Facebook virus (Free Instructions) - 2023 update
Facebook virus Removal Guide
What is Facebook virus?
Facebook virus can attack you at any time: here's what you should know
Facebook virus represents an array of scams and potential malware intrusions that could jeopardize the integrity of the Facebook social network at any given moment. The intentions of these cybercriminals deploying harmful software and misleading messages can vary significantly.
Some may disseminate fabricated messages through Messenger for amusement or as a practical joke. On the other hand, others harbor more nefarious intentions, attempting to infiltrate user accounts, pilfer personal information, or mislead individuals to fraudulent websites[1] with the ulterior motive of acquiring sensitive credit card details.
Facebook scams come in various shapes, as hackers are known to proliferate different malicious programs, such as cryptocurrency miners,[2] ransomware, data-stealers, and other dangerous cyber threats.[3] However, some versions just pollute the network and annoy its users.
According to experts, various forms of social engineering are used to make users believe whatever hackers want them to believe. Even in 2023, they are still suffering from the type of Facebook scam asking if the video, virus alert from Facebook, or sales summary is real.[4] However, the latest scams noticed on this social network are redirecting to Amazonaws domains after clicking on ads offering free Disneyland tickets, RayBan glasses, or sales summary.
Another type of scam is the one that spreads with the help of gullible users. Quite often, they get a message from a stranger that tries to threaten malware infections or other dangers and asks them for a message to be shared with friends. As a result, the hoaxes like “Be careful: I got a message from you” are spread further and cause users to suffer from spam.
The Amazonaws Facebook virus has been actively used to redirect users to fake websites impersonating YouTube, Twitter, or official domains offering users to update their “Adobe Flash Player.” Unfortunately, the file “flash player.dmg” was found to be infected.[5] Because of the YouTube name mentioned in the alert, this variant was named as Youtube Facebook virus.
Previously, Facebook scams reached their peak when they started spreading Digmine Monero cryptocurrency-mining botnet via Messenger.[6] The botnet was spread as a video_xxxx.zip file, which is actually an executable of the miner. All in all, this is the most dangerous campaign related to this social network.
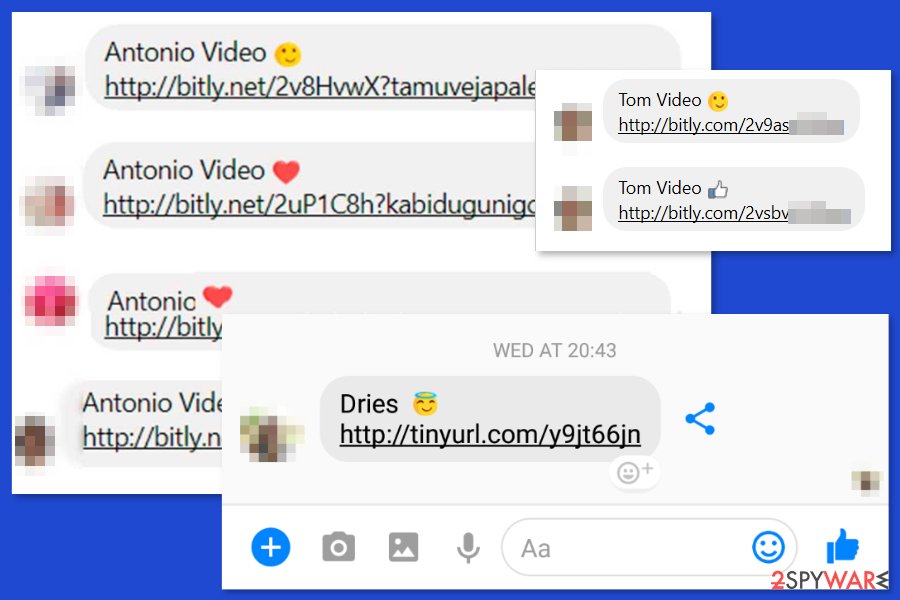
Undoubtedly, the Facebook video virus is the most popular version of malware that spreads via Messenger. With the help of a compromised account, criminals have been circulating a link named after the video_[random_characters].zip path. However, receiving files called video_5833.zip, video_6447.zip, or similar is a clear sign that your contact’s account was victimized, and the content provided in these files is harmful.
| Name | Facebook scams |
|---|---|
| Type | Many different types of malware and online scams: information-stealers, trojans, phishing messages, ransomware, etc. |
| Danger level | High, varies depending of the type of the scam. Example of infectious misleading domain: m.facebook.com-vm-auwlyduxgo.brahimsfood[.]com |
| Distribution |
Malicious texts via Messenger; infected links on unreliable pages; software-bundles; malicious spam emails; Browser extensions, software hacks |
| The damage and Most dangerous versions |
Damage may vary by type of malware/scam, most common issues include identity theft, overtaking victims computer, adding in to botnet or mining, stolen passwords or social accounts. Beware of these versions:
|
| Removal | You can get rid of various scams that affect Facebook by scanning the machine with anti-malware software |
| Recovery | Malware can cause damage to Windows or Mac system files. To recover from it and make sure your system is in the best shape, use FortectIntego |
Facebook malware has numerous features, including:
- Distributing spam messages to contact lists;
- Promoting fake contests used to obtain users' private information;
- Spreading spam via Facebook chat;
- Distributing malware.
Scammers also take advantage of users using hoaxes by giving them hope of winning two free Ryanair tickets and suggesting to purchase various things. Even if the announcement on Facebook claims that the offer is recommended by the reputable financial guru Martin Lewis, you should not fall for such a scam. Also, people can be redirected to sites promoting iPhones for 1 Euro. This may happen after clicking on infected Google search results. This way, scammers are trying to get personal information, including full name and credit card details.
Unfortunately, serious viruses have also been noticed spreading on the social network – users have already been infected with a notorious Locky virus,[7] which has been finding its way to target systems with the help of Nemucod downloader. This cyber threat was found hidden under the SVG Image file using photo_[random numbers].svg name. If you happen to see files, such as photo_4837.svg, photo_999.svg, or photo_8470.svg, in your Facebook Messages, make sure you stay away from it because its aim is to infect you with Locky ransomware.
If you don't take care of these scams, you can infect your friends and encourage this malware for future crimes. Every user who clicks the malicious link is involved in the distribution scheme. Steps that you can use to fix your account and remove Facebook virus sending messages are provided below this post.
