Messenger virus. 2023 update. A new threat for Facebook users.
Facebook Message virus Removal Guide
What is Facebook Message virus?
Messenger virus might infect your device with malware and take over your Facebook account
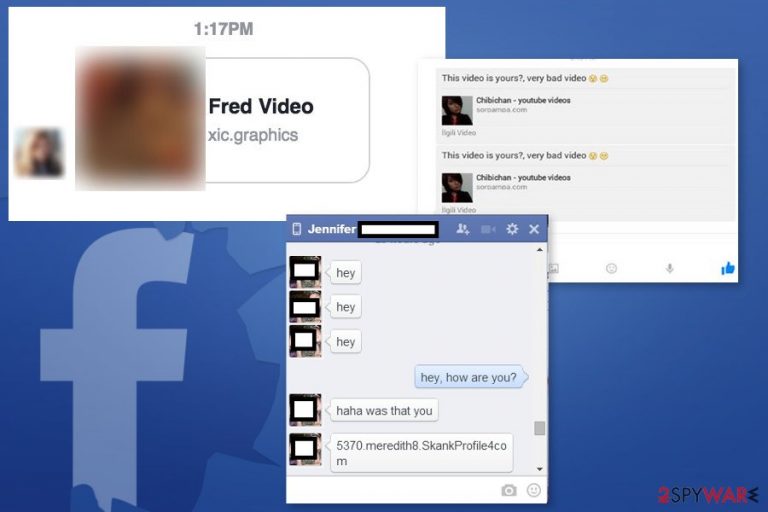
In the realm of online threats, the Facebook Messenger virus or Facebook video virus has proven to be a persistent and ever-evolving menace. Since its first appearance in 2013, this computer infection has continued to spread through the popular social media platform,[1] leveraging social engineering techniques to deceive users and compromise their accounts. In this article, we delve into the intricacies of the Facebook Messenger virus, exploring its various forms, its impact on users, and strategies for protection.
| Name | Messenger virus |
|---|---|
| Type | Facebook virus |
| Category | Malware; scam; spam |
| Active since | 2013 |
| Increased activity |
|
| Symptoms | Delivers questionable content, redirects, fake direct messages or notifications, malicious downloads, hyperlinks |
| Main danger | Infects the system with other malware, exposes to malicious content and steals sensitive information (login credentials, financial data, etc.) |
| Distribution | Messages with hyperlinks sent from compromised accounts |
| Avoidance tips |
Creating complex passwords that conclude from at least 12 alphanumeric characters. Avoid clicking hyperlinks in suspicious messages. |
| Removal | The removal depends on what type of infection threat actors were trying to spread. Nevertheless, most of the malware can be terminated with reputable anti-virus software like SpyHunter 5Combo Cleaner or Malwarebytes |
| Damage fix | Trojans and worms can infect computer system files, which anti-virus cannot remediate. As a result, Windows might start crashing or returning multiple errors after malware is removed. To fix virus damage, scan your machine with PC repair tool FortectIntego |
Understanding the Facebook Messenger virus
The Facebook Messenger virus is a type of malware that spreads its infection through compromised accounts. Victims receive messages from people on their friend list, which leads them to believe the message is genuine. These messages, however, frequently contain suspicious links or booby-trapped file attachments that launch malicious programs on the recipient's computer. Despite Facebook's new security measures, the virus has been infecting users since 2013 and continues to pose a significant threat.
The Facebook Messenger virus's goal is to gain unauthorized access to user accounts and use those accounts to spread malware further. When a user's account is compromised, the virus can send messages to the victim's contacts, increasing the likelihood of more people becoming infected. The virus's ability to self-replicate contributes to its widespread and persistent nature.
The deceptive tactics
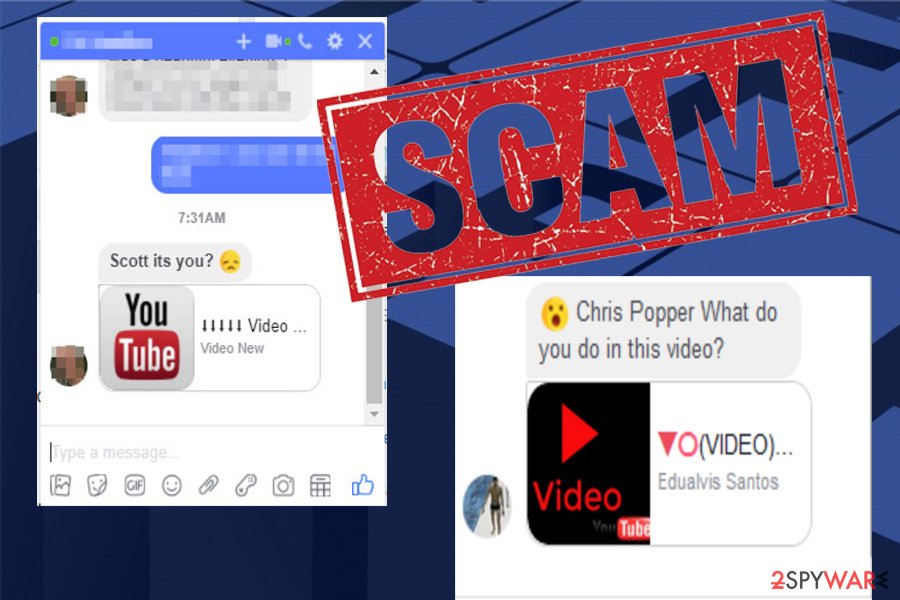
Social engineering is a key tactic used by the Facebook Messenger virus. Scammers employ a variety of methods to make their messages appear legitimate and appealing to users. They frequently include catchy headlines like “Is that you?” or “XXX video,” as well as an embedded icon that looks like the YouTube logo.[2] Because of the combination of familiar elements and intriguing content, users are more likely to click on malicious links.
The messages sent by the Facebook Messenger virus frequently take advantage of human curiosity, trust, or fear to trick users into acting. They may claim to have urgent or confidential information, or they may pose as a friend or family member in need of help. Scammers hope to bypass users' critical thinking by exploiting these emotions and convincing them to click on infected links or download malicious attachments.
In some cases, the Facebook Messenger virus may even use hijacked accounts to converse with users, establishing even more trust. These conversations frequently result in the sharing of more malicious links or the disclosure of personal information that cybercriminals can use for malicious purposes.
The wide range of malware associated with the Messenger virus
The Facebook Messenger virus is not limited to a single type of malware. It can deliver a variety of malicious programs, each with its own set of capabilities and potential risks. Some common types of malware associated with the Messenger virus include:
- Cryptominers: These malware strains hijack a victim's computer resources to mine cryptocurrencies,[3] slowing down the system and potentially causing financial losses due to increased electricity consumption.
- Data stealers: Some Messenger virus variants aim to steal sensitive information, such as login credentials, financial details, or personal data. This stolen information can be used for identity theft, financial fraud, or other malicious activities.
- Trojans: The Messenger virus can also deliver trojans like the notorious FormBook trojan. Trojans are designed to bypass security measures and provide cybercriminals with remote access to the victim's computer. This can result in unauthorized data access, additional malware installation, or the ability to control the infected system.
- Ransomware: While less common in Messenger virus attacks, ransomware variants have been observed in the past. Ransomware encrypts a victim's files and demands a ransom payment in exchange for the decryption key, causing significant disruption and potential data loss.
The impact on users and businesses
Both individual users and businesses are at risk from the Facebook Messenger virus. Individuals who become infected with the Messenger virus may experience personal data breaches, financial losses, and potential identity theft. Furthermore, compromised accounts can be used to spread the virus, causing harm to friends, family, and coworkers.
Businesses are also vulnerable to the Messenger virus. Cybercriminals frequently target businesses in order to obtain sensitive company data, financial information, or customer records. The virus can also be used to deliver targeted attacks, such as spear-phishing campaigns, with the goal of stealing valuable intellectual property or infiltrating corporate networks.
A Messenger virus infection can have serious consequences for businesses, including reputational damage, financial losses, and legal liabilities. Individuals and organizations must therefore remain vigilant and take proactive measures to protect themselves against this ever-present threat.
Protecting against the Facebook Messenger virus
While the Facebook Messenger virus continues to evolve, there are several steps users can take to protect themselves and mitigate the risks:
- Educate Yourself: Stay informed about the latest tactics employed by scammers and familiarize yourself with the signs of a potential Messenger virus infection. Being aware of common red flags can help you identify suspicious messages and avoid falling victim to the malware.
- Exercise Caution: Exercise caution when interacting with messages, especially those containing unexpected or enticing content. Avoid clicking on unfamiliar links or downloading suspicious file attachments. When in doubt, contact the sender through an alternative method to verify the message's authenticity before taking any action.
- Maintain Security Measures: Ensure your computer has up-to-date antivirus software installed, and regularly scan your system for potential threats. Antivirus software can help detect and remove malware associated with the Messenger virus, providing an additional layer of protection against infections.
- Strengthen Account Security: Enable two-factor authentication for your Facebook account and regularly change passwords. Two-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security by requiring an additional verification step, such as a temporary code sent to your mobile device, before granting access to your account.
- Promptly Respond to Infections: If you suspect your computer is infected with the Messenger virus or any other malware, seek professional assistance or use reputable antivirus tools to detect and remove the malicious programs. Swift action can help minimize the potential damage caused by the infection.
- Report Suspicious Messages: In the ongoing battle against the Messenger virus, it is essential to report suspicious messages and accounts to Facebook. By reporting such incidents, you can contribute to the efforts of security teams in identifying and mitigating the spread of the virus.
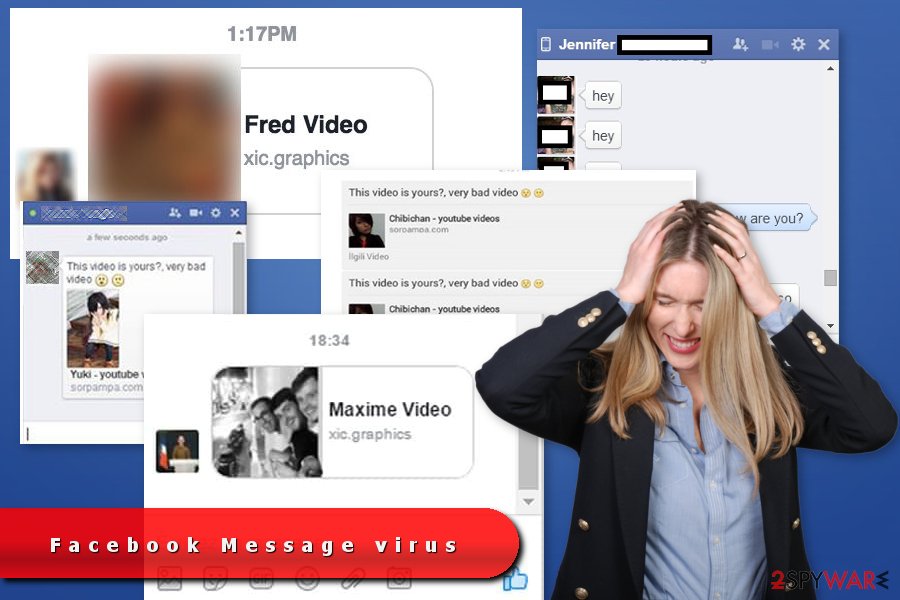
A timeline of attacks
Although the Messenger virus has been doing the rounds of Facebook for years, it seems that it's on the rise again. Recently, the National Agency for Computer Security[4] and numerous other organizations[5] alerted Internet users about new cases of this virus and urged them to delete any suspicious messages immediately.
2013 – Initial Infections: The first wave of the Facebook Messenger virus involved compromised accounts sending messages containing malicious links disguised as videos or images.[6] These links redirected users to websites hosting malware, resulting in widespread infections.
2014 – Clickjacking Attacks: Attackers began utilizing clickjacking techniques to trick users into unknowingly clicking on malicious links. By overlaying the “Like” or “Share” button on top of enticing content, scammers leveraged users' curiosity to spread the virus further.
