Sage ransomware / virus (Virus Removal Guide) - Oct 2017 update
Sage virus Removal Guide
What is Sage ransomware virus?
Sage ransomware gets active online again
Sage virus operates similarly to the infamous Cerber ransomware, which delivers a well-structured payment website for each victim. The crypto-malware infiltrates the computer system using illegal and fraudulent ways, and encodes files with RSA 4096 public key[1], adding .sage file extension on its way.
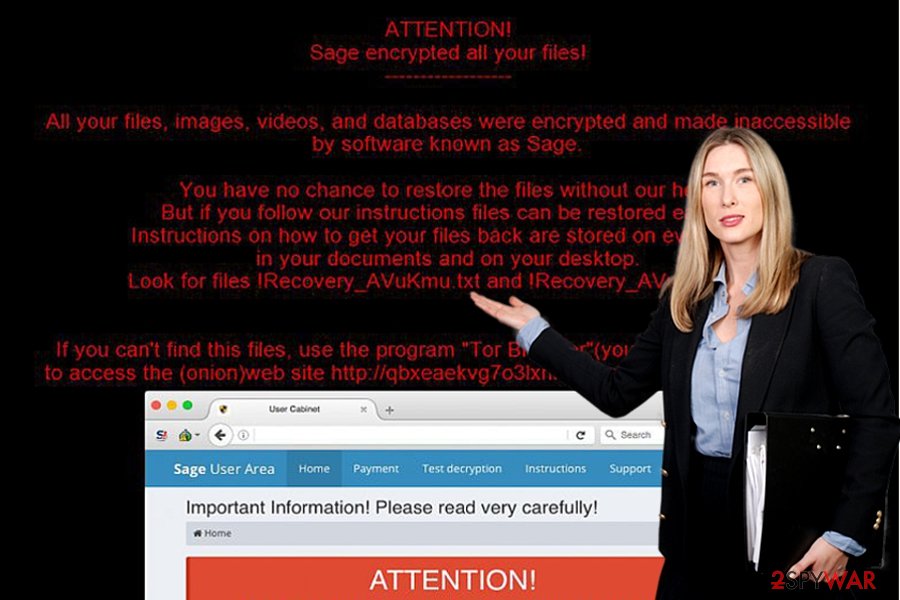
The private key is kept in criminals’ servers, and there is no way to reach it. The virus then changes desktop background with AVuKmu.bmp picture, which contains information about the ransomware attack. This desktop image commands the victim to download Tor Browser[2] and access secret payment website.
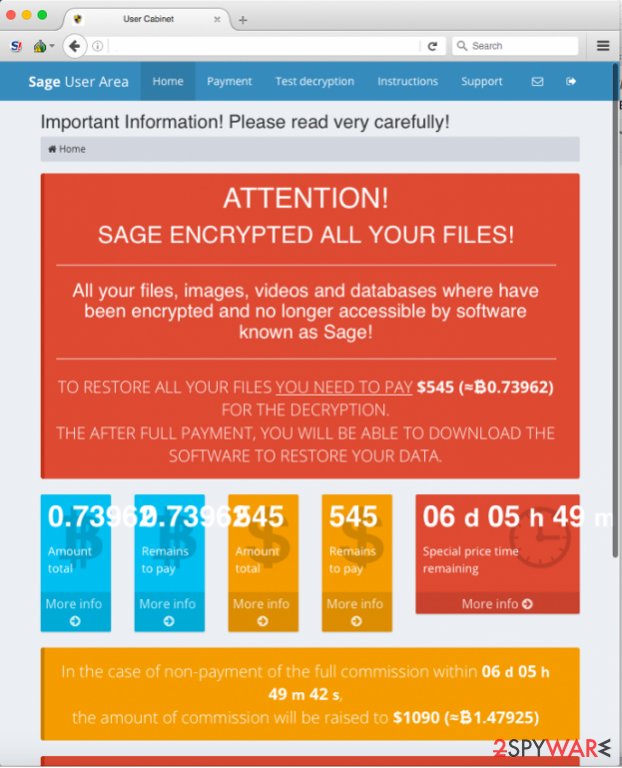
To access this site, the victim needs to know his personal ID, which is stored in !Recovery_AVuKmu.txt, AVuKmu.bmp and !Recovery_AVuKmu.html files. The personal payment site is entitled “Sage User Area” and has five sections – Home, Payment, Test Decryption, Instructions, and Support page.
The Home page informs the victim about the ransom price (0,73962 BTC) and displays a countdown clock, which urges the victim to pay up. According to the virus, the unique decryption key “will be destroyed” when the given period passes.
In the Payment page, virus explains how to buy Bitcoins[3]. What is interesting is that frauds set up individual Bitcoin wallets for each victim, in other words, victims do not transfer the money to the same wallet, but to thousands of them. Criminals even provide the QR code of the wallet so that victims would transfer the ransom to the correct wallet.
Just like Cerber or other advanced-level ransomware viruses, Sage malware offers decrypt-1-file service for free. This way, it gives the victim a proof that criminals actually can decrypt those encrypted files. Instructions page explains how to use the Sage Decryptor, and the Support page allows victims to communicate with malware authors.
Malware drops various files on the system, and inexperienced computer users might not be able to fetch all of them down. That is why we strongly recommend removing them with anti-malware programs like FortectIntego or SpyHunter 5Combo Cleaner. Before Sage removal, consider what anti-malware program you wish to use.
If you already have one, make sure you update it when the computer is in a Safe Mode with Networking. If you do not have an anti-malware program, remove Sage virus using our recommended ones or any other reliable anti-malware program. You can find useful software reviews in the Software section on our site.