After fixing it, don't forget to scan your computer with reliable security software to see if there is anything malicious on your computer. FortectIntego can help you to know if you are infected. Keep in mind that security experts have already reported the relation between Facebook redirect and ransomware-type viruses, trojan horses, and similar threats.
Identified 27 Facebook malware versions. Removal guides included
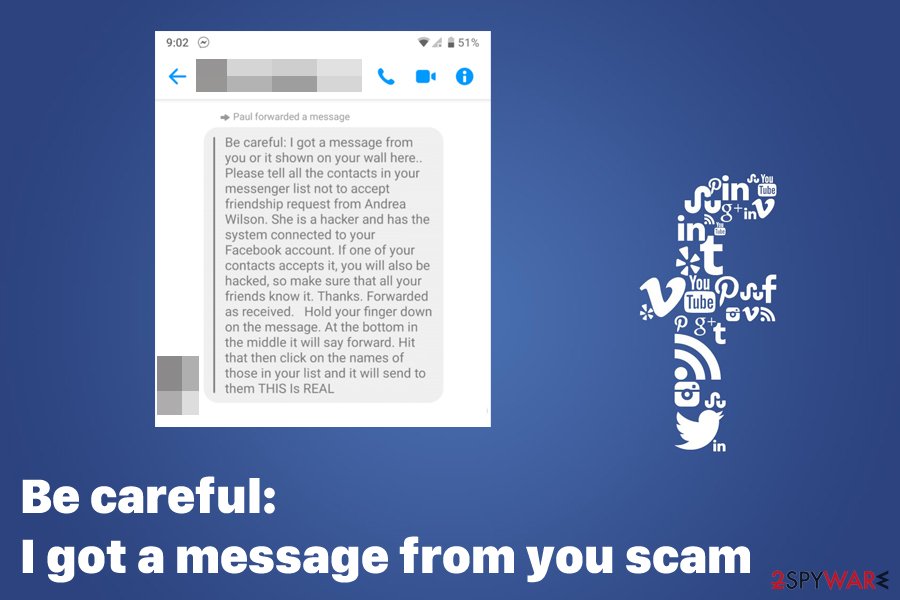
Be careful: I got a message from you scam
“Be careful: I got a message from you,” also known as “Andrea Wilson Friendship Request,” is a scam that has been targeting various Facebook users since the summer of 2019. This version propagates using social engineering but does not include any malware infection or personal data leak. Instead, threat actors seek to make users share the message to all friends on Facebook, consequently making the hoax spread further.
| Threat Type | Scam, hoax |
| Distribution | Typically, the fake message is delivered to users via the Messenger |
| Summary | Scam claims that the sender received a message from the user and that his/her Facebook account is connected to somebody named Andrea Wilson. Allegedly, if anyone from a person's friends accepts the friend request from her, his/her account will be hacked |
| Goal | The message asks users to forward it to everybody in their friends list, threatening with consequences |
“Be careful: I got a message from you” message can come at any time, and the sender can be a stranger or somebody in your friend list who got tricked by the scam. You should simply ignore it. Here's what the message says:
Be careful: I got a message from you or it shown on your wall here.. Please tell all the contacts in your messenger list not to accept friendship request from Andrea Wilson. She is a hacker and has the system connected to your Facebook account. If one of your contacts accepts it, you will also be hacked, so make sure that all your friends know it. Thanks. Forwarded as received. Hold your finger down on the message. At the bottom in the middle it will say forward. Hit that then click on the names of those in your list and it will send to them THIS Is REAL.
Users were asking if their accounts would be hacked if they shared the message or whether their friends' accounts had been hacked because of this. In reality, This threat is rather annoying but not harmful: there are no files to be downloaded and no links that could lead users to malicious or spoofing sites. As a result, “Be careful: I got a message from you” remains an annoying issue that keeps popping up from time to time.
Even though you can't get infected with anything or get your Facebook account compromised, you should not share the “Be careful: I got a message from you” hoax to prevent it from spreading further.
Facebook Malware warning
Facebook Malware warning is a scam that aims to infiltrate the system by using malicious or potentially unwanted programs (PUPs). Some time ago, it was the most active version of all versions, which was attacking people from all over the world. At the moment, threat activity seems to be decreased.
| Threat Type | Scam |
| Distribution means | Software bundles, insecure third-party sites |
| Details | A fake but legitimately looking Facebook warning appears claiming that user's computer is infected with malware |
| Termination | Scan your computer with anti-malware and reset all browsers |
Alert from Facebook is designed to deliver fraudulent messages about different infections found on the system. Once the users are intimidated, they are offered to purchase and run a full system scan with an antivirus. Unfortunately, such programs only promote useless or even potentially dangerous software and should never be trusted.
Suspicious software offered by Facebook Malware warning might actually be:
- Expensive and ineffective optimization tool;
- Ransomware;
- Banking Trojan;
- PUP.
Even though there were some reports about Facebook's Malware warning in 2017, it gained traction in 2018. Therefore, users are advised to use a professional malware removal tool downloaded from official websites only. This way, you will avoid any fake programs and protect your system.
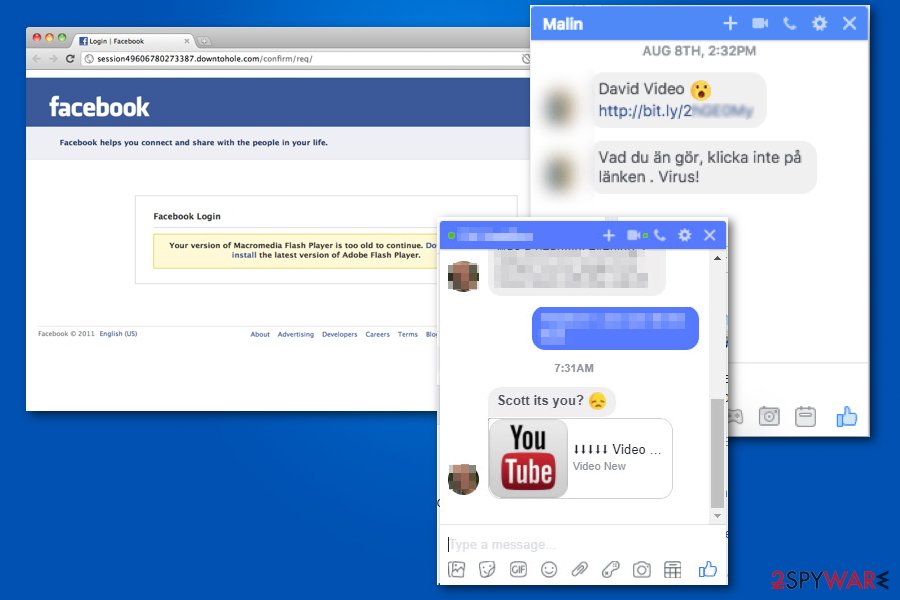
Facebook Messenger virus
Messenger virus is another variant of the scam that has been spread through the chat window of this social network. No matter that the threat is relatively old, it is still actively affecting users by using a tricky scheme that uses the victim's profile picture, name, and a link offering to check a specific video. The message creates an image that the video is saved on YouTube and that it is somehow related to the victim. As a result, this scam has affected numerous users worldwide.