2015 – Malicious Chrome Extensions: Cybercriminals started exploiting users' trust in browser extensions by distributing malicious Chrome extensions through the Messenger platform. These extensions often requested excessive permissions and injected unwanted advertisements or performed malicious actions on users' systems.
2016 – The Koobface Resurgence: The infamous Koobface worm, previously active on social media platforms like Facebook and MySpace, made a comeback through Facebook Messenger. The worm spread by sending messages containing links to fake video sites, ultimately leading to malware infections on users' devices.[7]
2017 – Image-based Attacks: Attackers began using image files as carriers for malware, like Locky ransomware. Users receiving these images would unknowingly download malicious files that executed malware upon opening, leading to system compromises and further propagation of the virus.[8]
2018 – Credential Harvesting: Phishing attacks became prevalent, with scammers sending deceptive messages pretending to be from Facebook or other trusted sources.[9] These messages requested users' login credentials under false pretenses, enabling attackers to gain unauthorized access to accounts.
2019 – Emotet Exploitation: The notorious Emotet malware leveraged Facebook Messenger as a distribution channel. Users received messages containing malicious Word documents claiming to contain important information. Opening these documents unleashed Emotet, which further propagated the infection and enabled additional malware installations.
2020 – COVID-19 Pandemic Exploitation: As the world grappled with the COVID-19 pandemic, scammers capitalized on the fear and uncertainty by sending messages related to pandemic updates, fake cures, or financial relief schemes. These messages contained malicious links that led to malware infections or phishing attempts.[10]
2021 – Voice Message Attacks: Attackers turned to voice messages as a means of delivering malware. Victims received messages instructing them to click on a link to listen to a voice message, which resulted in malware installation upon clicking.
2022 – Mobile Device Exploitation: The Messenger virus expanded its reach to mobile devices, targeting users through the Facebook Messenger app on smartphones and tablets. This shift increased the potential impact of the virus, as mobile devices are often interconnected with users' personal and professional lives.
2023 – Sophisticated Spear-Phishing Campaigns: Recent reports suggest an uptick in sophisticated spear-phishing campaigns delivered via Facebook Messenger. Attackers craft personalized messages that appear to come from trusted sources, deceiving users into divulging sensitive information or downloading malware-infected files.
As demonstrated by this timeline, the Facebook Messenger virus has continually adapted its tactics to exploit user trust, curiosity, and vulnerabilities. Users must remain vigilant and adapt their security practices accordingly to mitigate the risks associated with this persistent threat.
For the best threat removal results, we suggest using SpyHunter 5Combo Cleaner or Malwarebytes. Also, tools like the system optimizers can be used further to find corrupted system components and eliminate all errors on the system. When you eliminate the threat, make sure to clear other parts of the PUP and other infections, fix the damage to have the proper running machine again.
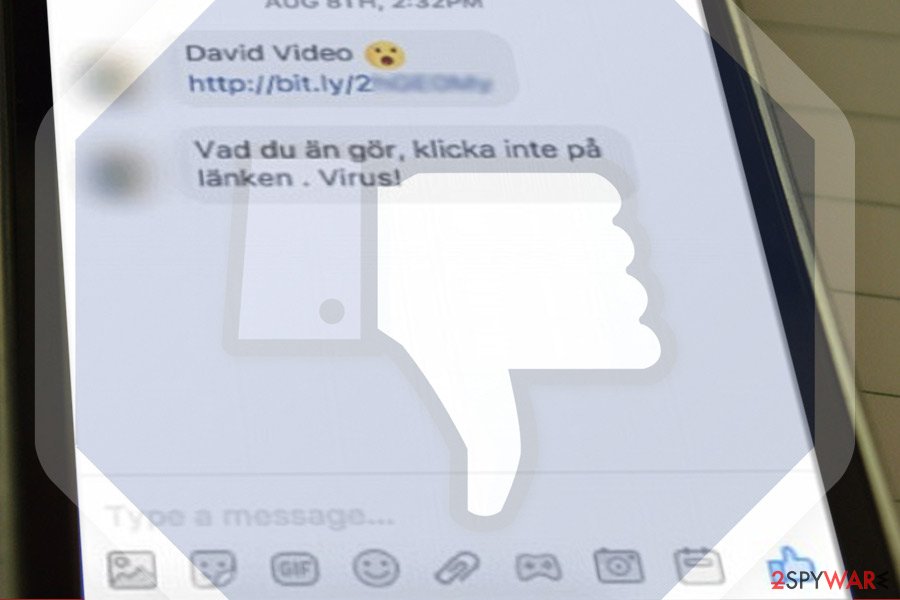
Goals of the Facebook Messenger virus: stealing passwords and more
The Facebook Messenger virus is a multifaceted threat with various goals and malicious activities. While its primary objective is to spread and infect as many devices as possible, the virus also aims to steal sensitive information, including passwords, personal data, and financial credentials. Understanding the goals and techniques employed by the Messenger virus is crucial in mitigating its impact and protecting oneself from potential harm.
- Password Theft: One of the primary objectives of the Messenger virus is to steal passwords.[11] Once a device is infected, the malware attempts to gain unauthorized access to various accounts associated with the user. This can include social media accounts, email accounts, online banking platforms, and other sensitive online services. By obtaining passwords, cybercriminals can gain control over victims' accounts, facilitating identity theft, financial fraud, and unauthorized access to personal information.
- Identity Theft: The Messenger virus is also designed to collect personal information from infected devices. This includes details such as full names, addresses, phone numbers, email addresses, and more. This stolen information can be used to perpetrate identity theft, wherein the cybercriminal assumes the victim's identity to carry out fraudulent activities, such as applying for loans, opening credit accounts, or making unauthorized purchases.
- Financial Fraud: The Messenger virus often targets users' financial information, including credit card numbers, bank account details, and payment credentials. By obtaining this information, cybercriminals can initiate fraudulent transactions, make unauthorized purchases, or even drain victims' bank accounts. Financial fraud is a significant concern for victims of the Messenger virus, as it can lead to severe financial loss and damage to their creditworthiness.
- Spreading Malware: In addition to its information theft objectives, the Messenger virus serves as a distribution mechanism for other forms of malware.[8] Once a device is infected, the virus can download and install additional malicious software, such as keyloggers, ransomware, or remote access trojans. This secondary malware can further compromise the infected device, leading to additional privacy breaches, data loss, or system disruption.[12]
- Social Engineering: The Messenger virus often employs social engineering techniques to deceive users and manipulate their actions. This can include sending fake messages from trusted contacts, enticing users to click on malicious links, or downloading infected files. By exploiting the trust users have in their friends and contacts, the virus aims to trick individuals into taking actions that facilitate its spread and compromise their devices.
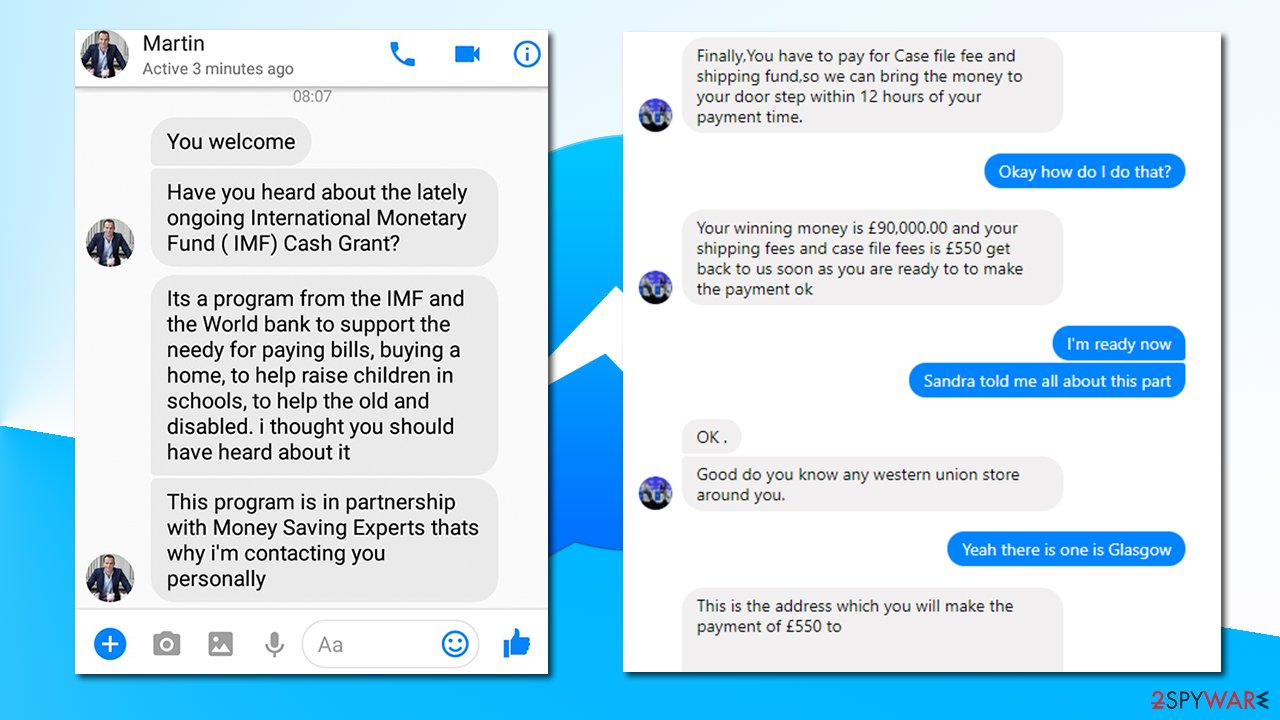
What to do when you get a suspicious message
This virus's chain messages frequently use deceptive text, such as “Is that You,” to entice users to click on malicious links. No matter how curious you are, never click on anything that raises even the slightest suspicion. By clicking on such links, you run the risk of infecting your computer with more dangerous malware, which could lead to account hacking and the spread of the same message to your friends.
To protect yourself and prevent future infections, ignore any suspicious messages and delete the associated conversation, message, or notification as soon as possible. This eliminates the possibility of inadvertently clicking on the link at a later time without thinking about it.
It is recommended that mobile device users install protective antivirus tools designed specifically for mobile security. These applications can aid in mitigating the threat and potential risks posed by the Facebook Messenger virus. To ensure the highest level of protection, obtain such tools from the official app store and choose reputable security solutions.
You can significantly reduce your chances of becoming a victim of the Facebook Messenger virus and similar threats by remaining cautious, exercising skepticism, and implementing strong security measures. Keep up to date on the latest cybersecurity practices and take a proactive approach to protecting your devices and personal information.
System repair options
When a computer becomes infected with the Facebook Messenger virus, it can disrupt various files and functions within the system. The infection may alter the Windows registry database, startup preferences, and settings, resulting in erratic behavior and unexpected operations. If the virus corrupts or deletes crucial DLL (Dynamic Link Library) files, it can lead to the failure of certain functions and generate error messages. Additionally, broken file attachments can pose a problem for many users.
We recommend using a dependable system care tool like FortectIntego to effectively address these issues and restore your system's proper functioning. While this program does not specifically detect and remove malicious files, it is critical in repairing the virus's damage after it has been removed. You can address and repair various Windows-related issues that may not be directly caused by malware infections by removing all traces of the infection and then running this application.
One of the primary benefits of using a system care tool like FortectIntego is its ability to resolve a wide range of Windows-related issues that can negatively impact system performance. It can deal with issues that, if left unresolved, can lead to Blue Screen errors, system freezes, and other problems. You can restore stability and functionality to your computer by thoroughly scanning and repairing the affected parts of your system.
Because the Facebook Messenger virus is known to spread silently and to leave behind residual files that can cause additional problems, it is critical to perform a thorough check of your machine to identify and resolve any remaining issues. You can reduce the risk of persistent system instability and future infections by ensuring a thorough examination and recovery process.
Remove the virus and protect your privacy
While the Facebook Messenger virus may appear as spam on social media platforms, it is critical to take the necessary precautions to ensure your computer's security. If you have come across any suspicious links or downloaded unknown content, you should run an anti-malware scan on your computer to check for any potential infections.