Other Sage variations
Sage 2.0 ransomware virus. This variation did not only become a big headache for the virtual community but it also attracted scientific interest. Due to emerging new versions, the malware fortified the assumptions that the same menacing Cerber virus is in the shell of this new threat. It activates itself with the help of a VBScript.
During the very hijack process, it deletes the initial executable file, and places its copy in %AppData%. The felons make a diversion by naming the executable files differently in each infected machine. In the !Recovery_ .html instructions, victims find further information how to access a unique Sage 2.0 payment site. Speaking of which it, it greatly resembles another rapidly evolving threat – Spora ransomware.
Sage 2.0 is also able to delete shadow volume copies leaving fewer data recovery options for the virtual community. In addition, it places its link in the Startup folder which enables the malware to continue the decryption process even if a computer is rebooted. Its distribution campaigns include phishing and spam emails.
Do not rush to open the emails which are addressed personally, e.g. EMAIL_[random set of numbers]_recipient.zip. It contains JavaScippt, one of the key files responsible for the activation.
Sage 2.2 ransomware virus. This time the felons decided to improve the technical capabilities of the threat, but its veneer as well. The ransom text changed from red to green. Additionally, the name of the instructions file has been also altered. Now the necessary information about payment and data recovery is presented in !HELP_SOS.bmp file. It redirects to a specific website, where victims are required to pay a specific amount of money. It may vary from $99 to 2000 dollars.
Interestingly, that this version shows more Cerber' s features. Sage 2.2 contains an audio file which alerts victims even more and encourages making the transactions. The ticking clock with the elapsing time becomes a nerve-wracking site as well. Speaking of the encryption, it appends the same .sage file extension.
Regarding its payment site, it presents the residents of targeted 18 countries the ability to choose their language preference. Like in the case of Cerber, it also omits several countries such as Ukraine, Belarus, Kazakstan, Russia, Latvia. If you occasionally review the processes in the Task Manager, you might notice that the threat ends or limits several crucial processes in order for the encryption process to go smoothly.
It seems that the malware does not target common system directories, but may paralyze your “League of Legends” game as well. Spam and phishing emails remain to be the main distribution method. Note that it might benefit from exploit kits as well.
Updated October 23, 2017. The latest version has kept a low profile since the emergence in the beginning of 2017. Currently distributed versions do not seem to have been significantly altered. It still speaks up to users using Microsoft SAPI command. There is a small but crucial amendment – now the malware deletes backup catalogs.
Unfortunately, there is no free Safe 2.2 Decrypter available yet. The malware demands 0.17720 bitcoin which is approximately 1000 dollars. The payment site is divided into Payment, Test decryption, Instructions, and Support tab. There are no changes concerning the file extension. The ransomware still attaches .sage to mark the encrypted data.
Ways to infect users with the ransomware
Sage virus is distributed via advanced malware dissemination techniques[4]. In most cases, malware can be downloaded from malicious websites, compromised sites, deceptive email attachments, malware-laden ads, or exploit kits.
In some cases, malware can be installed along legitimate programs, but only if you download them from suspicious websites. Sometimes it is easy to avoid malware attacks, but in the vast majority cases, malicious programs travel using Trojan horse techniques, which means that they are masked.
For instance, they can pretend to be legitimate Flash Player or Java updates[5], free games, files, documents, and other records that do not seem dangerous at first sight. However, if you open such file or program without realizing that it is an infectious one, the computer gets contaminated rapidly. To avoid such situations, we strongly recommend you protect your PC with anti-malware software.
Sage 2 makes its appearance in February 2017
The developers of this ransomware project seem to be serious about their goals, and therefore they have recently developed a new version of the infamous ransomware. Sage 2 virus is currently distributed via spam emails that have a .ZIP file added to them. This file is named as EMAIL_[random chars]_recipient.zip or just [random chars].zip. This archive might contain another .zip file with either JS or Word file inside of it.
Once executed, JS file will download ransomware from an online server, whereas the Word file requires the victim to enable Macros function first. If the victim does that, it also downloads malware onto the PC. First of all, the ransomware stays idle for a while and then saves a copy of itself to computer's \AppData\Roaming folder.
This file automatically opens and triggers User Account Control table. The ransomware then encrypts all files described in its target list and saves !Recovery_[3 random chars].html as a ransom note on the desktop. The ransom note commands the victim to visit Sage 2.0 payment website. Here, the victim finds out how much money this virus demands – it wants to get $2000 in Bitcoins.
If the victim fails to pay the ransom in 7 days, the ransom price doubles. Sadly, this virus cannot be decrypted using any free data recovery tools. For more information about Sage 2.0, we suggest reading this article.
Sage ransomware elimination options
Sage virus drops a variety of malicious files, including AVuKmu.bmp, 1.tmp, hPBic1zL.tmp, VIxkxhFa.lnk, and more. The virus assigns itself to Startup programs to automatically run itself whenever the victim boots the PC.
To remove Sage ransomware, we suggest you reboot your PC in a Safe Mode w/ Networking[6] (instructions on how to do it are already prepared and awaits for your attention – you can find them below!).
Do not start Sage removal without rebooting your PC as explained because the virus might simply disable your antivirus every time you attempt to run it. Although at the moment we cannot offer you any 100% efficient data decryption tools that could decrypt .sage file extension files, please take a look at data recovery options provided below.
Getting rid of Sage virus. Follow these steps
Manual removal using Safe Mode
This method is specifically designed for dealing with severe threats. Some of them tend to lock the computer screen and turn off other crucial functions. In case Sage ransomware also deprives you of the complete control, restart the device in Safe Mode.