| Threat Type | Scam |
| Spread via | Facebook Messenger |
| Details | Victims receive a message from somebody on the friend's list. The short message compiles of a profile picture, name, and the link to an alleged video. As soon as it is clicked, it leads to the spoofed login page. Those who proceed hand in login credentials to cybercriminals |
| Remedy | Before clicking on any links, make sure that the person actually messaged it to you |
The fake messages distributed around may vary, but some of them read as follows:
- Is this a video of you?
- Hahaha
- [your name] Its you
- [your first name] Video
- Is this you?
- I just made a photoshop of you
- Look who died, etc.
Unfortunately, the link included in the fake Message does not lead to Youtube. It reroutes unaware PC users to fake sites, either requiring them to connect to their account again or offering to enter their answers to some survey. Beware that this method has been actively used to swindle users' personal information, such as logins, passwords, and similar data. Besides, there is a huge possibility of being infected with malware.
Whenever your device is infected with the Facebook Messanger virus, you might immediately notice that your account is behaving in an uncharacteristic manner, generating spam and dubious links. Simultaneously, it seems to be responsible for transmitting unsolicited messages, which might be concerning to those receiving them.
Upon inspecting your account history, you might notice peculiar login locations that don't align with your typical usage pattern, which further intensifies the suspicion. In addition, odd actions appearing in your activity log can also signify a breach, leaving you with a trail of unusual activity that you don't recall initiating. These combined factors hint towards potential unauthorized access or compromise of your account's security, demanding immediate attention.
Facebook video virus
Facebook video virus is malware that controls a victim's account and automatically posts “My private video,” “My video,” “Private video,” and similarly entitled malicious links on the victim's timeline. What is more, it tags random victims' Facebook friends in these posts to draw their attention and invite them to click on the link.
| Threat Type | Malware, scam |
| Spread via | Facebook Messenger |
| Infection means | Users receive a message that contains “My Private video” or similar message and a link to the alleged video. Nevertheless, if clicked, users might immediately install malware |
| Remedy | Scan your computer for malware and |
| Prevention | Never click on suspicious links, even if they come from your friends |
Private video Facebook virus also sends messages having malicious links included. They go directly to the victim's friends. We strongly advise you NOT to click on these links as they can automatically download malware to your computer.
The main danger related to video scams is their ability to redirect victims to malicious websites. Beware that the content you can be redirected to can end up with malware. There is also a possibility that your computer will be included in the botnet sending spam all around the network. Finally, a malicious file can also be installed just by clicking on this link. As a result, you can get infected with ransomware, a rootkit, a worm, or a Trojan horse.
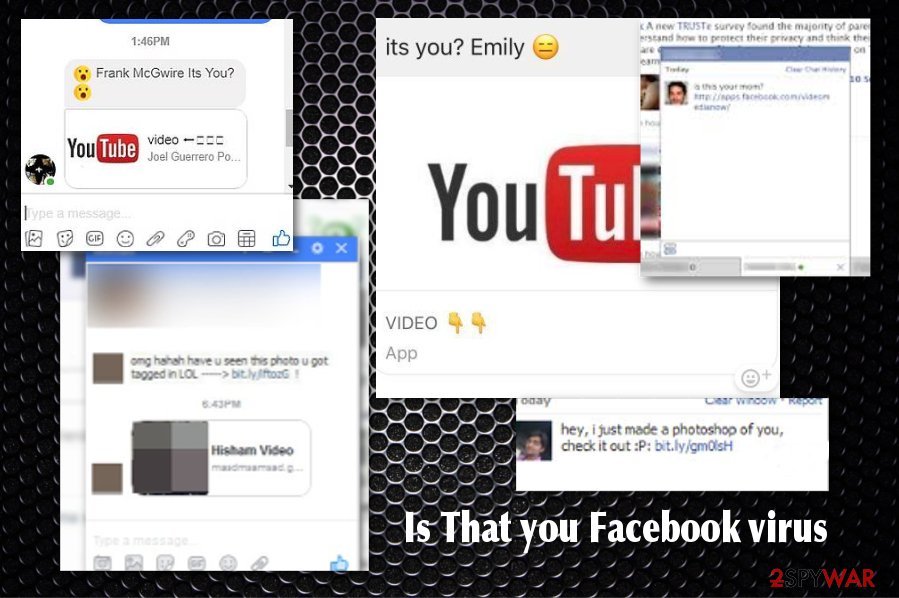
“Is that you” Facebook virus
“Is that you” Facebook virus is yet another version of the threat that involves the Messenger app and a video sent by users' social media friends' accounts. This scam tries to intimidate users by showing a link to an allegedly compromising video that was leaked online. However, as evident, these claims are fake, and it is merely a trick used to make users click on the malicious link.
The message itself may display various text from “Is this you?” YouTube video or only state your name and a question mark alongside the link to the video on youtube or any similar platform. In most cases, you cannot even see the thumbnail of the video to know if the video is really of you.
The main red flag is that there is no context besides that message with a hyperlink or a direct video, so you can be sure that the person who sent this message is not the one responsible. Criminals can hack those accounts with the only aim – to send this scam campaign.
Make sure to notify the person from the other side since he or she is the one that got this message and needs to have a full system cleaning done to get rid of the initial malware. Their device may get damaged besides infecting oper peoples' machines. Once the person falls for such a scam the account credentials get used to login into the profile and spread this malware further.
OMG Facebook game virus
OMG Facebook Game is an instant game platform that gained popularity recently. However, users have experienced issues which have already been reported as playing the OMG game resulted in a monetary loss. Fortunately, in this particular incident, the victim got the money back because she contacted Google Play's customer service.
| Threat Type | Malicious ads |
| Spread via | Games in Facebook client |
| Details | Malicious ads in games might lead users to automatic payments for never-ordered services |
| Remedy | Contact Google Play, Facebook, or any other involved parties |
| Prevention | Do not click on suspicious ads that pop-up in games |
As the victim stated, she was playing the game on Facebook and clicking around the application. The game contained various advertisements, and clicking on them resulted in redirects to suspicious websites. However, quickly after that, a notification about successful payment via Google Play Account was delivered.