We recommend scanning your computer with reputable anti-malware programs such as SpyHunter 5Combo Cleaner or Malwarebytes to effectively remove the Facebook Messenger virus. These applications are intended to detect and remove various types of malware, including the Messenger virus. Following the initial removal, it is critical to update your chosen anti-malware program to ensure it has the most up-to-date virus definitions and capabilities. This will improve its ability to detect and remove any remaining virus damage.
If you prefer a more hands-on approach, you can try manually removing the Messenger virus-related files by following specific steps in Safe Mode. Safe Mode gives you limited access to your computer, preventing unnecessary processes from running and potentially interfering with the removal process. Detailed removal instructions are provided below.
It is critical to change your passwords in addition to removing the Messenger virus to protect your online accounts. If hackers gain access to your Facebook account, they may have obtained your login credentials for other accounts, such as email, banking, and other sensitive services. Set a strong password for each account to protect your privacy and prevent unauthorized access.
When creating a new password, keep the following guidelines in mind:
- Length: Ensure that your password is at least 12 characters long. Longer passwords are generally more secure.
- Complexity: Include a combination of numbers, uppercase and lowercase letters, and symbols (if allowed). This mix of characters makes the password harder to guess or crack.
- Avoid personal information: Do not include your name, surname, or any other personal information in your password. Hackers can easily obtain this information and use it to guess your password.
- Non-dictionary words: Avoid using common words found in dictionaries, as they are easily guessed by automated password-cracking tools. Instead, consider using a combination of random words or phrases.
Changing your passwords regularly and using different passwords for each account adds an extra layer of protection against potential unauthorized access.
By following these recommended steps for removing the Facebook Messenger virus and strengthening your computer's security, you can significantly reduce the risk of future infections and protect your personal information from falling into the wrong hands. Remember, maintaining a proactive approach to cybersecurity is essential in today's digital landscape.
Getting rid of Facebook Message virus. Follow these steps
Uninstall from Windows
Instructions for Windows 10/8 machines:
- Enter Control Panel into Windows search box and hit Enter or click on the search result.
- Under Programs, select Uninstall a program.
- From the list, find the entry of the suspicious program.
- Right-click on the application and select Uninstall.
- If User Account Control shows up, click Yes.
- Wait till uninstallation process is complete and click OK.
If you are Windows 7/XP user, proceed with the following instructions:
- Click on Windows Start > Control Panel located on the right pane (if you are Windows XP user, click on Add/Remove Programs).
- In Control Panel, select Programs > Uninstall a program.
- Pick the unwanted application by clicking on it once.
- At the top, click Uninstall/Change.
- In the confirmation prompt, pick Yes.
- Click OK once the removal process is finished.
Delete from macOS
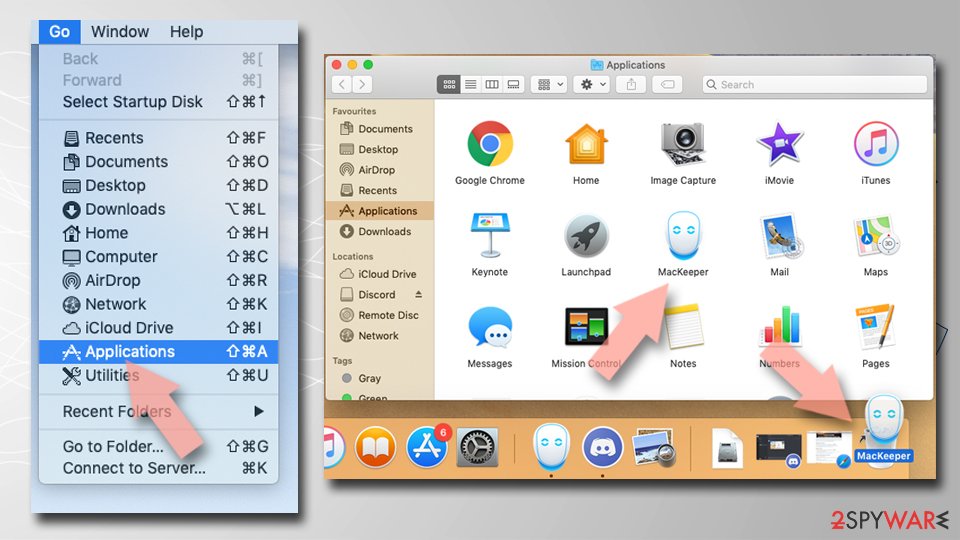
Remove items from Applications folder:
- From the menu bar, select Go > Applications.
- In the Applications folder, look for all related entries.
- Click on the app and drag it to Trash (or right-click and pick Move to Trash)
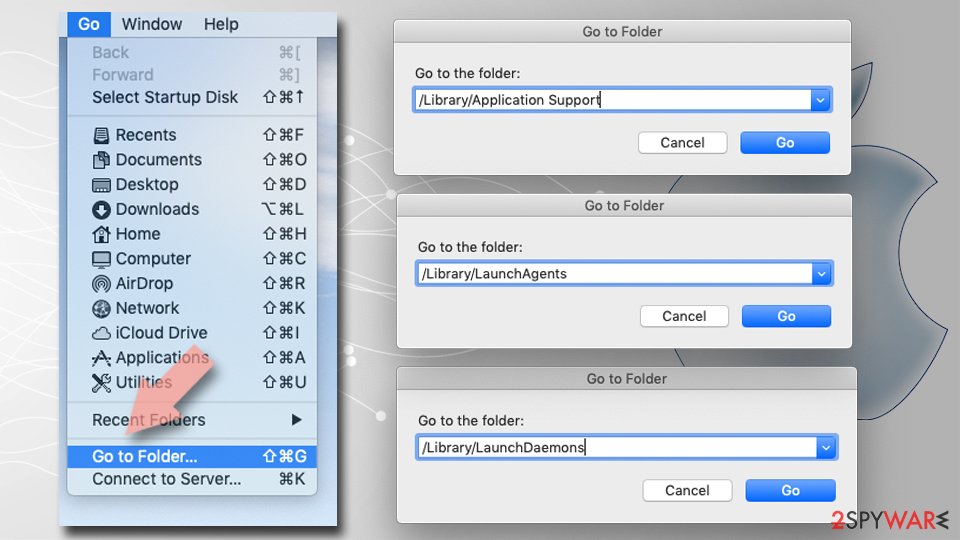
To fully remove an unwanted app, you need to access Application Support, LaunchAgents, and LaunchDaemons folders and delete relevant files:
- Select Go > Go to Folder.
- Enter /Library/Application Support and click Go or press Enter.
- In the Application Support folder, look for any dubious entries and then delete them.
- Now enter /Library/LaunchAgents and /Library/LaunchDaemons folders the same way and terminate all the related .plist files.
Uninstall from Android
Uninstall unwanted programs from Android device:
- Go to Settings -> Apps/Applications.
- Expand the full list of the installed apps.
- Scroll through the list and tap on a suspicious application once.
- Tap on it and select Uninstall.
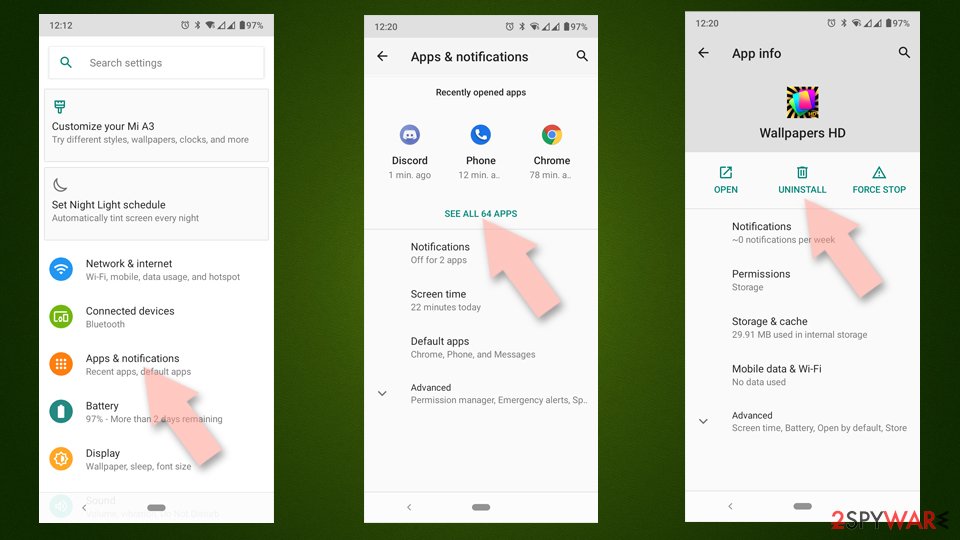
- Reboot the device.
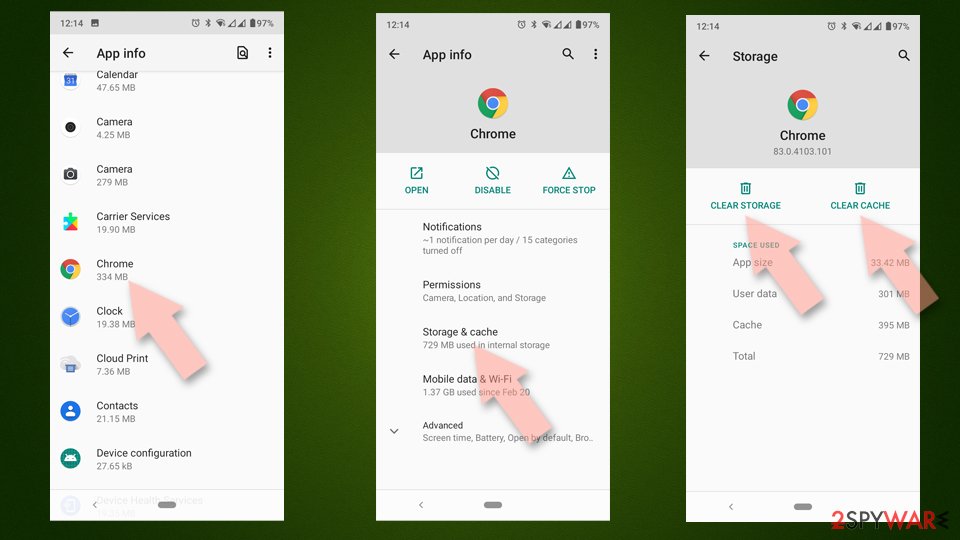
Clear Storage and data files on Android from Google Chrome or other apps:
- Go to Settings > Apps/Applications.
- Expand the full list of the installed apps.
- Tap on Chrome and select Storage & cache.
- Clear storage and clear cache of the app.
If you are seeing ads on top of other apps but are not sure what is causing it, perform the following steps:
- Go to Apps/Applications.
- Tap Advanced.
- Select Special App access.
- Tap on Display over other apps.
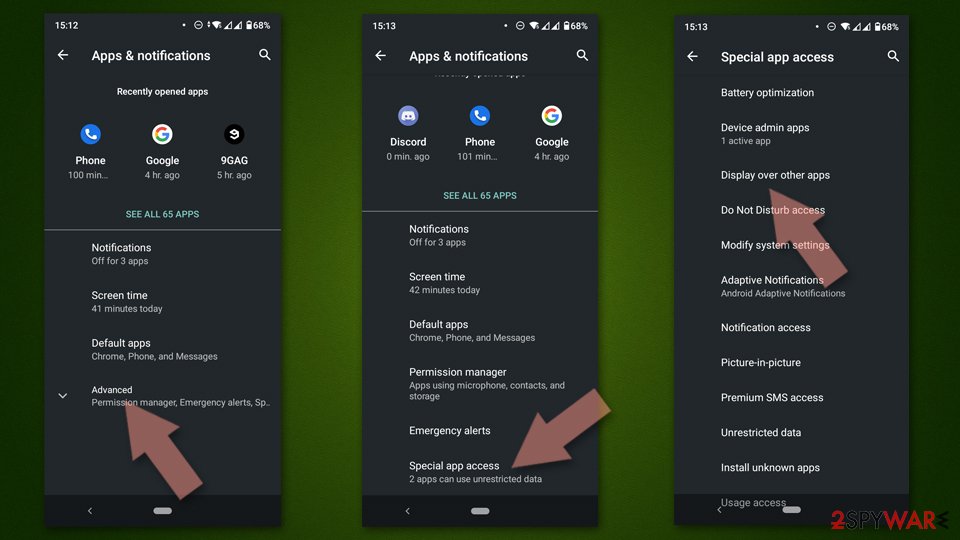
- Eliminate apps with these access rights enabled.