Important! →
Manual removal guide might be too complicated for regular computer users. It requires advanced IT knowledge to be performed correctly (if vital system files are removed or damaged, it might result in full Windows compromise), and it also might take hours to complete. Therefore, we highly advise using the automatic method provided above instead.
Step 1. Access Safe Mode with Networking
Manual malware removal should be best performed in the Safe Mode environment.
Windows 7 / Vista / XP
- Click Start > Shutdown > Restart > OK.
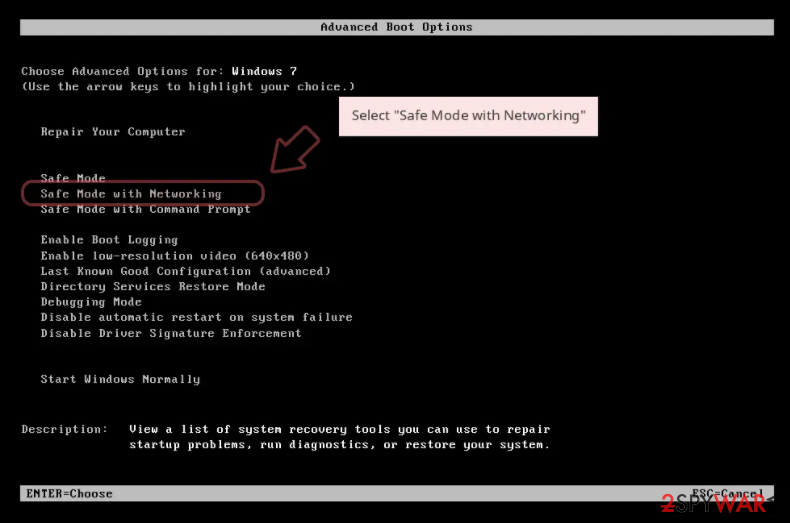
- When your computer becomes active, start pressing F8 button (if that does not work, try F2, F12, Del, etc. – it all depends on your motherboard model) multiple times until you see the Advanced Boot Options window.
- Select Safe Mode with Networking from the list.
Windows 10 / Windows 8
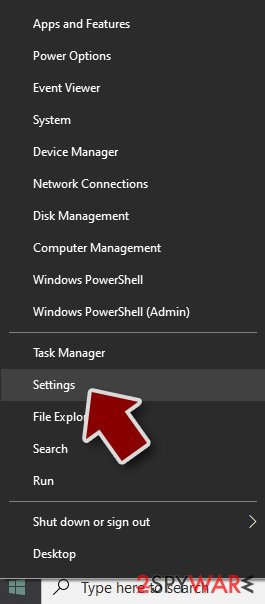
- Right-click on Start button and select Settings.
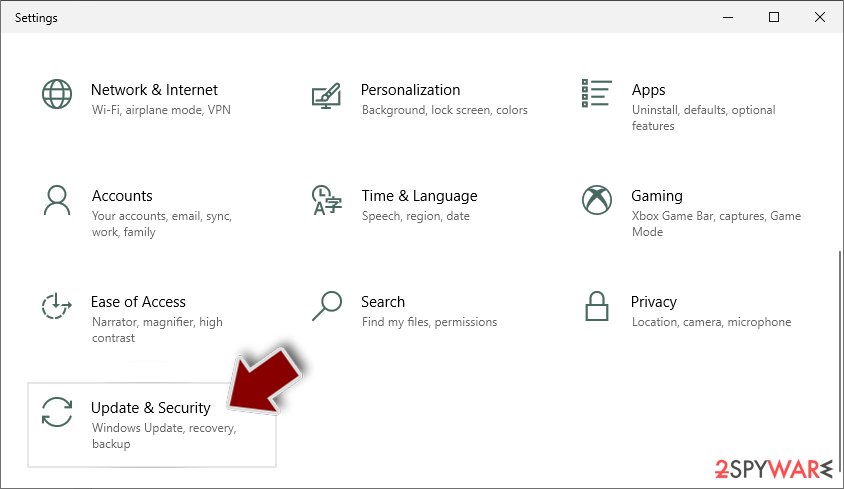
- Scroll down to pick Update & Security.
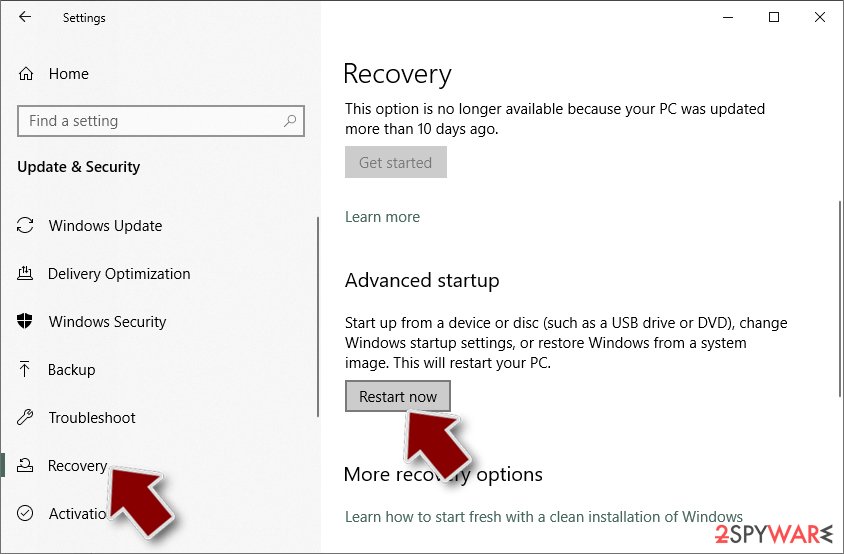
- On the left side of the window, pick Recovery.