Beware that clicking on various third-party advertisements can result in various cyber infections, so you should keep in mind this fact even while browsing on social media and playing in-website games. The OMG creators reported that this sudden charge has nothing to do with the app and that the game is free and doesn't ask for any payment and that the data collected and used by this program include public information only. They stated that the issue is noted, and they are working on improving the experience of Facebook Games.
Facebook “iPhone for 1 Euro” scam
At the beginning of February 2018, researchers revealed a new wave of scams. This time, scammers tried to trick people by using false offers to buy iPhones for 1 Euro. According to Phil Tully, a researcher from ZeroFox,[8] any free or cheap iPhone offer should be marked with a red flag. This way, scammers may try to extort people's personal information, including full names and credit card details.
| Threat Type | Survey scam |
| Distribution | Malicious Google search result redirecting to bogus Facebook sites |
| Peculiarities | Users are offered an iPhone for one euro. In reality, crooks are trying to defraud users' personal information or attempt to subscribe them to a bogus service |
| Prevalent in | France |
| Prevention | Do not engage in any “free iPhone” or “iPhone for 1 euro” offers. If you want a new iPhone buy it from official sources |
The “iPhone for 1 Euro” scam has been spreading via infected Google search results used to redirect victims to a Facebook site with a fake iPhone offer. If you happen to come across this iPhone scam, please report it to support immediately. Besides, check your web browser for unwanted extensions and run a scan with an anti-virus program.
Clearance sales summary of 2019 Facebook virus
Clearance sales summary of 2019 Facebook threat is an extremely aggressive scam that keeps posting a specific ad/image on the user's profile every few hours. Additionally, it tags random victims' friends (40-50 of them) to catch their attention and keep spreading. It has also been seen on Instagram and other social networks.
| Threat Type | Scam |
| Details | Facebook users might come across ads that offer expensive and high-profile brand clothing due to Clearance sales. Nevertheless, if the ad is clicked, users are linked to spoofed websites where, after payments, users never receive the discounted goods |
| Prevention | Do not click on deals that are too-good-to-be-true |
| Further action if affected | Contact your bank and local authorities dealing with scams |
The pop-up posted by Clearance sales summary of 2019 displays impressive discounts on famous clothes and shoe brands. The names include The North Face, UGG, Adidas, Nike, Timberland, Dr. Martens, Canada Goose, and others. Additionally, the scam also includes links redirecting victims to sites that look like their official webshops.
Beware that these sites and goods which are presented there are fake. No matter how cheap they are, these scammers can send you anything once you pay. Besides, you will be asked to enter your credit card details which can additionally lead you to the loss of your financial information and money. If you found this ad on your wall, delete it immediately or remove the tag. If such activity continues, report the alert to Facebook and follow the steps provided at the end of this post.
Faceliker virus
Faceliker is a click-fraud Trojan that can infect the victim's computer as soon as he/she visits a compromised web page. It gets access to the account, but instead of hacking it, it silently uses it to like very specific content. The malicious software redirects the victim's clicks on “Like” buttons and likes completely different content instead. This way, Faceliker Trojan operators can fraudulently promote pages, links, fake news, and other content.
| Threat Type | Trojan |
| Infection means | Malicious websites, spam emails, cracked software, etc. |
| Details | If infected, user's account is used to automatically like predetermined Facebook pages, which allows cybercriminals promote Facebook groups, individuals and posts |
| Termination | Scan your computer with powerful anti-malware software |
In case you suspect the presence of a Faceliker, immediately check your activity log on Facebook. In case you see some unauthorized likes on posts, links, or pages that you didn't authorize, scan your computer with powerful anti-malware software to remove Faceliker for good.
Facebook “Following Me” scam
The scam seeks to promote the post offering you to identify strangers who are following you. At the moment, the network allows unknown people to follow you by clicking the “follow” button, but it does not identify them. According to the scam note, once you enter Settings, Blocking, and then Block and then type following Me,” you will see the list of secret followers[9].
| Threat Type | Scam |
| Spreads | Via bogus posts |
| Peculiarities | The scam offers to reveal people who are following you (Facebook does not provide such option) |
| Precautions | Be aware that Facebook does not post specific instructions, and bogus functionality of the app is only promoted by cybercriminals |
In reality, Facebook delivers you the names of people whose names comprise the “following me” letters. Fortunately, this hoax does not have negative effects as in other cases when you are tempted to visit infected websites and install corrupted apps. Note that Facebook does not grant such the privilege of revealing your followers.
Facebook Money Scam
Money scam was first spotted in August 2017, when unknown cybercriminals tried to defraud the personal information of naive users, such as credit card numbers, money, or even identity, by using the name of famous and reputable people.
| Threat Type | Fraud, scam |
| First spotted | August 2017 |
| Details | Fake adverts that use a well-known personality name try to swindle Facebook users' personal information |
| Precautions | Before trusting posts, first verify that they are coming from a legitimate account of a the person of interest |
One of the persons involved was a well-known financial advisor and the founder of the MoneySavingExpert.com website Martin Lewis. According to a video published on Twitter,[10] people should be careful with such hoaxes that give fake recommendations or use the picture of Lewis illegally.
One of these scams claims that Martin Lewis invested half a million pounds into a cloud trading scheme because it’s the best what you can do with your money. However, it’s not true. Fraudsters also use his picture for boiler cover incentives, heating incentives, and PPI companies that Lewis has nothing in common with.
However, if you find an advert using his name and offer to invest or purchase some products, do not get tricked and report such an advert to Facebook. The financial guru clearly stated that he does not do adverts or endorsements unless it’s a charitable activity.
Facebook Ryanair scam
The purpose of this scam is to trick users that they can win two free tickets to fly with airlines on their 35th anniversary. However, the company is only 33 years old. The Ryanair scam was first noticed in 2016; [11] however, it continues spreading further.[12]

The post includes a picture of a boarding pass with the Ryanair logo. However, vigilant people noticed a ridiculous seat arrangement or an unusual usage of the QF code. This post also redirects to numerous fake websites, for instance, “ryanair-airways.us.”
