Trojan.Win32.Krepper.ab is a very dangerous and extremely destructive parasite, which can cause serious issues related to your PC's stability. Usually, it gets into the system from insecure Internet resources, file sharing networks, or online chats. It silently works in the background waiting for the specified date to run its payload.
On the specified date, Krepper virus can try to affect Windows Registry, deleting several critical system folders and initiate other destructive actions. The parasite detects, terminates, and totally disables running antivirus software installed on the target computer. Moreover, the Trojan can connect to various malicious servers and download other harmful parasites from there.
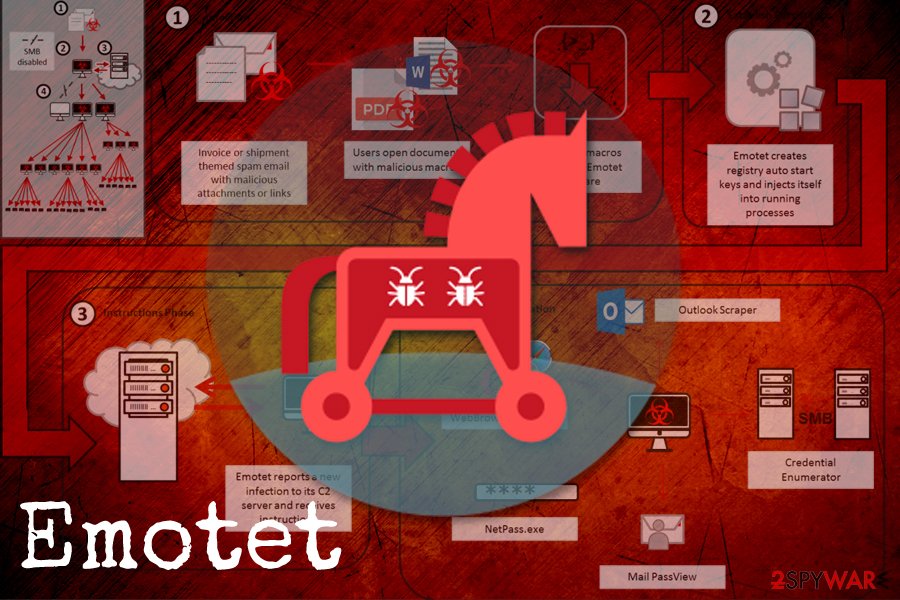
Emotet
Emotet is over five years old by now and is still going strong. This modular banking Trojan started infecting victims back in 2014 and mainly used malspam for the purpose. It used the infected host machine to send out malicious emails with JavaScript or Macro-induced attachments to the victim's contact list, making its delivery so much more effective. In 2018, Emotet was spotted targeting healthcare, manufacturing, education, and other sectors with the help of credential brute-forcing and software vulnerabilities.[13]
Emotet is polymorphic, so it evades signature-based detection and does not enter virtual machines, as well as sandbox environments which are used by security researchers for the sample analysis.[14] Upon infiltration, it contacts a remote C&C server and starts intercepting traffic in order to steal banking credentials and crypto-wallet information. Emotet was also observed dropping other malware on the system, such as Dridex or Qakbot, which are banking Trojans as well.
Removal of Trojans and avoidance techniques
Trojans are advanced and versatile computer threats that induce hundreds or even thousands of changes on the infected system, be it Windows, Linux, macOS, or others. Some Trojan variants are particularly hard to get rid of, as gain root access and might even infect the kernel by using privilege escalation flaws.[15] In some of the extreme cases, the malware can change the system so much that even the reinstallation of the operating system will not remove the Trojan.
While removing sophisticated malware manually is entirely possible, it would be an impossible task for regular computer users. For that reason, experts recommend downloading and installing a robust anti-malware program and performing a thorough system scan. Due to advanced Trojan functionality, however, users should access Safe Mode with Networking which would temporarily disable malware's functions and allow security software to eliminate all the malicious components and revert the damage done to the system.

However, the best solution would not get infected in the first place. While no protection method is perfect, users who follow adequate security measures have a much lower chance of getting their financial information stolen. Here's what you should do:
- Install reputable security software and set its automated scans to be performed daily. Make sure the program also employs the real-time protection feature.
- Make sure that your operating system and the installed software is running on the latest version, and all the security patches are applied regularly.
- Never open suspicious email attachments, especially if they ask you to enable macro[16] function.
- Enable Firewall and employ ad-blocking extension.
- Do not engage in pirating software or executing cracks/keygens.
- When using Remote Desktop, avoid the default port and protect the connection with a strong password.
- Enable two-factor authentication where possible.
- Backup your personal data.
- ^ Nate Lord. Social Engineering Attacks: Common Techniques & How to Prevent an Attack. Digital Guardian. Enterprise IP & DLP Software.
- ^ What is a Trojan? Is it a virus or is it malware?. Norton by Symantec. Security blog.
- ^ Zack Whittaker. Meet Coldroot, a nasty Mac trojan that went undetected for years. ZDNet. Technology News, Analysis, Comments and Product Reviews.
- ^ Nikita Buchka, Anton Kivva, Dmitry Galov. Jack of all trades. Kaspersky. Securelist blog.
- ^ Number of users attacked by banking Trojans grew by 16% in 2018 reaching almost 900,000. Kaspersky. Official blog.
- ^ David Bisson. Godlua Backdoor Capable of Performing DDoS Attacks. SecurityIntelligence. Threat research blog.
- ^ Michael Kassner. Rootkits: Is removing them even possible?. TechRepublic. News, Tips, and Advice for Technology Professionals.
- ^ Vulnerability (computing). Wikipedia. The free encyclopedia.
- ^ Brian Krebs. Software Cracks: A Great Way to Infect Your PC. Krebsonsecurity. Computer security expert analysis.
- ^ Dan Goodin. Amazon cloud hosts nasty banking trojan. The Register. Biting the hand that feeds IT.
- ^ Linda McGlasson. 19 Nabbed in Zeus-Based Scam. BankinfoSecurity. Bank information security news, training, education.
- ^ Lucian Constantin. The ZeroAccess botnet is back in business. Computerworld. IT news, careers, business technology, reviews.
- ^ Emotet Trojan Targets Education, Gov and Healthcare. Vietnam Security Summit. Official blog.
- ^ Rubio Wu. New EMOTET Hijacks a Windows API, Evades Sandbox and Analysis. Trend Micro. Security Intelligence blog.
- ^ Tom Spring. Driver Disaster: Over 40 Signed Drivers Can’t Pass Security Muster. Threat Post. The first stop for security news.
- ^ Macro virus. Wikiepdia. The free encyclopedia.
Latest Trojans added to the database
Removal of Trojan:HTML/Phish!pz
Vagus RAT removal instructions
How to remove Puabundler:win32/msetup virus
Information updated: 2021-01-11