- Now scroll down to find Advanced Startup section.
- Click Restart now.
- Select Troubleshoot.
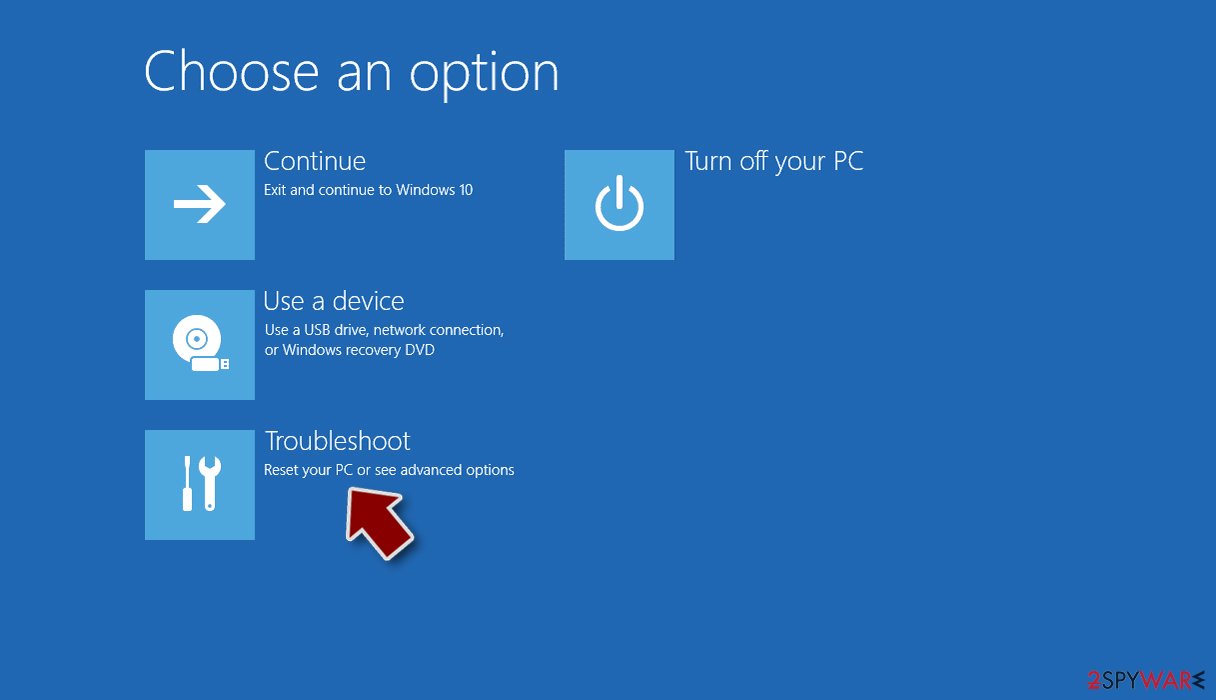
- Go to Advanced options.
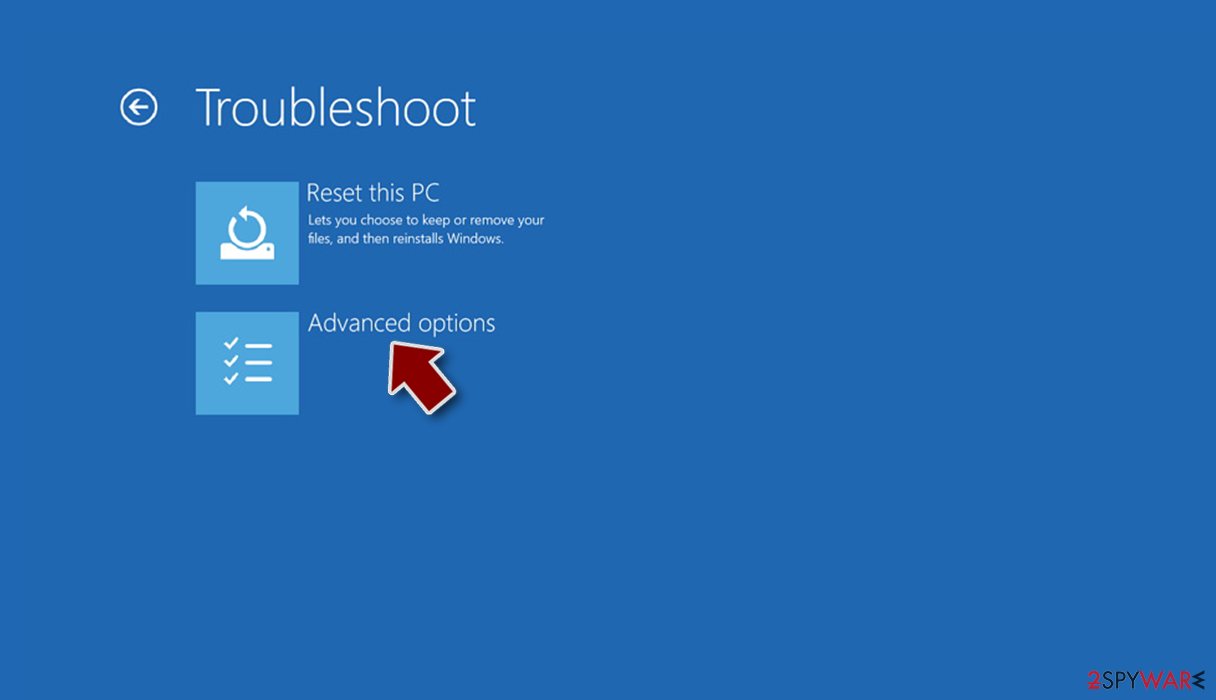
- Select Startup Settings.