On the scam website, users have to enter a bunch of personal information that becomes accessible to cybercriminals. Some reports also claim that some of these fake sites are infected and spread malware. Therefore, users are advised to stay away from such posts on Facebook. The official Ryanair Facebook account is verified. It means that it has a “blue tick” icon. Hence, if you see other accounts spreading such contests, it’s a clear sign that they are fake.
Facebook Ray Ban virus
If you are a Facebook user, you probably noticed Ray Ban spam on your timeline at least one time. Criminals are using hacked accounts to promote illegal and fake Ray-Ban online shops offering the famous eyewear brand products for a fraction of their original price. Ray-Bans on sale? This social engineering trick can attract everyone who desires to obtain these fashionable eyeglasses for less. Sadly, attempts to buy them for a ridiculously small price lead to unexpected consequences.
| Threat Type | Sales scam, malware |
| Specifics | The scam revolves around users getting infected with data-stealing malware. After that, the host account is used to tag friends in fake Ray Ban glasses sales posts or create groups. In such a way, the hijacked account can promote malicious links, which other users can click and get their personal data stolen or infected with malware |
| Remedy | If you were a victim of the Ray Ban scam, you should immediately scan your device with anti-malware software and change your Facebook, as well as other accounts, credentials |
The victims of the Facebook Ray Ban virus usually have password-stealing malware installed on their computers. As soon as frauds find out the victim’s login details, they access the account and use it to post images promoting fake Ray-Ban deals, tag the victim’s friends in them, create groups and events, and take other illegal actions.
These phishing websites will never provide any glasses to potential buyers because their only purpose is to rob the victims and steal their credit card details. If you bought something from those fake websites, you should contact your bank ASAP and cancel the transaction. You should also change all of your bank passwords and take other steps to protect your privacy.
In case you notice that your friend posts these Ray-Ban-related posts and tags others in them, you should contact him/her and tell them to check their computer with anti-malware software. The culprit might be an obfuscated keylogger set to steal all of the passwords and login details.
At the same time, they should change their password and disconnect all devices that are logged into their account. Victims should also untag themselves from such posts.
If your account was hacked by the Ray-Ban virus, you should go to Facebook Hacked page and report a compromised account.
Facebook Disneyland scam
Facebook Disneyland scam offers an opportunity to win free passes for the Disneyland theme park. Unfortunately, Disney is not giving away any free tickets to their theme park. People who accessed the provided link and then entered their personal information, such as email addresses and cell phone numbers, got scammed and put themselves at risk of identity theft.
Being spread by using various posts, the scam redirected its victims to a page asking them to answer survey questions about different products or services. Additionally, the victims were tricked into agreeing to receive calls and text messages from salespeople. Besides, the victims were asked to provide their email addresses, full name, and similar data.
We should also add that there is yet another version of the scam stating that Disneyland celebrates 110 years of service and offers free tickets to 500 families. However, Disney was not sponsoring any of this. The scam offering 5 free tickets was taken for real because of the artwork similar to Disneylands' trademark used in it. When users clicked on the picture, users were presented with the following message:
Congratulations! You have been selected to take part in our short survey to get 2 free Disneyland tickets.
The “winner” was announced after three questions, but there was no prize given. People who participated and “won” were tricked into liking the message and sharing it with their friends on Facebook. By using this strategy, scammers.

Jayden K. Smith scam
In the middle of summer'17, a new Facebook hoax emerged. This time, a fake message circulates the social network, urging users not to accept a friend request from someone named Jayden K. Smith. The fraudulent message states that the victim's account will be hacked as soon as one accepts the friend request from this so-called “hacker.”
| Threat Type | Scam |
| Specifics | A fake message that warns about a bogus hacker Jayden K. Smith, and urges users not to accept friend request, but rather inform everybody in the friend list about the alleged danger |
| Further actions | Do not believe random messages that come your way on social media |
On top of that, the message suggests forwarding the news to all of the user's friends to help spread the knowledge about the non-existing person. This apparently accelerates the spread of this hoax.
The truth is, there is no Jayden K. Smith, and there's no reason to worry about him. As always, remember that you should never accept friend requests from strangers because your social media account and your friends lists can provide scammers a lot of valuable information about you.
Congratulations! Your profile has been selected by Facebook
“Congratulations! Your profile has been selected by Facebook” is a malvertising technique that created a scam based on the old trick – fake lottery notifications. After getting infected with this adware, you will be bothered by regular pops up stating that you have won an iPhone. In order to retrieve the prize, you need to click on the indicated “Select” button.
| Threat Type | Adware |
| Peculiarities | Users are redirected to suspicious sites that display fake pop-ups. The messages claim that users were selected by Facebook to receive a prize, but users are required to provide financial information to allegedly be able to collect it |
| Risks | Money loss, sensitive data theft, malware infections |
| Further actions | Scan your computer for malware with anti-virus software and reset all of your browsers. If you entered your banking data into a spoofed site, contact your bank and local authorities that deal with scams |
Needless to say, you will not receive any prize at all. In fact, you might be asked to provide such confidential details as credit card numbers, verification codes, email, and shipping addresses. Such data serves as a valuable material for cybercriminals to improve their hacking techniques. In the best-case scenario, your computer screen and email Inbox will be crammed with personal spam messages.
Otherwise, you might be infected with a more serious threat. This adware spreads the same way as other samples of the same category. “Your profile has been selected by Facebook” might infect your computer via a recently installed freeware or a plug-in. Illegal file-sharing domains might also deliver this virtual annoyance. If you notice these notifications, ignore them, scan your PC with an anti-spyware program, and reset the settings.
Facebook hahaha virus
Facebook “hahaha” virus is yet another version of scams. It is a serious malware that is spread via this social network and used for turning the computer into a Bitcoin mining machine.
| Threat Type | Cryptominer |
| Details | Users are tricked to download a malicious .zip file that extracts the malicious payload, and crypto-mining activities begin |
| Consequences | Computer slowdown, hardware wear-and-tear, increased electricity bills, other malware infections |
| Recovery | Remove malware with security application and reset all your browsers |
Once it tricks its victims into downloading a malicious .zip file, it starts initiating serious system slowdowns and similar issues. Please, don't let this malicious software stay on your computer because you can never know what malicious activities it can be used for.