Remove from Microsoft Edge
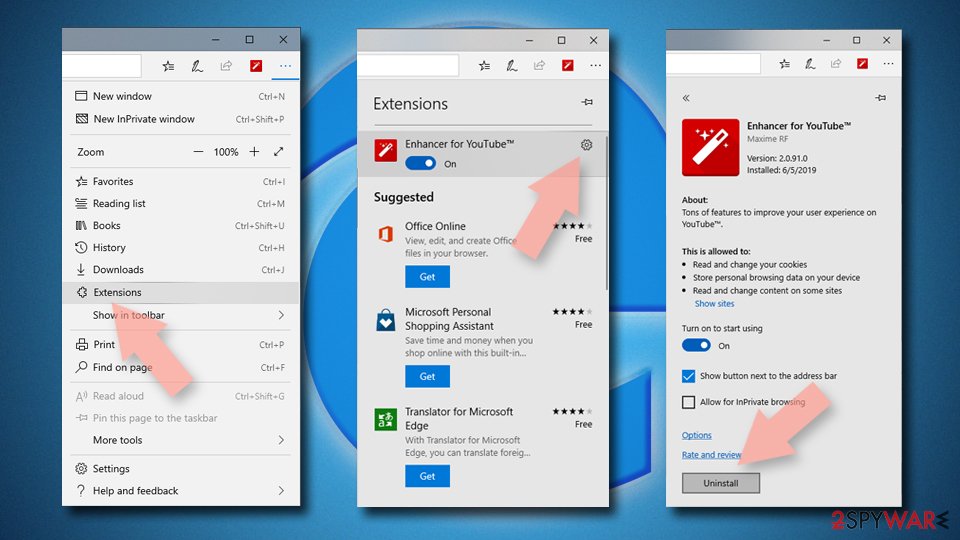
Delete unwanted extensions from MS Edge:
- Select Menu (three horizontal dots at the top-right of the browser window) and pick Extensions.
- From the list, pick the extension and click on the Gear icon.
- Click on Uninstall at the bottom.
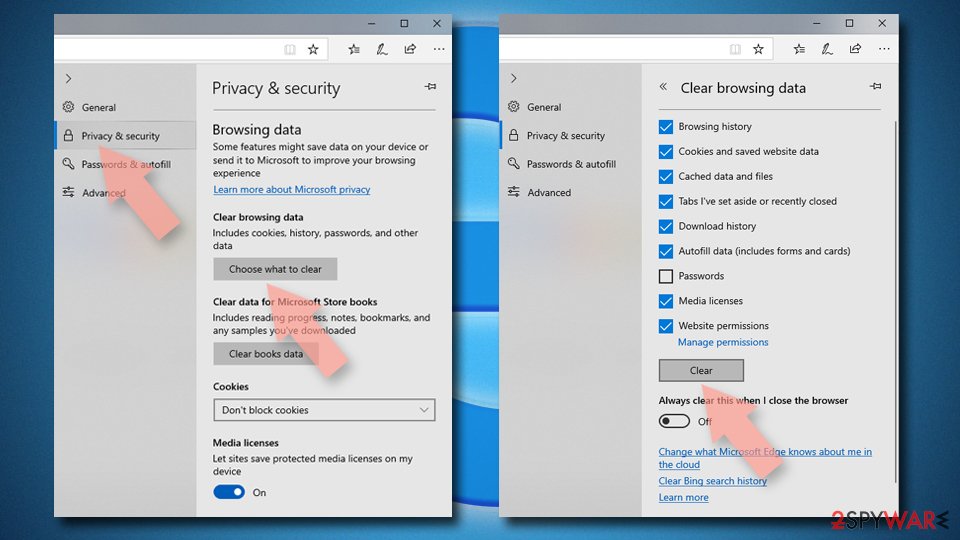
Clear cookies and other browser data:
- Click on the Menu (three horizontal dots at the top-right of the browser window) and select Privacy & security.
- Under Clear browsing data, pick Choose what to clear.
- Select everything (apart from passwords, although you might want to include Media licenses as well, if applicable) and click on Clear.
Restore new tab and homepage settings:
- Click the menu icon and choose Settings.
- Then find On startup section.
- Click Disable if you found any suspicious domain.
Reset MS Edge if the above steps did not work:
- Press on Ctrl + Shift + Esc to open Task Manager.
- Click on More details arrow at the bottom of the window.
- Select Details tab.
- Now scroll down and locate every entry with Microsoft Edge name in it. Right-click on each of them and select End Task to stop MS Edge from running.
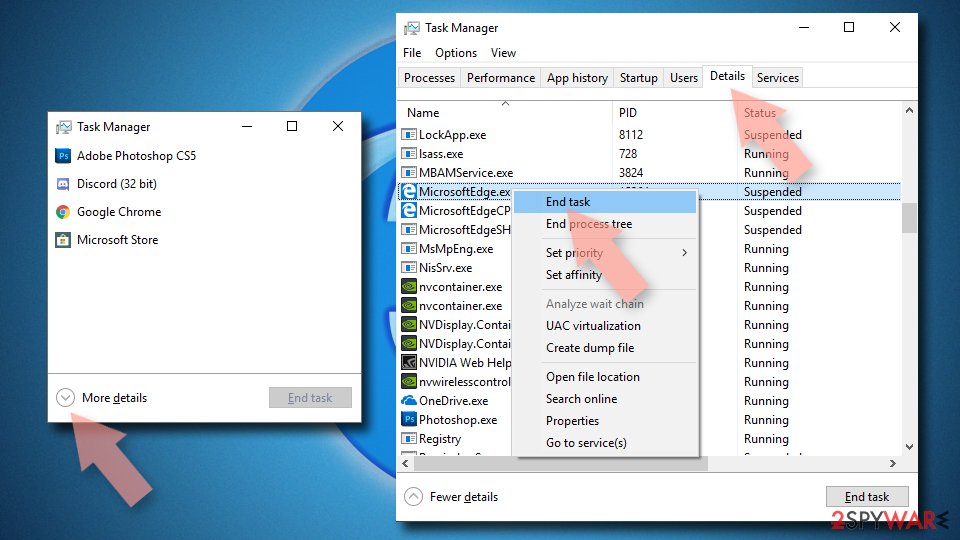
If this solution failed to help you, you need to use an advanced Edge reset method. Note that you need to backup your data before proceeding.
- Find the following folder on your computer: C:\\Users\\%username%\\AppData\\Local\\Packages\\Microsoft.MicrosoftEdge_8wekyb3d8bbwe.
- Press Ctrl + A on your keyboard to select all folders.
- Right-click on them and pick Delete
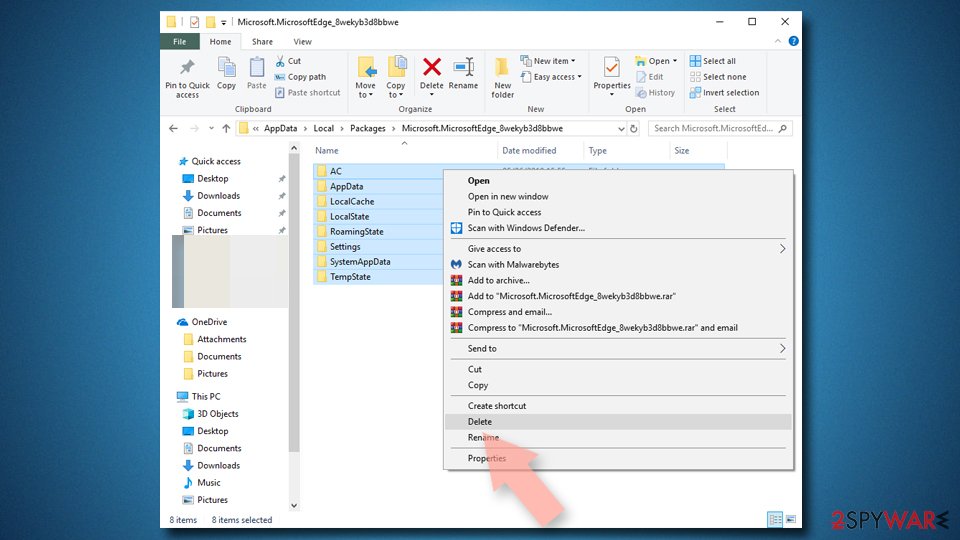
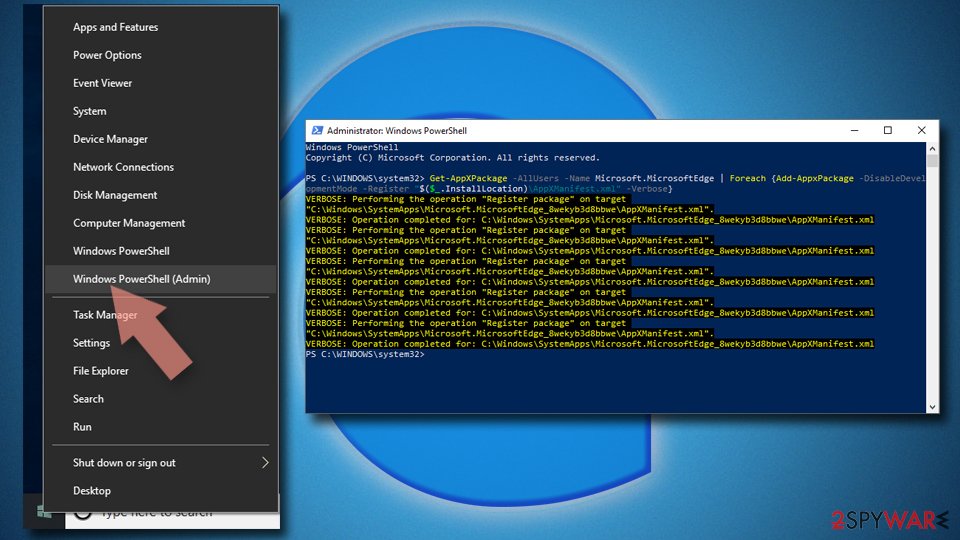
- Now right-click on the Start button and pick Windows PowerShell (Admin).
- When the new window opens, copy and paste the following command, and then press Enter:
Get-AppXPackage -AllUsers -Name Microsoft.MicrosoftEdge | Foreach {Add-AppxPackage -DisableDevelopmentMode -Register “$($_.InstallLocation)\\AppXManifest.xml” -Verbose
Instructions for Chromium-based Edge
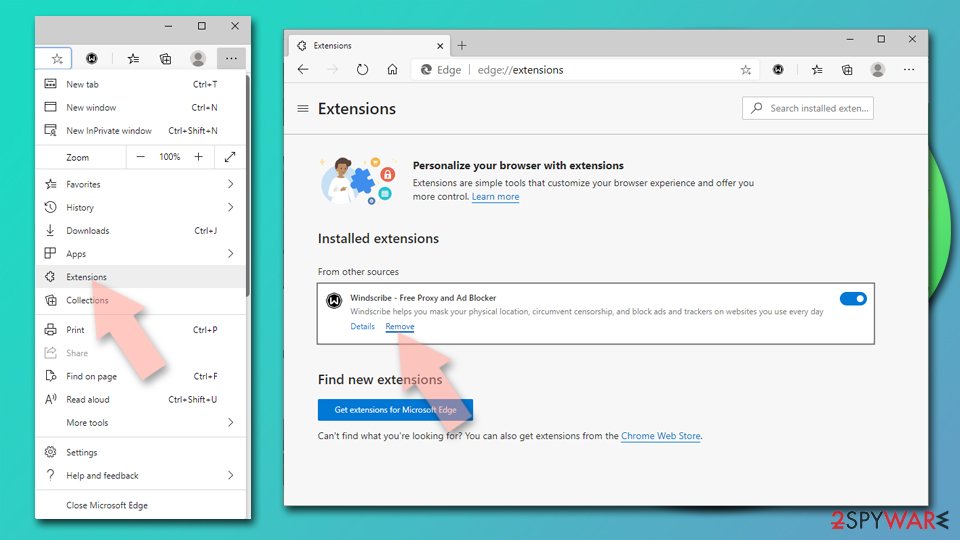
Delete extensions from MS Edge (Chromium):
- Open Edge and click select Settings > Extensions.