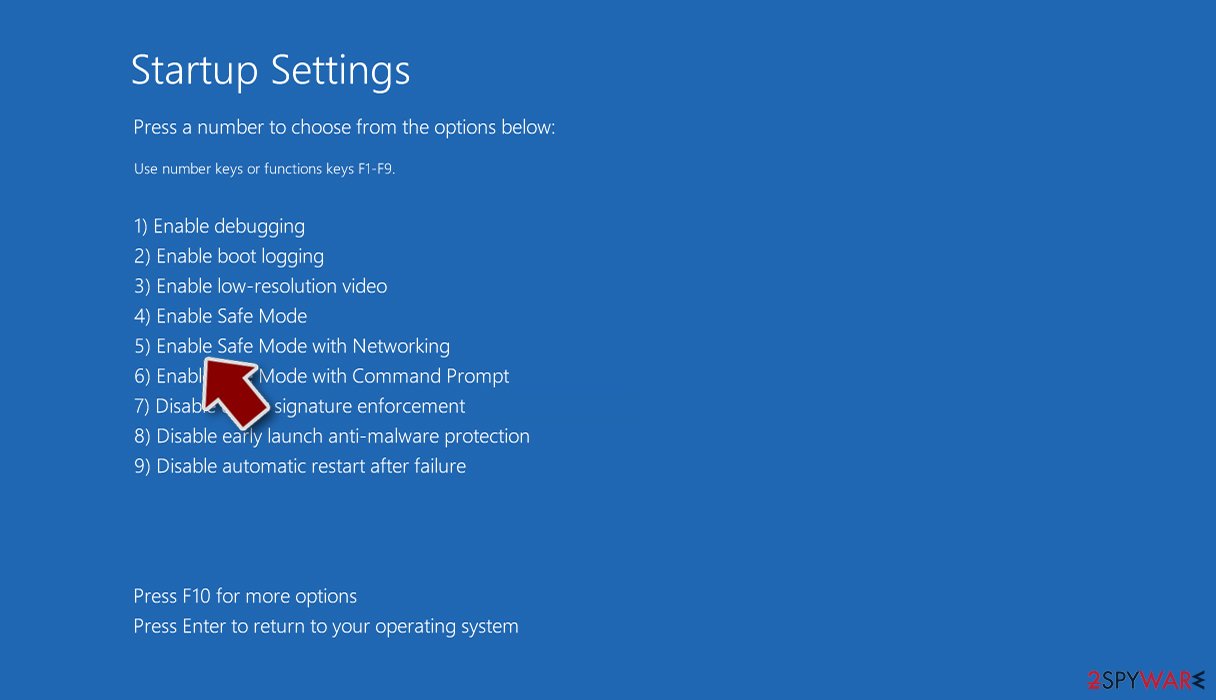
- Press Restart.
- Now press 5 or click 5) Enable Safe Mode with Networking.
Step 2. Shut down suspicious processes
Windows Task Manager is a useful tool that shows all the processes running in the background. If malware is running a process, you need to shut it down:
- Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc on your keyboard to open Windows Task Manager.
- Click on More details.
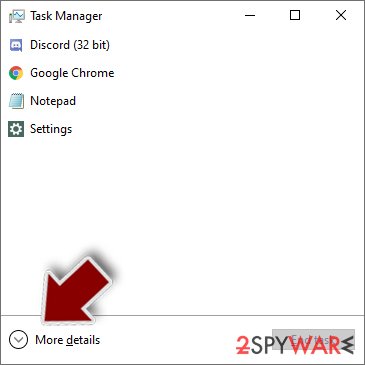
- Scroll down to Background processes section, and look for anything suspicious.
- Right-click and select Open file location.
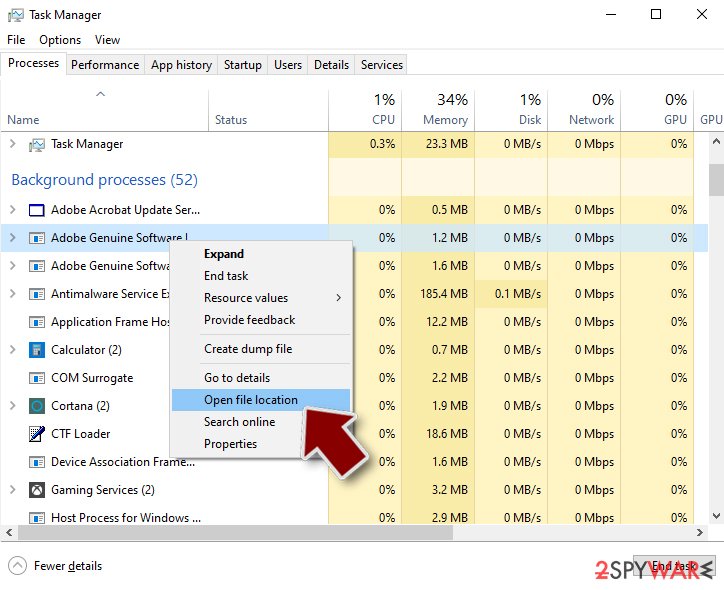
- Go back to the process, right-click and pick End Task.