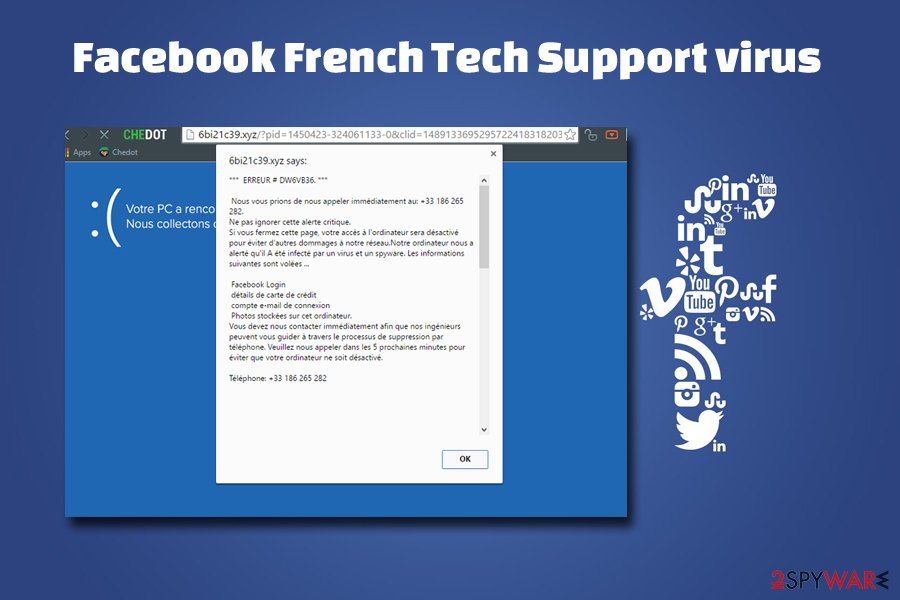
Facebook French Tech Support scam
A new Facebook scam campaign has just been launched, this time focusing on French-speaking users. The hackers are now modifying ads and using fake news articles to redirect victims to a malicious Tech Support scam page located on the “hxxp://scansecure21.online/virus-alerte/” domain.
| Type | Technical support scam |
| The way it works | Crooks create malicious ads that redirect users to a website that imitates Blue Screen of Death error and plays an audio file that claims that visitors' PCs are infected with Zeus banking trojan. To remediate the issue, users are prompted to call fake tech support |
| Ramifications | Users who call fake tech support might get their machines infected with malware, or lose their money for false tech support services |
| Prevention | Never call any numbers provided in the error message, even if it seems like it comes from a legitimate body (Microsoft, Apple, Facebook, etc.). Legitimate messages include error code but never provide any contact information for the alleged tech support |
Once the users land on this page, they are “greeted” by a BSoD imitating window and a 29-second audio file (1.mp3) reading out a text in French. Users are being threatened that their computers have been infected with Zeus trojan, and the only way to protect their banking information and other sensitive details from leaking to hackers is to call Microsoft support technicians by the given number.
It is yet unknown what follows after calling this number, but we can only presume that this Facebook scam works like any other Tech Support scam, and the scammer is trying to convince the callers to purchase questionable software or get remote access to their computers.
Be careful with the ads leading to the following domains: hxxp://actu.com-vnv.com/1; hxxp://actu-europe.com/camp1/; hxxp://actulist.com/adv1/; hxxp://hebdo-actu.com/ad-s1/; hxxp://twimflp.com/ads-03/; hxxp://25608498.com/ and hxxp://com-uknewsnow.com/.
Facebook stalker virus
Facebook Stalker is a dangerous FB application that is actively spread on this social network. It belongs to scammers, and it is used for stealing sensitive user information, not for helping people find out who is secretly watching their FB profile.
| Threat Type | Scam, malware |
| Distribution | Bogus messages on Facebook |
| Peculiarities | Users are urged to click on malicious links. These links can redirect users to malware-laden sites that contain information-stealing trojan payload |
| Risk factors | Money loss, identity theft, malware infections, etc. |
| Recovery | Scan your computer for malware and change all your passwords |
If you happen to all for the FB Stalker app, you can be redirected to a malicious site that looks like a typical login page of Facebook. Please, do not enter your personal information on it because you will disclose it to malicious actors and lose your account!
Your page will be unpublished scam
“Your page will be unpublished” campaign started in 2016 when scammers started creating bogus Facebook pages titled Advert Solution, Ads-Info., Ads Department Social, Team Advert, and similar.
All these pages find pages that belong to business owners and try to scare them by sharing their posts and adding such messages to the post:
WARNING: Your Page will be unpublished! Your account has been reported by others. Our system has received the following reports […] To prevent fraud, please re-confirm your Account to avoid blocking here: [link to a phishing Facebook page].
If some suspicious-looking page has shared your post stating that your page will be disabled, ignore it, and report that person/page to real Facebook staff. If you provide your login details to these scammers, they are going to hack your account immediately and use it for malignant purposes, for example, scam your friends by asking them to lend money.
Facebook suspension Scam
Facebook Suspension comes in the form of an official message alerting the victim of the account suspension. In the email, the hackers claim that due to the violation of certain terms of use, the requisite account is to be suspended. However, if this message is sent by mistake, the user should verify their account by clicking the indicated link.
Do not click on it, as you may accidentally download a trojan or enable the full hack of your account. There is also a possibility that you might be misled to the infected domain after clicking the link.
Hackers did a pretty good job impersonating the official support team by giving credentials. However, you might still notice type and grammar mistakes. The sender's email might raise suspicions as well. This version can be eliminated with the help of anti-spyware and anti-virus programs.
Facebook Invite scam
Invitation Facebook virus is a different kind of virus that has been spreading for years. It spreads via emails and message boards and announces about a great danger on this social network.[13]
| Threat Type | Scam |
| Distribution | Spam emails, fake posts |
| Details | Scammers spread fake messages that warn about an alleged “Olympic torch” virus, which is actually fake. Victims are asked to forward the message to everyone on their friend list to allegedly protect them from danger. |
| Further action | Do not forward any hoax messages to your friends – it's a scam and “Olympic torch” does not exist |
To be more precise, it foolishly warns its victims about the threat that comes as a message with an attachment called Invitation Facebook, and the message states:
Opens an Olympic torch and will take the whole hard disk C of your computer.
However, security experts have revealed that this message includes trojan horse and other types of viruses. You should remove this scam letter as soon as you receive it.
Facebook Automatic wall post
Automatic Wall Post is a cyber infection created to increase the traffic to specific domains. Besides, it may negatively affect your computer's security and try to steal your personal information.
This virus makes people visit the website by showing a tricky message which claims “Sexiest Video ever” and includes a link leading to an unknown website. Also, it automatically makes a post on your wall and spreads in this way. If you see such a message, which seems like it has been posted by your friend, you should remove it from your wall immediately.