- Delete unwanted extensions by clicking Remove.
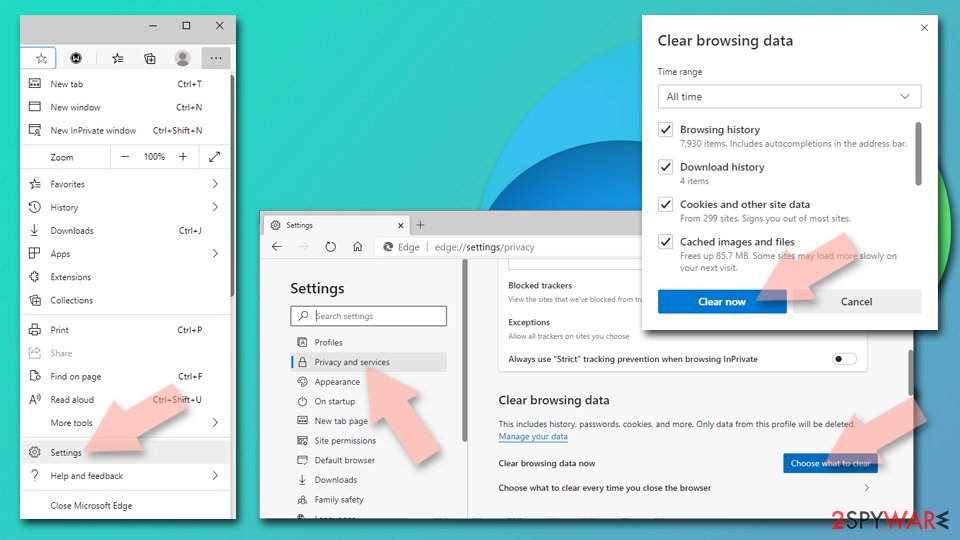
Clear cache and site data:
- Click on Menu and go to Settings.
- Select Privacy, search and services.
- Under Clear browsing data, pick Choose what to clear.
- Under Time range, pick All time.
- Select Clear now.
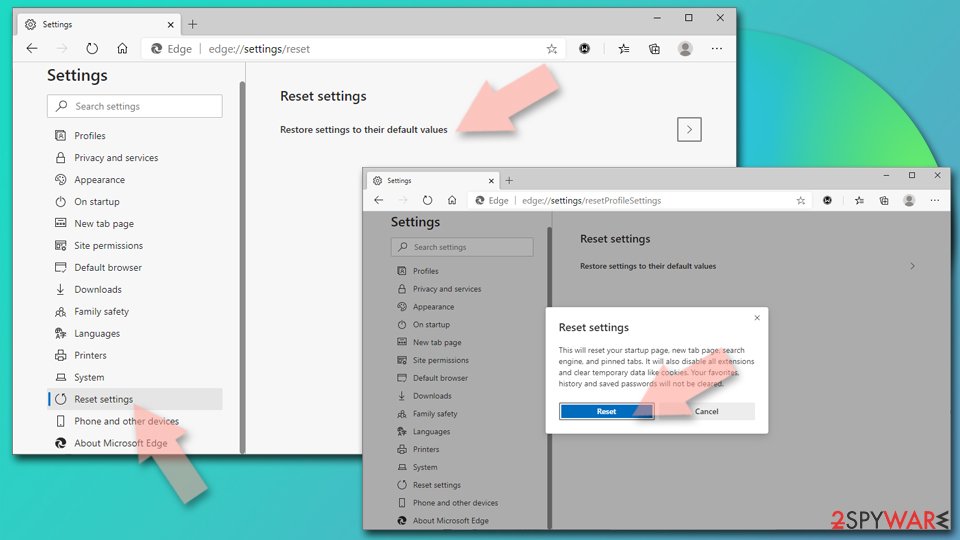
Reset Chromium-based MS Edge:
- Click on Menu and select Settings.
- On the left side, pick Reset settings.
- Select Restore settings to their default values.
- Confirm with Reset.
Remove from Mozilla Firefox (FF)
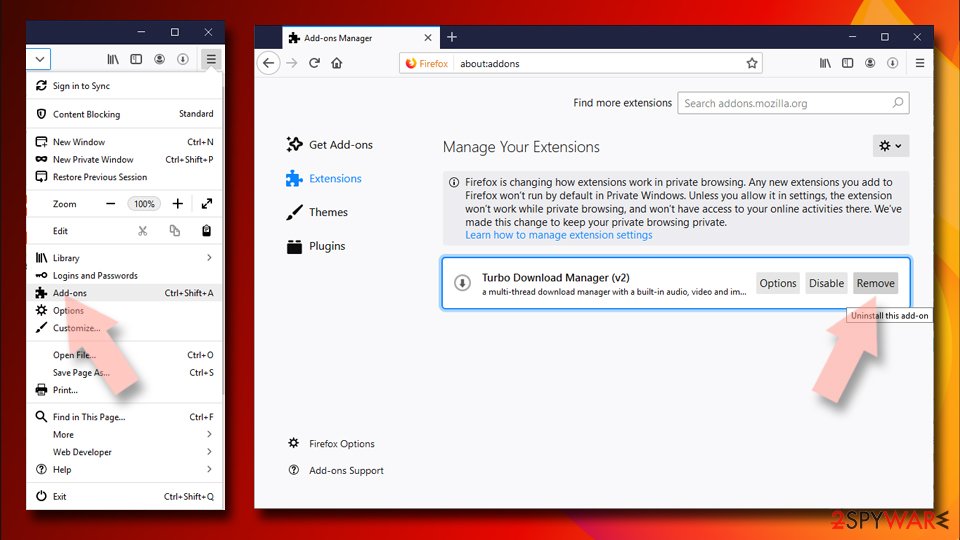
Remove dangerous extensions:
- Open Mozilla Firefox browser and click on the Menu (three horizontal lines at the top-right of the window).
- Select Add-ons.
- In here, select unwanted plugin and click Remove.
Reset the homepage:
- Click three horizontal lines at the top right corner to open the menu.
- Choose Options.
- Under Home options, enter your preferred site that will open every time you newly open the Mozilla Firefox.
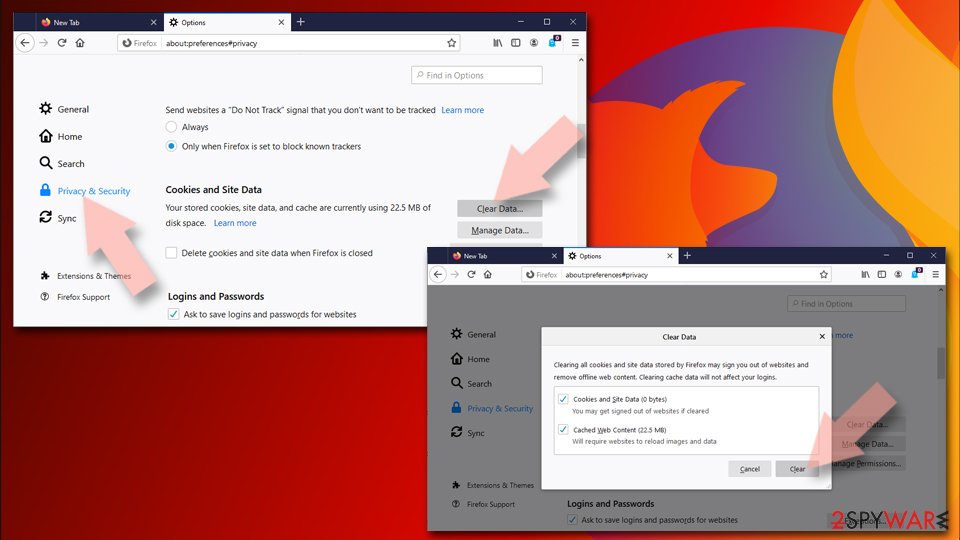
Clear cookies and site data:
- Click Menu and pick Settings.
- Go to Privacy & Security section.
- Scroll down to locate Cookies and Site Data.
- Click on Clear Data…
- Select Cookies and Site Data, as well as Cached Web Content and press Clear.
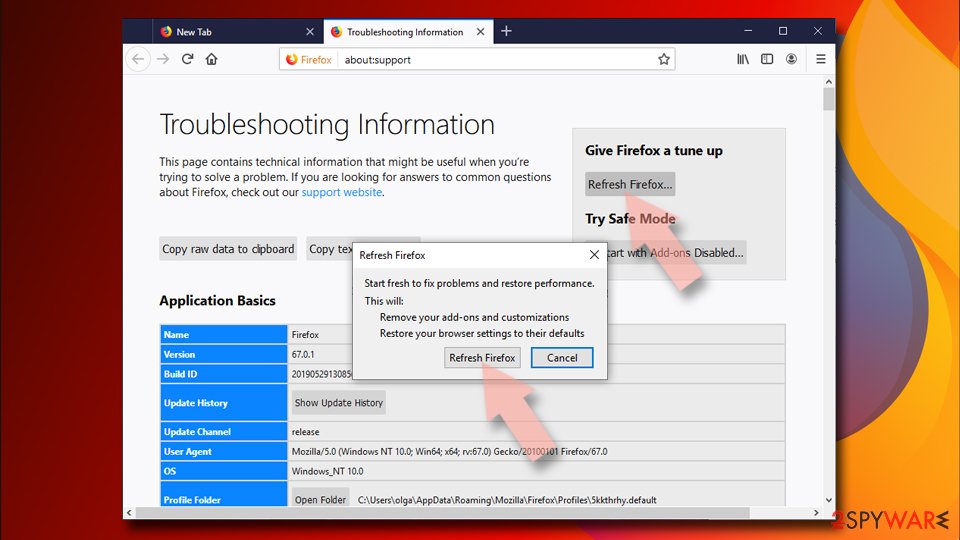
Reset Mozilla Firefox
If clearing the browser as explained above did not help, reset Mozilla Firefox:
- Open Mozilla Firefox browser and click the Menu.
- Go to Help and then choose Troubleshooting Information.
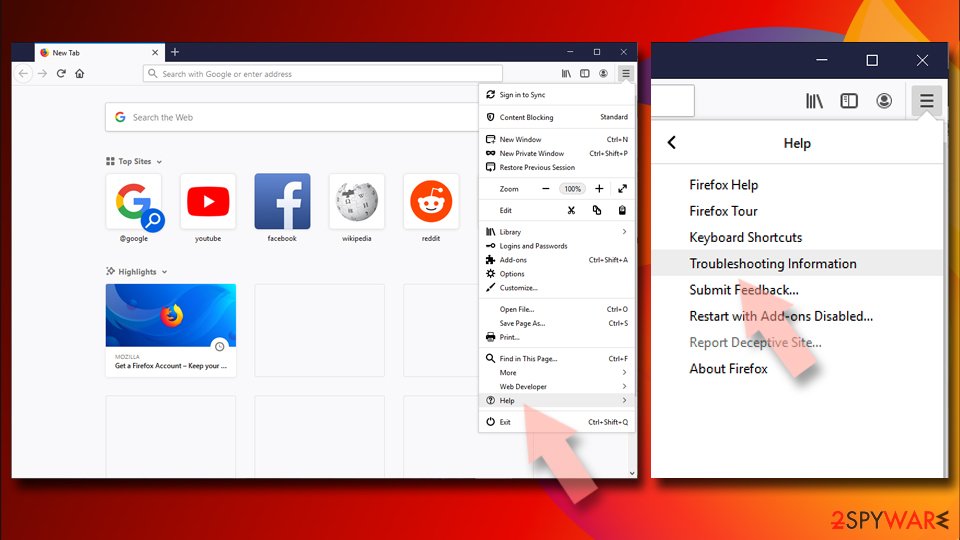
- Under Give Firefox a tune up section, click on Refresh Firefox…
- Once the pop-up shows up, confirm the action by pressing on Refresh Firefox.