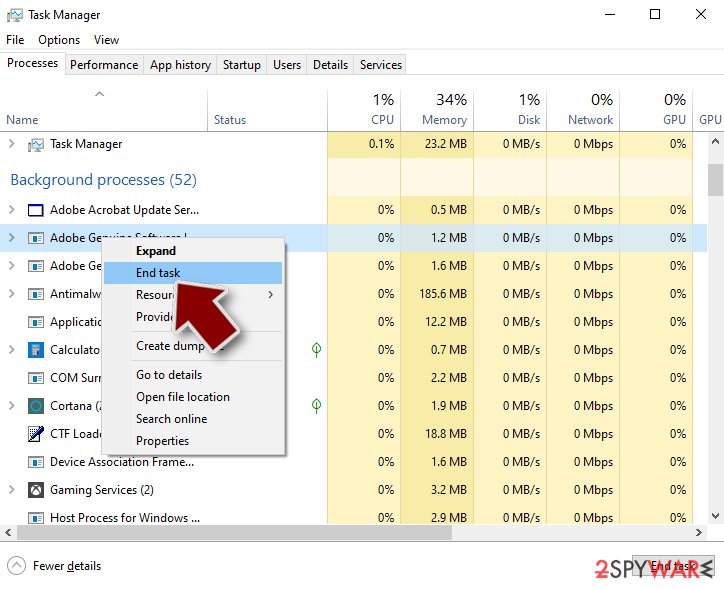
- Delete the contents of the malicious folder.
Step 3. Check program Startup
- Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc on your keyboard to open Windows Task Manager.
- Go to Startup tab.
- Right-click on the suspicious program and pick Disable.
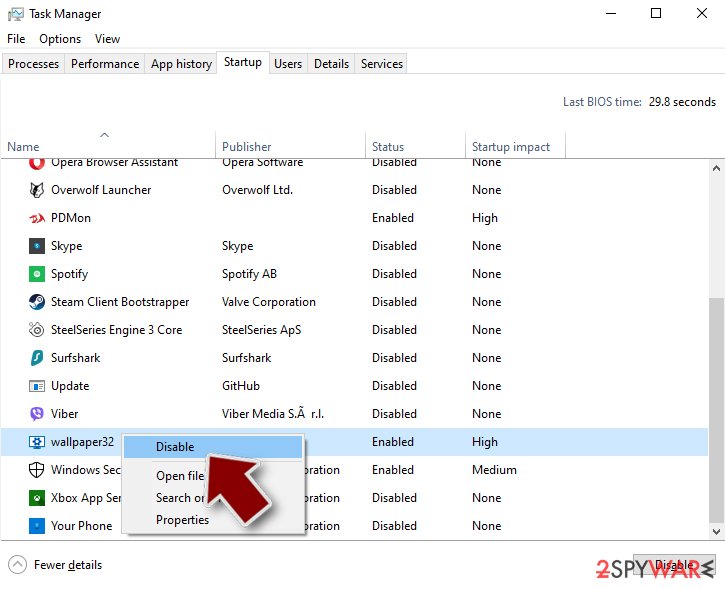
Step 4. Delete virus files
Malware-related files can be found in various places within your computer. Here are instructions that could help you find them:
- Type in Disk Cleanup in Windows search and press Enter.
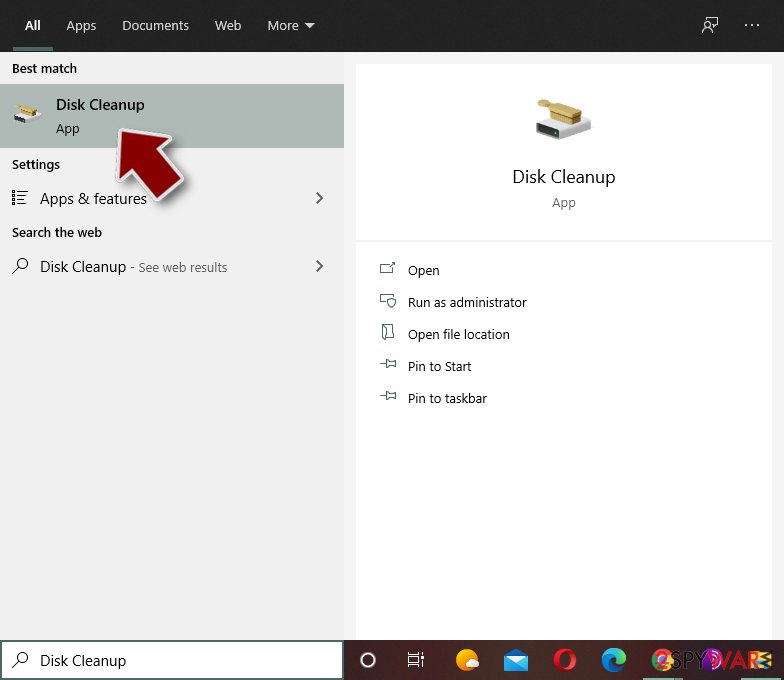
- Select the drive you want to clean (C: is your main drive by default and is likely to be the one that has malicious files in).
- Scroll through the Files to delete list and select the following:
Temporary Internet Files
Downloads
Recycle Bin
Temporary files - Pick Clean up system files.
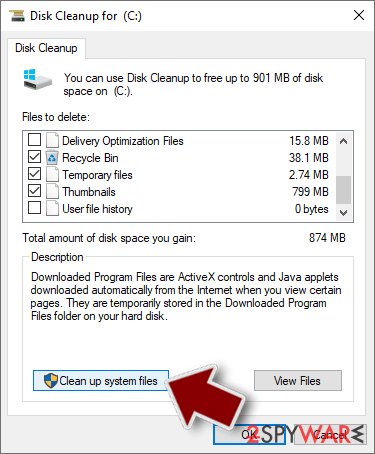
- You can also look for other malicious files hidden in the following folders (type these entries in Windows Search and press Enter):
%AppData%
%LocalAppData%
%ProgramData%
%WinDir%
After you are finished, reboot the PC in normal mode.