Facebook friend request
Facebook Friend Request is a dangerous threat that sends friend requests from a user's account to unknown people or, even worse, the ones who have been already blocked by a user. It has been reported that sometimes this virus manages to send more than 100 invites to random people.
| Threat Type | Spam bot, malware |
| Details | The infection sends hundreds of friend requests to unknown people on Facebook |
| Dangers | Infected users might get their personal information stolen |
| Fix | Scan your computer for malware and reset all your passwords |
The point of creating and using this hasn't still been revealed. However, some experts claim that this threat may be used for taking over computers, shutting down their anti-virus programs, and similar activities.
Facebook Change color scam
Facebook Change Color is a sneaky variant of the virus relying on a message offering to change your social network's background to pink, red, black, or another color.
| Threat Type | Survey scam |
| Distribution | Messenger, spam emails |
| Peculiarities | Users are offered to change their background on social media to different colors. For that, they need to click on a malicious link, which consequently leads users to a survey scam site |
| Remedy | Do not click on suspicious links on spam emails or Messenger |
Just like other types of this threat, it may come to your inbox from one of your contacts, which has also been tricked by this scam message. Typically, it includes a malicious link helping scammers to drive more traffic to their online survey. If you click on this link, you will send this scam message to all your contacts.
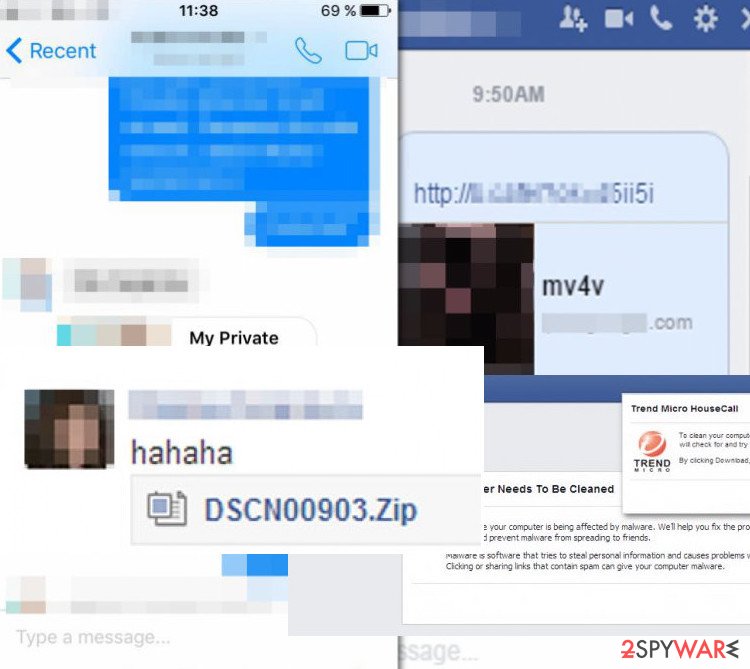
Facebook Child Porn
Facebook Child Porn is a dangerous application circulating in the form of a pornographic video. It may seem that the message, which has this video attached, was sent by your friend, and it is safe. However, after opening it, it becomes clear that it's related to child pornography.
Some victims report that it contains the phrase “watch this if you're curious.” Once opened, the virus automatically attaches to your account and shares this video with all of your Facebook friends.
Locky ransomware is distributed via Facebook Messenger
One of the versions of the threat is designed to send deceptive messages via Messenger to infiltrate the system with Locky ransomware. Usually, the person receives an innocent-looking text and a link that can appear as photo_4837.svg or photo_8470.svg. As soon as the user clicks on it, the system is infected with a file-encrypting virus.
Additionally, the criminals are trying their best to make the message seem convincing, so they add the following phrases:
- Look at this video;
- My newest video;
- OMG! I can't believe this!, etc.
We should also add that most of these links look like they were sent to you by one of your friends, so there is no surprise that the latest attack threat (it was initiated at the end of September 2016) managed to infect more than 800,000 users[14]. It is unknown how many users were tricked in November 2016 attack, but the number is suspected to be similar.
By clicking such a link, you infect your account and start spreading scams yourself. Besides, such malware can easily infect your computer with the most dangerous computer viruses that are active during the distribution.
Besides, such threats have actively been used for acquiring sensitive information, such as logins, financial information, and other data which is considered confidential. Unfortunately, hackers have already managed to release multiple versions of this threat. All of them are listed below.
If you think that you are dealing with problems with your account, you might be infected. Check your wall for spammy posts, go thru your Messages for misleading links. If you can remember clicking them, you must remove the scam ASAP. There are several ways to fix your account and the affected PC system.
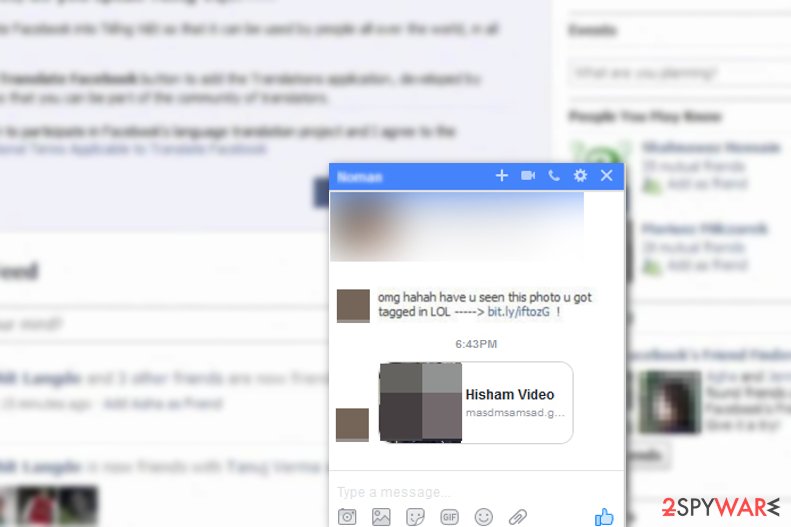
Facebook Video viruses still infecting computers in 2023
Facebook video scam is a tricky scam that is particularly created to distribute potentially unwanted programs (PUPs) or even malware via messages on Messenger. Experts noted that it was still active in 2023, so people must be extremely cautious. Those who have been infected say that they have received a direct text from one of their Facebook friends, which includes several elements and a suspicious link:
- targeted victim’s name;
- word “video”;
- random emoji.