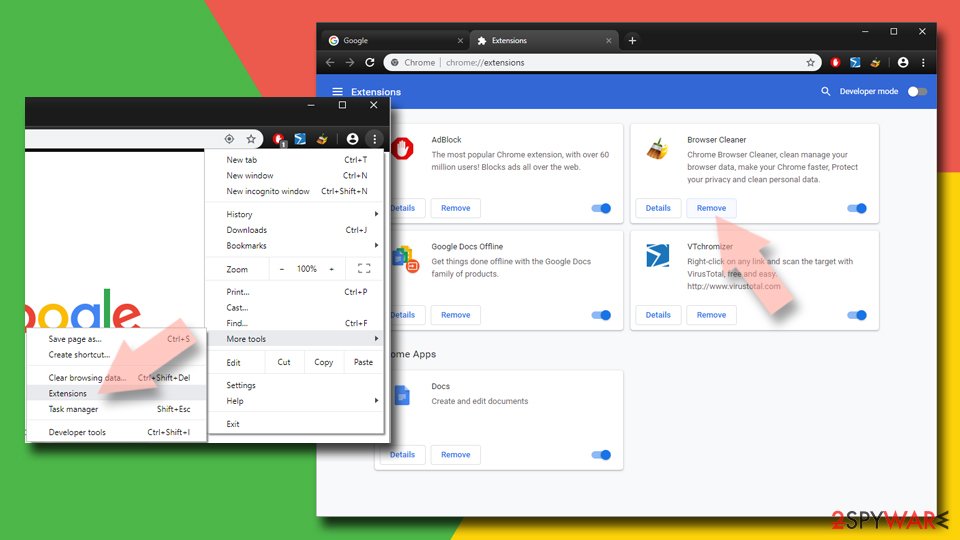
Remove from Google Chrome
Delete malicious extensions from Google Chrome:
- Open Google Chrome, click on the Menu (three vertical dots at the top-right corner) and select More tools > Extensions.
- In the newly opened window, you will see all the installed extensions. Uninstall all the suspicious plugins that might be related to the unwanted program by clicking Remove.
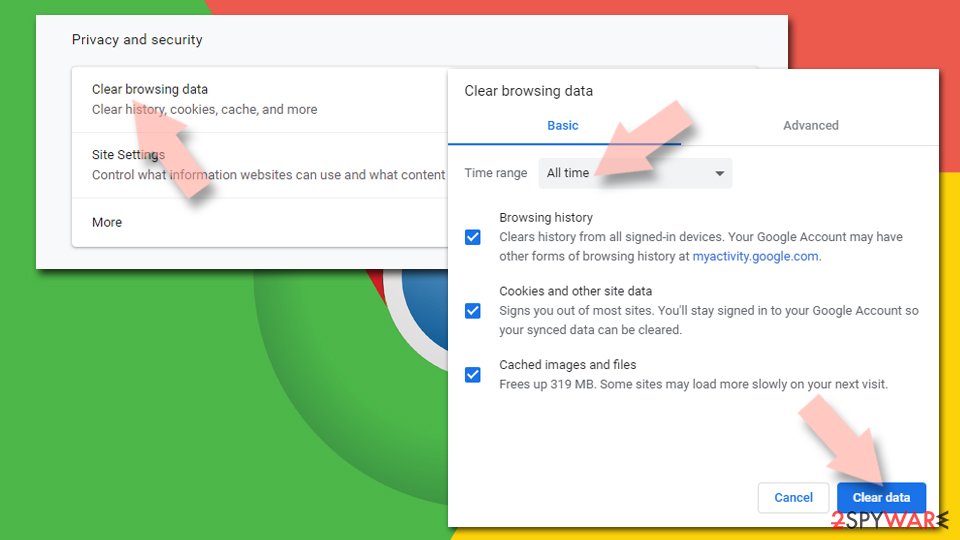
Clear cache and web data from Chrome:
- Click on Menu and pick Settings.
- Under Privacy and security, select Clear browsing data.
- Select Browsing history, Cookies and other site data, as well as Cached images and files.
- Click Clear data.
Change your homepage:
- Click menu and choose Settings.
- Look for a suspicious site in the On startup section.
- Click on Open a specific or set of pages and click on three dots to find the Remove option.
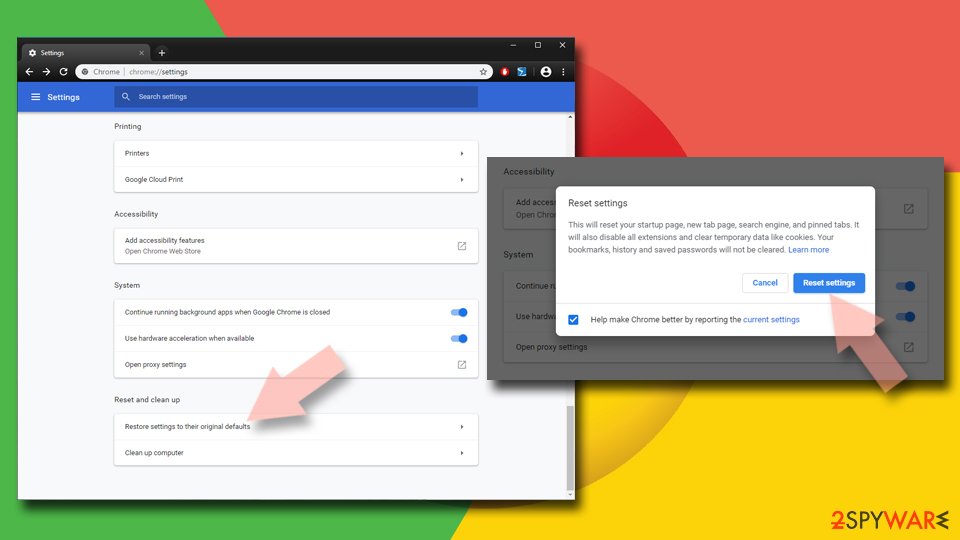
Reset Google Chrome:
If the previous methods did not help you, reset Google Chrome to eliminate all the unwanted components:
- Click on Menu and select Settings.
- In the Settings, scroll down and click Advanced.
- Scroll down and locate Reset and clean up section.
- Now click Restore settings to their original defaults.
- Confirm with Reset settings.
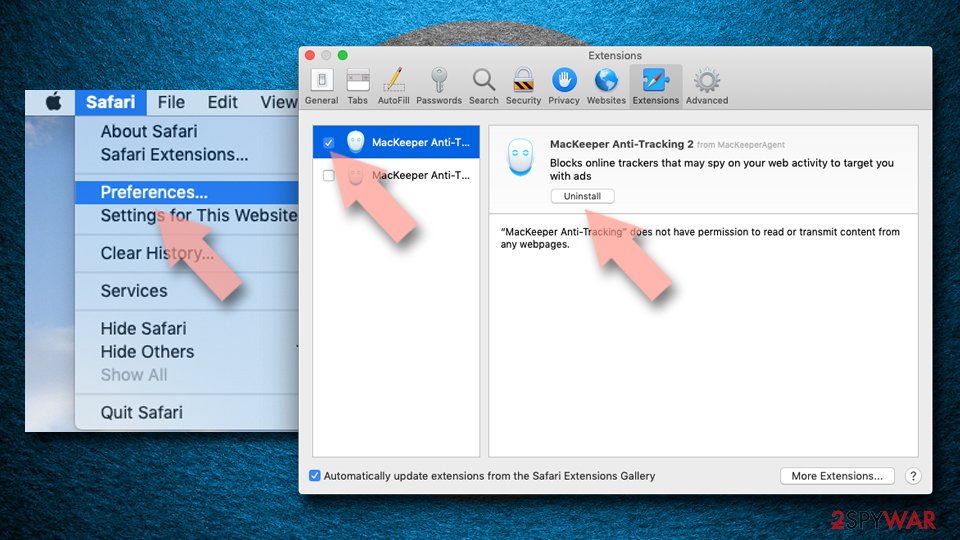
Delete from Safari
Remove unwanted extensions from Safari:
- Click Safari > Preferences…
- In the new window, pick Extensions.
- Select the unwanted extension and select Uninstall.
Clear cookies and other website data from Safari:
- Click Safari > Clear History…
- From the drop-down menu under Clear, pick all history.
- Confirm with Clear History.

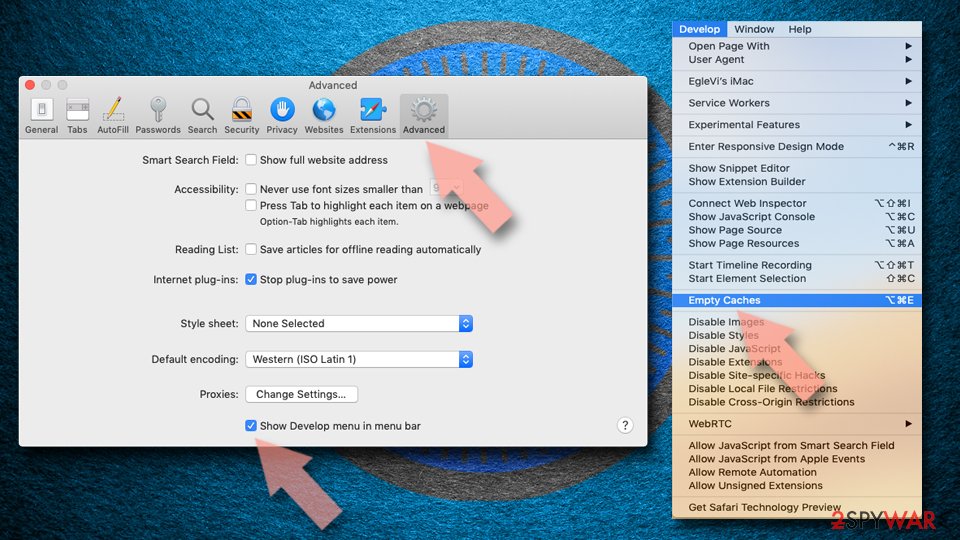
Reset Safari if the above-mentioned steps did not help you:
- Click Safari > Preferences…
- Go to Advanced tab.
- Tick the Show Develop menu in menu bar.
- From the menu bar, click Develop, and then select Empty Caches.
Scan your system with anti-malware
If you are a victim of ransomware, you should employ anti-malware software for its removal. Some ransomware can self-destruct after the file encryption process is finished. Even in such cases, malware might leave various data-stealing modules or could operate in conjunction with other malicious programs on your device.
SpyHunter 5Combo Cleaner or Malwarebytes can detect and eliminate all ransomware-related files, additional modules, along with other viruses that could be hiding on your system. The security software is really easy to use and does not require any prior IT knowledge to succeed in the malware removal process.
Manual removal using Safe Mode
Important! →
Manual removal guide might be too complicated for regular computer users. It requires advanced IT knowledge to be performed correctly (if vital system files are removed or damaged, it might result in full Windows compromise), and it also might take hours to complete. Therefore, we highly advise using the automatic method provided above instead.
Step 1. Access Safe Mode with Networking
Manual malware removal should be best performed in the Safe Mode environment.