Remove Sage using System Restore
You might benefit from System Restore as well. It should grant you the access in case the first option did not succeed.
-
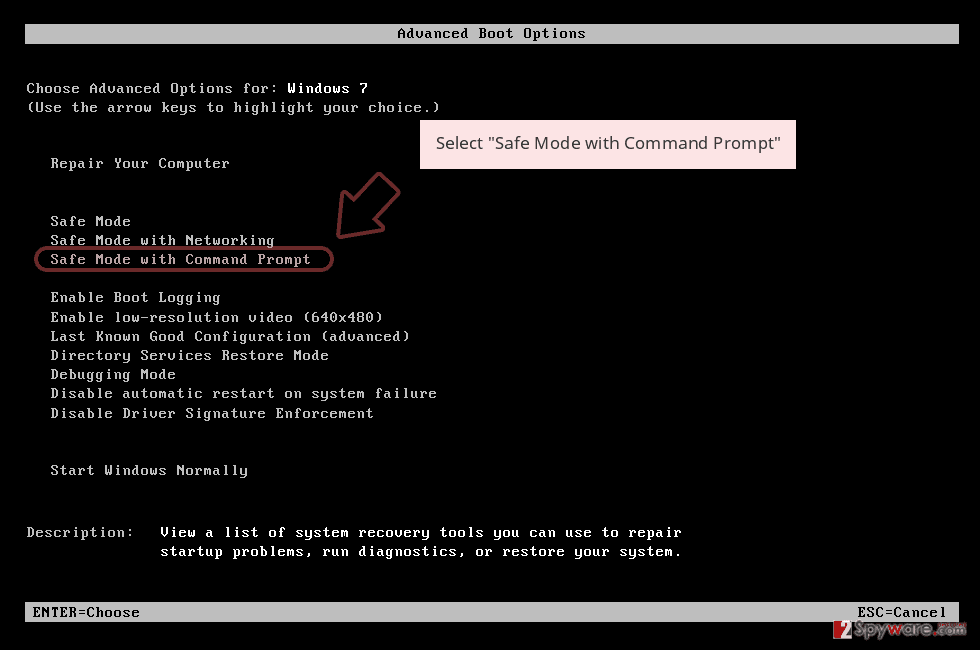
Step 1: Reboot your computer to Safe Mode with Command Prompt
Windows 7 / Vista / XP- Click Start → Shutdown → Restart → OK.
- When your computer becomes active, start pressing F8 multiple times until you see the Advanced Boot Options window.
-
Select Command Prompt from the list

Windows 10 / Windows 8- Press the Power button at the Windows login screen. Now press and hold Shift, which is on your keyboard, and click Restart..
- Now select Troubleshoot → Advanced options → Startup Settings and finally press Restart.
-
Once your computer becomes active, select Enable Safe Mode with Command Prompt in Startup Settings window.

-
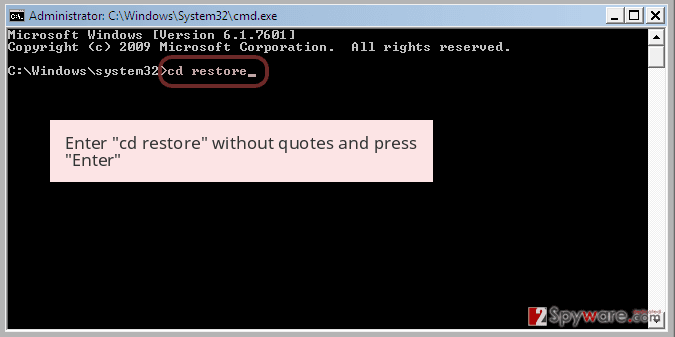
Step 2: Restore your system files and settings
-
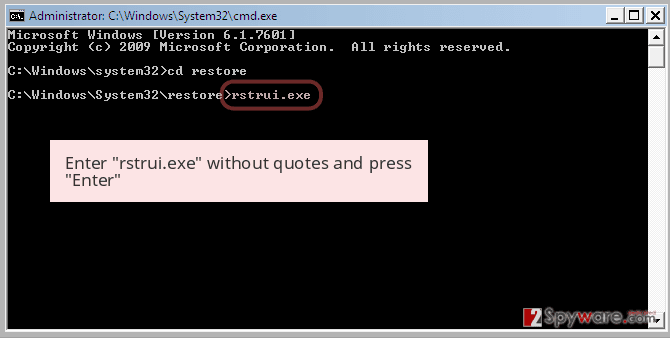
Once the Command Prompt window shows up, enter cd restore and click Enter.

-
Now type rstrui.exe and press Enter again..

