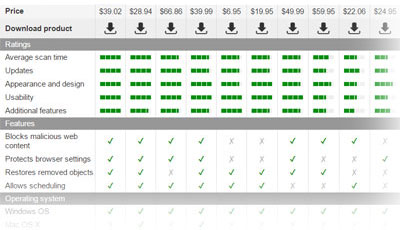
Antiviruses
Antivirus is computer software, designed to detect, indicate, eliminate and prevent cyber infections. Programs that belong to this category have been developing through the years, continuously learning to adapt to new challenges. Beginning with the late 80’s, these programs have become an inseparable part of millions of computers around the world. Even today, the creators of the most sophisticated virus-fighting utilities have to be quick to react to the never-ending malware releases and new versions of the already existing infections.
To put that in more concrete numbers, around 390,000 of potentially dangerous programs enter the web daily. Of course, the hard work of antivirus professionals does not go to waste and computer users can feel a lot more confident about the security of their devices, safety of their files as well as their privacy. Yet again, antivirus success provides the virus creators with motivation to keep on looking for other ways to bypass the defense. This cyber war antivirus software is fighting to ensure the safety of our computers is virtually never-ending. Because we deal with these programs every day, it is beneficial to learn more about them: how they actually work, what types of antivirus there are, what do they protect against and what are their vulnerabilities.
What are the primary functions of an antivirus?
As we have already mentioned, the primary foci of any virus-fighting utility are:
- malware detection
- virus removal
- system defense
To be able to detect the malicious files or programs, the software must be equipped with a powerful scanning system which would discover potentially dangerous tendencies in specific directories or files. Of course, even the best antivirus scanner would be useless without a proper virus database. Regular virus descriptions updates are crucial for the antivirus to perform to its fullest potential. Luckily, most antivirus utilities allow scheduling the updates, so this is another entry you can scratch from the list of things to remember. System scans can be scheduled as well. You can customize the frequency and the focus of these scans according to your needs. It means that you can choose to scan your whole system or focus on a specific drive, file, external storage drive, etc.
When it comes to the elimination of the already detected infections, most programs will deal with the whole situation automatically. Other utilities can allow you to quarantine the files before deciding whether you wish to remove them or not. Either way, most programs will display the scan results and offer general statistics about your computer’s current state, so you could evaluate the situation better.
Although virus detection and removal are crucial aspects of a reputable antivirus utility, yet success rate of the malware prevention is probably one of the first aspects users pay attention to when they decide to obtain a virus defender. According to the computer users, professional antivirus software should be able to provide a real-time protection while browsing online, stop you from entering insecure pages or downloading malicious software on your computer. Most programs do just that, but it is important to keep in mind that there are numerous ways the defense shields can be bypassed. Later on, we will elaborate more about the vulnerabilities of antivirus software.
Types of antiviruses
Antivirus is probably the most general term to define contemporary virus-fighting software including numerous specialized software, such as:
Usually, these programs fall under “antivirus” umbrella term and, in fact, they are often integrated into what is called an “antivirus suite”. However, no matter that their collaboration should make a single and very powerful tool, the old saying that too many cooks spoil the broth is really true to such suites. It is always more reliable to have several reliable software which would be designed for specific purposes, rather than one utility which packs everything together, perhaps, leaving some of the important functions behind.
Besides the virus protection, there are also a few other options that antivirus developers offer for their users:
- Cloud antivirus
This novel antivirus technology is based on a virtual software which is installed on the user’s computer and can only be accessed when there is a network connection available. The major benefit of such software is because it almost does not take up any space on the computer and does not slow down its performance while running the scan because most of the analysis is carried out on remote antivirus provider’s server. What is more, this technology allows the data to be investigated with several antivirus and malware detection engines simultaneously, increasing the virus detection and removal rate.
- Online scanning
Online scanning is similar to the antivirus cloud service, though it works a lot more like a regular antivirus utility. It allows scanning the computers with lesser performance capabilities, choosing specific areas or entire device at a time. You should be careful though because there are numerous fake antivirus utilities which supposedly offer to scan your computer but install additional malware instead.
Antivirus weaknesses and future prospects
As already noted in this article, antivirus software is not almighty and often needs backup programs to be able to provide a more sophisticated protection. Note that no antivirus software can protect your computer by a full 100%, so it would not be wise to rely on these tools unconditionally. Another drawback of these utilities is slow system performance. It is typical that the system and network performance significantly slow down during the scan, because of the massive amount of information that is being processed. Finally, antivirus utilities take up a lot of memory and disk space which can be another factor why your computer is working slower after you install such a tool on your device.
All in all, antiviruses might not be the smoothest or the most effective defense mechanisms, but despite their drawbacks and vulnerabilities, they are still the best protection we have got. We can only hope that virus-fighting technology will only improve in the future and we will be able to enjoy much faster and more efficient virus-fighting utilities.
Latest Software Reviews
Get BullGuard Mobile Security
Norton Internet Security
Defender Pro Ultimate review
Information updated: 2017-05-11