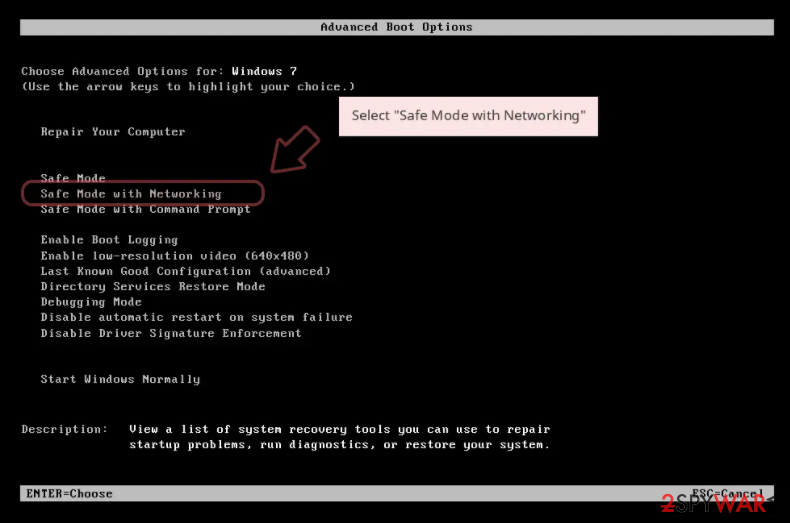
Windows 7 / Vista / XP
- Click Start > Shutdown > Restart > OK.
- When your computer becomes active, start pressing F8 button (if that does not work, try F2, F12, Del, etc. – it all depends on your motherboard model) multiple times until you see the Advanced Boot Options window.
- Select Safe Mode with Networking from the list.
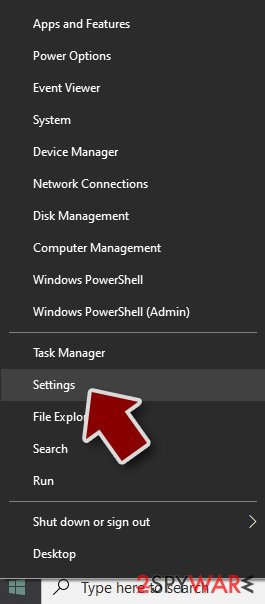
Windows 10 / Windows 8
- Right-click on Start button and select Settings.
- Scroll down to pick Update & Security.
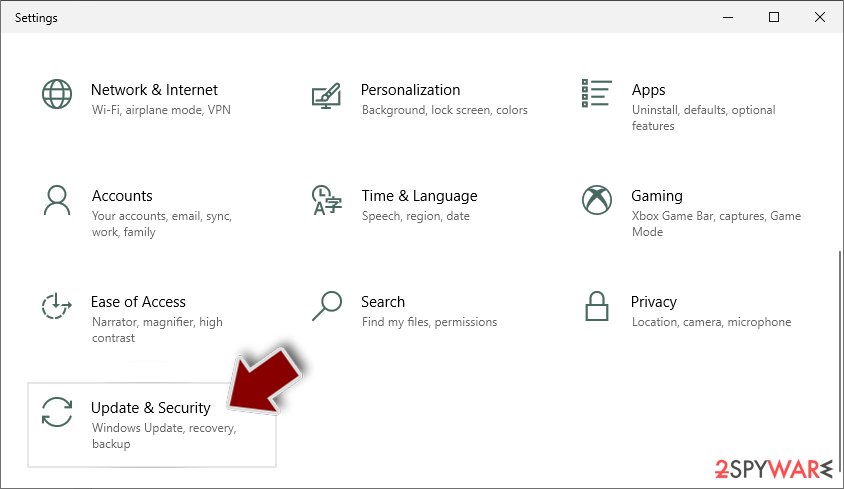
- On the left side of the window, pick Recovery.
- Now scroll down to find Advanced Startup section.
- Click Restart now.
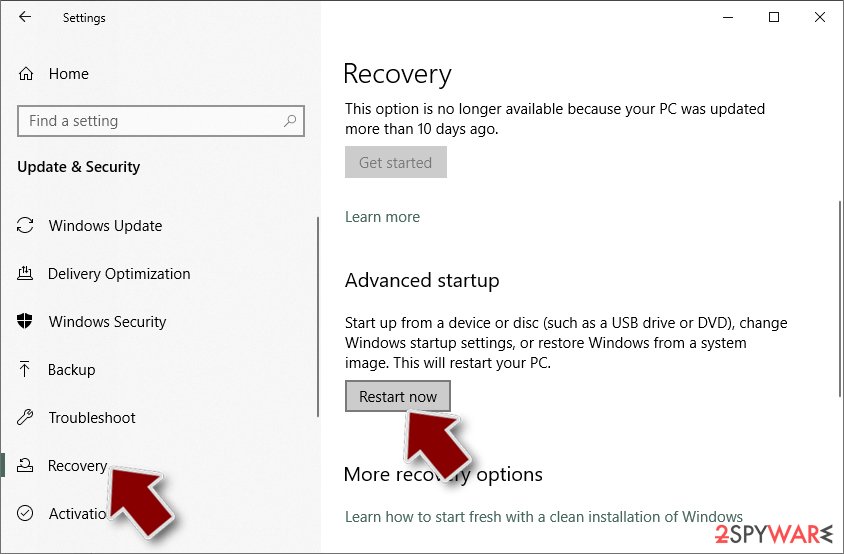
- Select Troubleshoot.
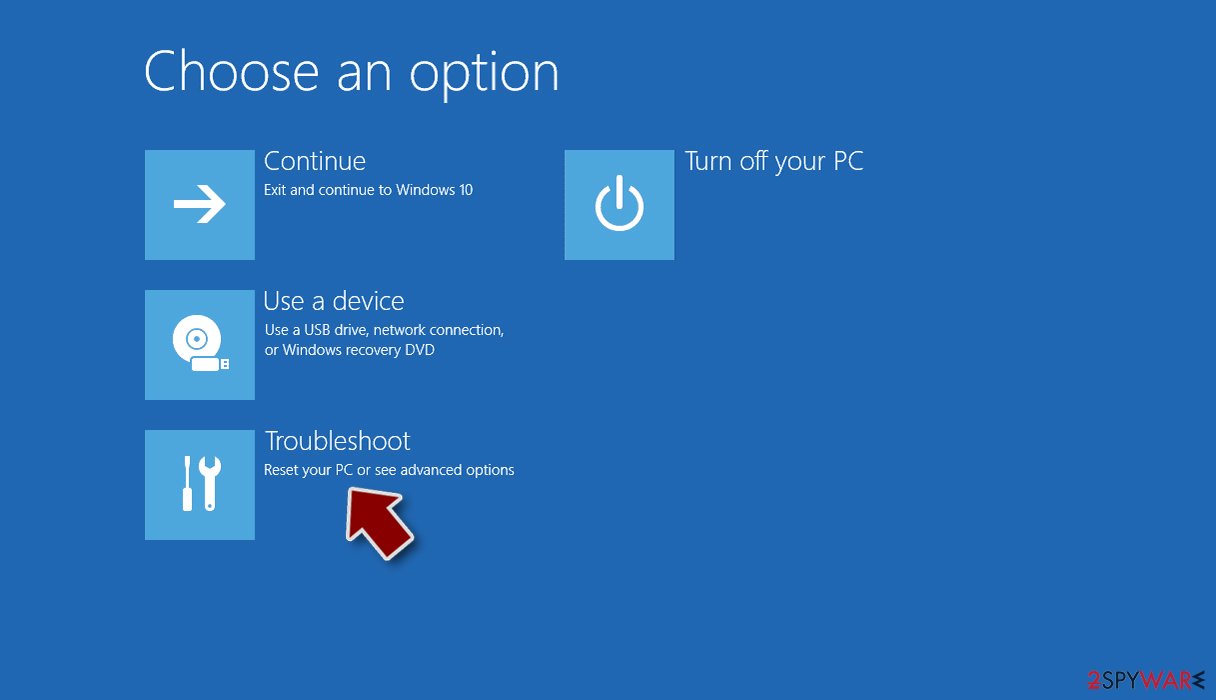
- Go to Advanced options.
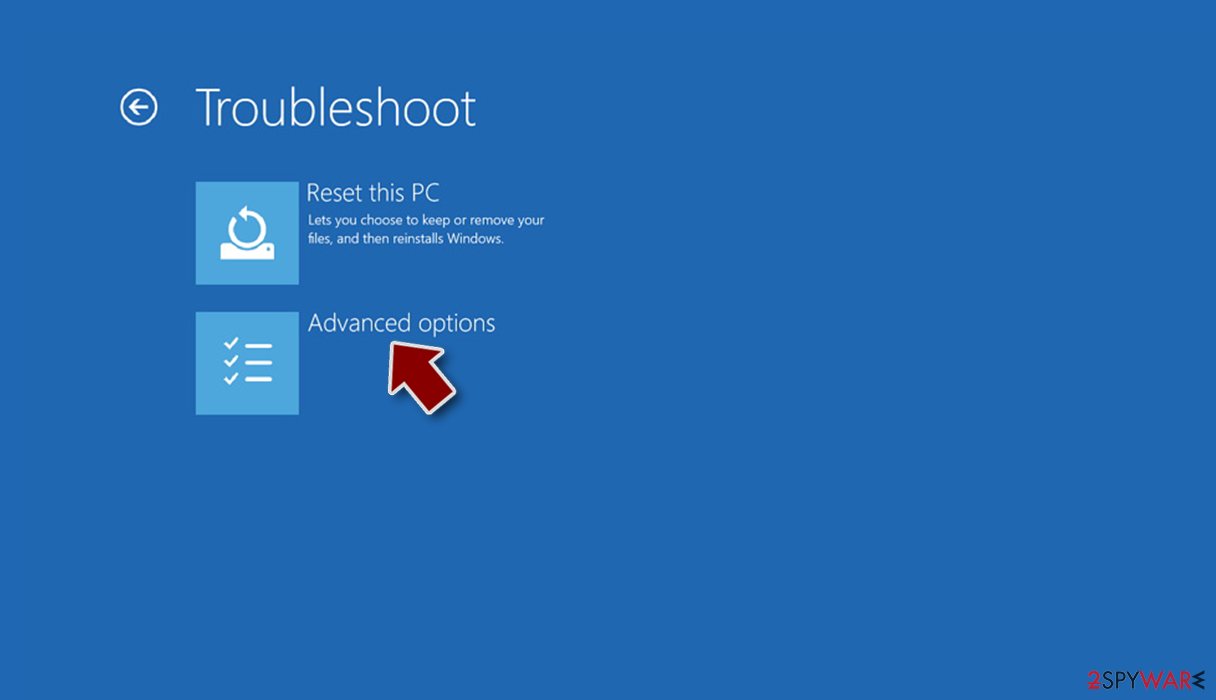
- Select Startup Settings.

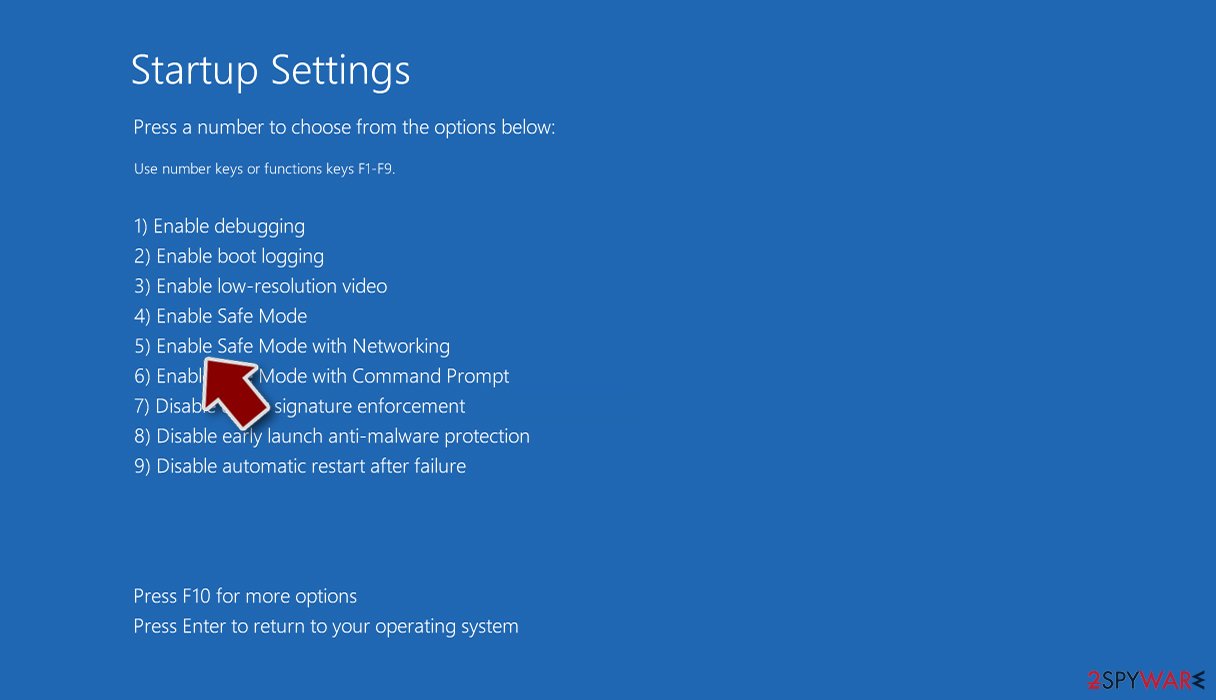
- Press Restart.