-
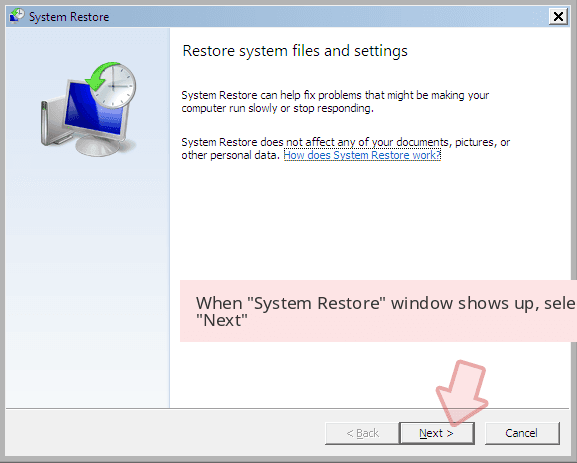
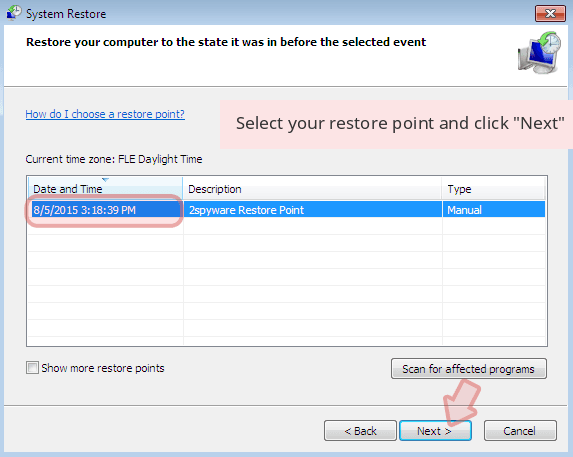
When a new window shows up, click Next and select your restore point that is prior the infiltration of Sage. After doing that, click Next.


-
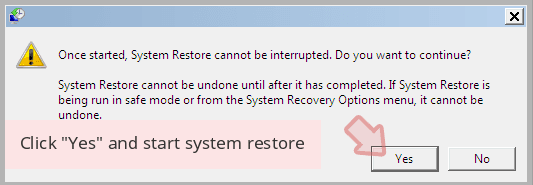
Now click Yes to start system restore.

-
Once the Command Prompt window shows up, enter cd restore and click Enter.
Bonus: Recover your data
Guide which is presented above is supposed to help you remove Sage from your computer. To recover your encrypted files, we recommend using a detailed guide prepared by 2-spyware.com security experts.Sadly, the only way to recover all of your data is to have a backup.
If your files are encrypted by Sage, you can use several methods to restore them:
Make use of Data Recovery Pro
This is one of the alternative data recovery programs. One of the key practical features is its ability to restore deleted files as well.
- Download Data Recovery Pro;
- Follow the steps of Data Recovery Setup and install the program on your computer;
- Launch it and scan your computer for files encrypted by Sage ransomware;
- Restore them.
Try to find Windows Previous Versions
If you enabled System Restore function in the past, you can use this method to recover the most important files one by one. Follow these steps:
- Find an encrypted file you need to restore and right-click on it;
- Select “Properties” and go to “Previous versions” tab;
- Here, check each of available copies of the file in “Folder versions”. You should select the version you want to recover and click “Restore”.
Shadow Explorer option
This program works on the basis of shadow volume copies. Unfortunately, Sage malware deletes these copies beforehand. However, if you notice the first signs early, you might have a chance to save your data if you make a rush.
- Download Shadow Explorer (http://shadowexplorer.com/);
- Follow a Shadow Explorer Setup Wizard and install this application on your computer;
- Launch the program and go through the drop down menu on the top left corner to select the disk of your encrypted data. Check what folders are there;
- Right-click on the folder you want to restore and select “Export”. You can also select where you want it to be stored.
Sage Decrypter
Due to its exquisite structure, there is no released decryption tool yet.
Finally, you should always think about the protection of crypto-ransomwares. In order to protect your computer from Sage and other ransomwares, use a reputable anti-spyware, such as FortectIntego, SpyHunter 5Combo Cleaner or Malwarebytes
How to prevent from getting ransomware
Do not let government spy on you
The government has many issues in regards to tracking users' data and spying on citizens, so you should take this into consideration and learn more about shady information gathering practices. Avoid any unwanted government tracking or spying by going totally anonymous on the internet.
You can choose a different location when you go online and access any material you want without particular content restrictions. You can easily enjoy internet connection without any risks of being hacked by using Private Internet Access VPN.
Control the information that can be accessed by government any other unwanted party and surf online without being spied on. Even if you are not involved in illegal activities or trust your selection of services, platforms, be suspicious for your own security and take precautionary measures by using the VPN service.
Backup files for the later use, in case of the malware attack
Computer users can suffer from data losses due to cyber infections or their own faulty doings. Ransomware can encrypt and hold files hostage, while unforeseen power cuts might cause a loss of important documents. If you have proper up-to-date backups, you can easily recover after such an incident and get back to work. It is also equally important to update backups on a regular basis so that the newest information remains intact – you can set this process to be performed automatically.
When you have the previous version of every important document or project you can avoid frustration and breakdowns. It comes in handy when malware strikes out of nowhere. Use Data Recovery Pro for the data restoration process.
- ^ RSA. Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia.
- ^ Thorin Klosowski. What Is Tor and Should I Use It?. Lifehacker. Daily weblog on software and personal productivity recommends downloads, web sites and shortcuts that help you work smarter and save time.
- ^ What is Bitcoin?. Coindesk. The world leader in news, prices and information on bitcoin and other digital currencies.
- ^ How does malware infect your PC. Microsoft Malware Protection Center. Committed to helping Microsoft customers keep their computers secure.
- ^ Topher Kessler. Beware of fake Java updates. CNET. The world's leader in tech product reviews, news, prices, videos, forums, how-tos and more.
- ^ Chris Hoffman. How to Use Safe Mode to Fix Your Windows PC (and When You Should). How-to Geek. Includes help, tutorials, tips and how-to guides for Windows and Linux.