- Now press 5 or click 5) Enable Safe Mode with Networking.
Step 2. Shut down suspicious processes
Windows Task Manager is a useful tool that shows all the processes running in the background. If malware is running a process, you need to shut it down:
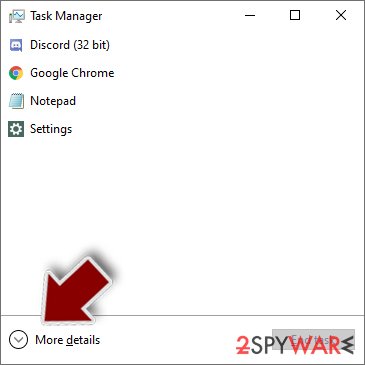
- Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc on your keyboard to open Windows Task Manager.
- Click on More details.
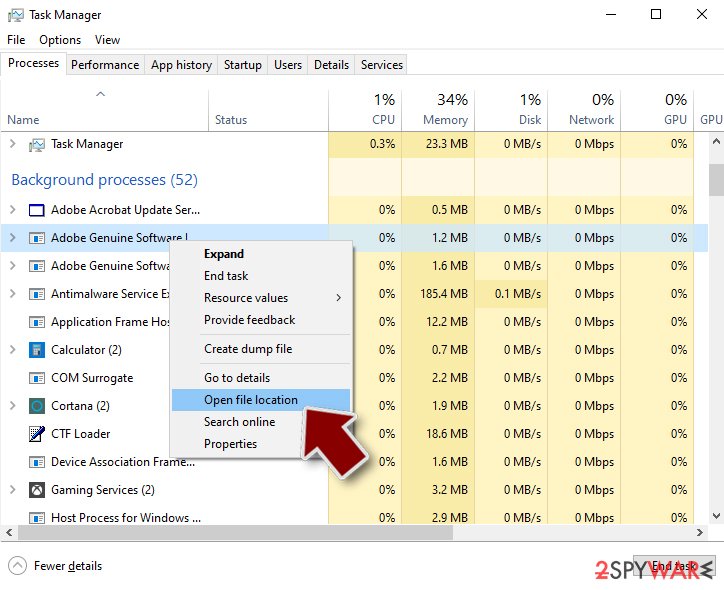
- Scroll down to Background processes section, and look for anything suspicious.
- Right-click and select Open file location.
- Go back to the process, right-click and pick End Task.
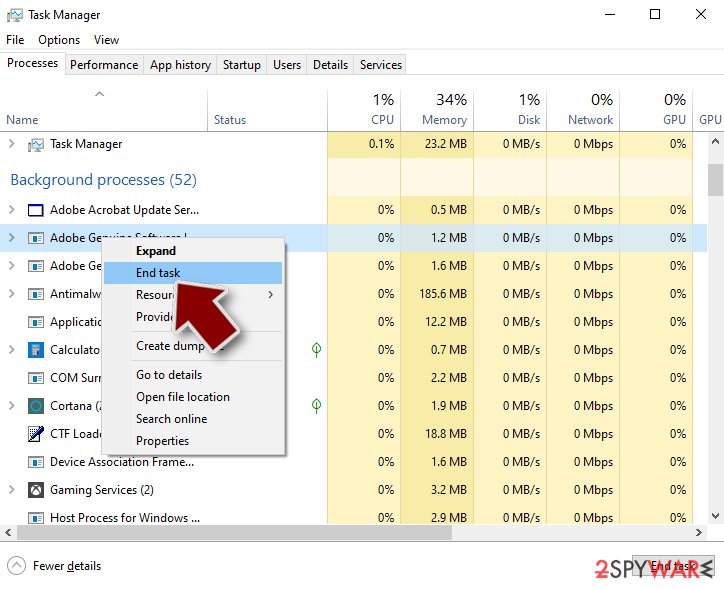
- Delete the contents of the malicious folder.
Step 3. Check program Startup
- Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc on your keyboard to open Windows Task Manager.
- Go to Startup tab.
- Right-click on the suspicious program and pick Disable.
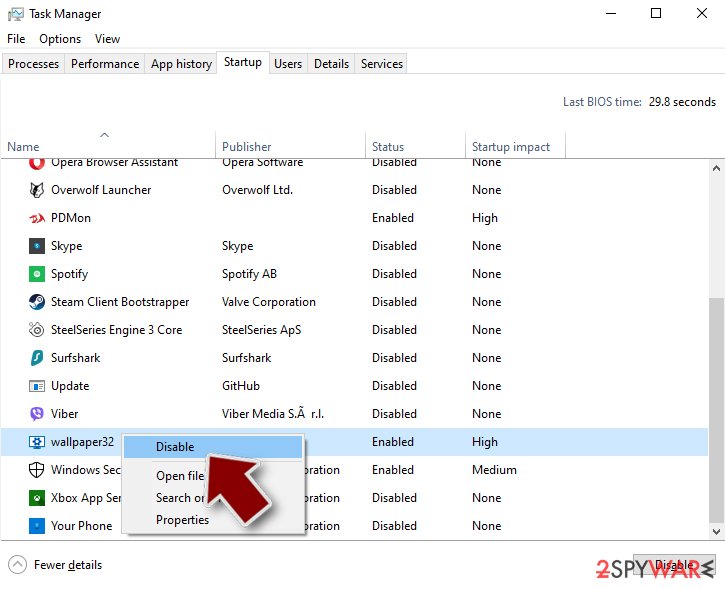
Step 4. Delete virus files
Malware-related files can be found in various places within your computer. Here are instructions that could help you find them:
- Type in Disk Cleanup in Windows search and press Enter.
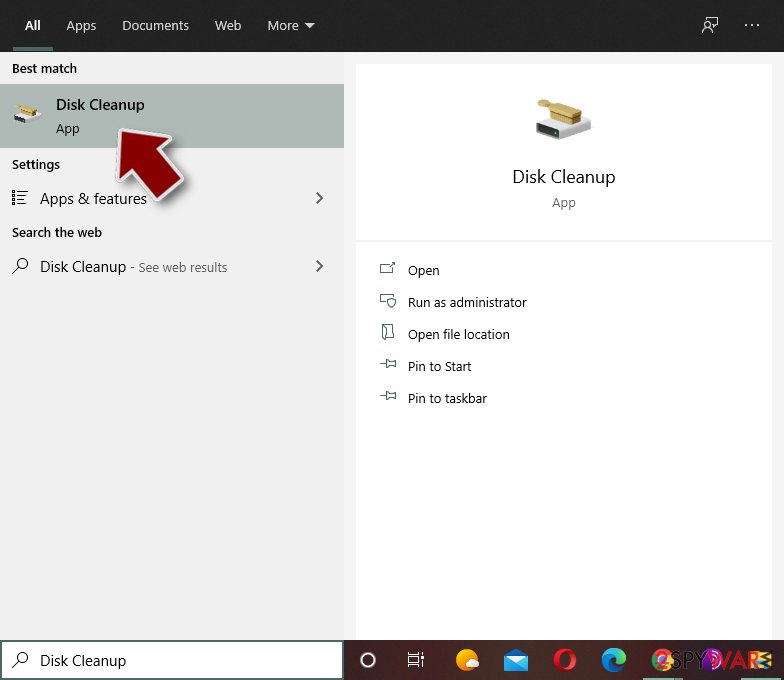
- Select the drive you want to clean (C: is your main drive by default and is likely to be the one that has malicious files in).
- Scroll through the Files to delete list and select the following:
Temporary Internet Files
Downloads
Recycle Bin
Temporary files - Pick Clean up system files.
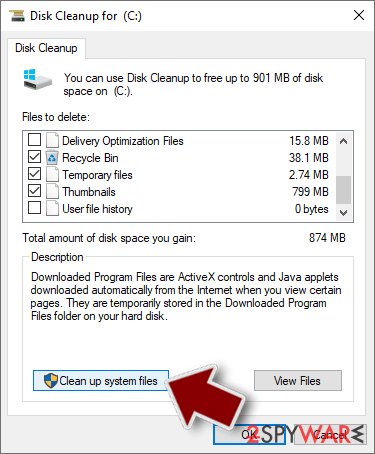
- You can also look for other malicious files hidden in the following folders (type these entries in Windows Search and press Enter):
%AppData%
%LocalAppData%
%ProgramData%
%WinDir%
After you are finished, reboot the PC in normal mode.
How to prevent from getting malware
Protect your privacy – employ a VPN
There are several ways how to make your online time more private – you can access an incognito tab. However, there is no secret that even in this mode, you are tracked for advertising purposes. There is a way to add an extra layer of protection and create a completely anonymous web browsing practice with the help of Private Internet Access VPN. This software reroutes traffic through different servers, thus leaving your IP address and geolocation in disguise. Besides, it is based on a strict no-log policy, meaning that no data will be recorded, leaked, and available for both first and third parties. The combination of a secure web browser and Private Internet Access VPN will let you browse the Internet without a feeling of being spied or targeted by criminals.
No backups? No problem. Use a data recovery tool
If you wonder how data loss can occur, you should not look any further for answers – human errors, malware attacks, hardware failures, power cuts, natural disasters, or even simple negligence. In some cases, lost files are extremely important, and many straight out panic when such an unfortunate course of events happen. Due to this, you should always ensure that you prepare proper data backups on a regular basis.
If you were caught by surprise and did not have any backups to restore your files from, not everything is lost. Data Recovery Pro is one of the leading file recovery solutions you can find on the market – it is likely to restore even lost emails or data located on an external device.
- ^ Number of monthly active Facebook users worldwide as of 2nd quarter 2020. Statista. Statistics portal.
- ^ Brett M. Christensen. Beware of Scam “YouTube Video” Facebook Messages. Hoax-Slayer. Website that helps to make the Internet a safer, more pleasant and more productive environment.
- ^ Olivia Morelli. FacexWorm cryptocurrency mining virus spreads via Facebook Messenger. 2-spyware news and virus removal guides.
- ^ Tunisie : L’Ansi prévient contre un nouveau virus sur Facebook. Kapitalis. News site oriented to Tunisian PC users.
- ^ Video virus su Facebook, cosa non bisogna fare: qualche suggerimento. Ci siamo. Notizie d'Italia.
- ^ Facebook users hit with “You are in this video?” malware scam. HackRead. InfoSec, Cyber Crime, Privacy, Surveillance, and Hacking News .
- ^ LesVirus. LesVirus. French site about virus news, malware and removal instructions.
- ^ David Jacoby. New multi platform malware/adware spreading via Facebook Messenger. Securelist. Information about Viruses, Hackers and Spam.
- ^ Vorsicht, neuer Virus verbreitet sich gerade über Facebook!. Brigitte. Breaking news for German-speaking community.
- ^ Marc Saltzman. Friend or foe? Be on the alert for imposters and scammers on Facebook Messenger. USA Today. Latest World and US News.
- ^ Cara McGoogan. Facebook Messenger scam steals passwords and hijacks accounts. The Telegraph. Latest news, business, sport, comment, lifestyle and culture.
- ^ David Bisson. Eko Facebook Messenger Malware Targeting French Users via PM Scams. Tripwire. Advanced Threat Protection & File Integrity Monitoring.