When a user clicks on the infected link, the virus starts spreading the same message to all victim’s contact lists. Therefore, it works like a chain reaction. Therefore, it is also reported that it can send messages in a different language. For instance, in the Netherlands, these messages are written in the Dutch language.[15]
The recent version of the Facebook video threat is suspected to be spreading via Google Chrome extensions. However, it is designed to prevent victims from removing it easily. This happens when the malware does the following:
- Performs arbitrary modifications on the browser;
- Blocks user’s access to browser’s extensions;
- Might close Chrome when a user tries to open them.
After the attack, users are advised to reset Google Chrome. However, this may not work. If your friends continue reporting messages sent from your account, you have to uninstall Chrome from your device.
What is more, if your account is hacked, you should also set a new password and change other accounts' passwords. It’s unknown what information cybercriminals can access and what damage they might cause to the personal user’s information. Therefore, victims are suggested to protect sensitive data.
The malware has infected computers worldwide for 4 years in a row
This dangerous cyber threat has already infected computers all across the globe. Cybersecurity specialists have reported about the Facebook Youtube video version of the malware. At the end of 2017, these scams have tried to deceive credulous people and open a malicious link. It has also spread via Messenger with the following elements:
- Link to the video;
- Profile picture of the receiver;
- “Ohh! det är verkligen du?” (“Oh! Is it really you?”) message.[16]
The link directed victims to a YouTube page. It asked you to download a specific plug-in to play the video. Though it may seem more credulous, note that once a proper video link is attached in a chat window, it displays the video's icon with a screenshot of the video content.
In this scam, the link does not reveal anything except the YouTube brand name. Like previous versions, the scam is spread to all the contacts of an infected user. The developers of this scam might have set up a few fake accounts as well to keep the distribution of the scam.
Unfortunately, the Facebook virus revealed its new capabilities in December 2021. First of all, it started attacking new countries, such as Vietnam, Netherlands, and Spain. The virus still tries to spread around as Youtube-related video, so make sure you ignore messages that use “video_ (4 random numbers)” name.
After clicking this message, you can run into two different scenarios:
- It can redirect you to a fake Youtube page asking to update Adobe Flash Player. According to the latest news, this way you can get infected with an adware-type program that can potentially redirect you to malicious websites or track your browsing.
- You can get infected with an infamous Monero miner, alternatively known as Digmine. In this case, your computer's resources can be used to mine virtual currency. Besides, this attack involves a malicious Chrome extension that misuses the auto-login feature and connects to the victim's account to continue distributing the malicious video link.
Facebook viruses and scams are distributed via extensions
The primary and most successful distribution technique of the malware is malicious Messenger messages that contain an infected link.[5] They are well-designed to make sure that people would fall for the fraud. This way, once the link is clicked, hackers can hijack an account and start the chain reaction of infections.
Also, if not eliminated, malware can infect your computer with a trojan horse that starts its activity as soon as it enters the system. It can track you for years to steal your personal information or download other viruses to your computer, including ransomware-type threats that can encrypt your files with an advanced encryption algorithm and then ask you to pay a ransom.
An alternative way malware infects its victims is related to hacked apps. If you are tricked into granting them access to your account, you can find that your social account was hijacked. Finally, using a weak password is also considered one of the main ways Facebook malware uses to affect its users.
The latest version of malware is noticed to be spreading via Google Chrome extensions. The problem with this distribution method is that users were forbidden from accessing Chrome settings and removing the malicious app unless they reset the browser or uninstalled it entirely.
Tips for safe social media usage and malware avoidance
Facebook scams and malware pose significant threats to user security. However, you can employ various strategies to protect yourself and your data.
Firstly, exercise caution when clicking on links, even those sent by friends. Cybercriminals often hijack accounts to spread harmful links. If a link seems suspicious or out of character for the person sending it, avoid clicking it.
Secondly, use strong, unique passwords for your Facebook account and change them regularly. Consider using a password manager to help remember these. Two-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security, requiring a second form of verification before granting access.
Be wary of friend requests from people you don't know or duplicate friend requests from people you're already connected with. These could be fake accounts intending to gain your trust and subsequently scam you.
Moreover, avoid sharing sensitive personal information like your home address, phone number, or financial information on Facebook, as these details can be used by scammers. Always check your privacy settings to ensure only trusted contacts can view your personal details.
Ensure that your device has a reliable and updated antivirus program installed. This software can help detect and remove any malware that might have been inadvertently downloaded.
Lastly, regularly review your Facebook account activity. If you notice any suspicious behavior, like posts you didn't make or messages you didn't send, change your password immediately and report it to Facebook. Remember, staying vigilant and proactive can go a long way in securing your online presence against cyber threats.
Use uninstall guides to remove Facebook viruses
It is essential to understand that hackers are good at social engineering tactics and you shouldn't trust unknown people on the social media platform. You can avoid threats if you never click on:
- Suspicious links;
- Messages from unknown people;
- Unreliable file downloads.
If you can't resist the temptation, send your friend a message BEFORE clicking the provided link and ask him or her about it. Additionally, avoid accessing every game, site, or app on the social network because it may be hacked by cybercriminals.
If you have been tricked by any of these types of Scams, you should change your password ASAP in order to avoid identity theft and the loss of personal information. Additionally, contact your friends and let them know that your account is hacked. Finally, download a security program to scan your computer and prevent the infiltration of malware. It can remove the Facebook virus and its outcomes within several minutes. For best results, use FortectIntego.
Do not forget to update the software before running a scan to ensure that your PC is safe. Some of you might try to perform manual removal on their computers. While you can fix your account manually, we would like to warn you that the threat which travels around together with this threat can remain undetected on your computer.
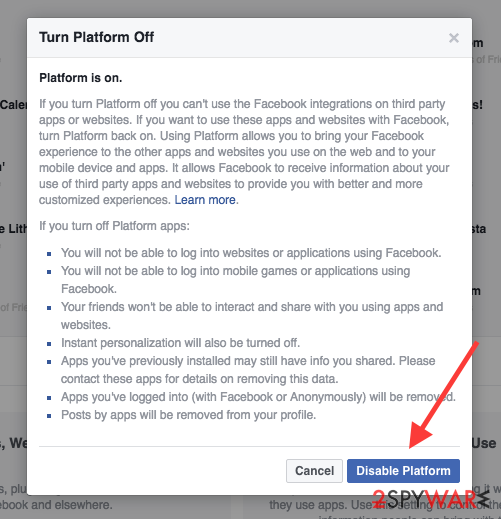
Turn off Platform
You can switch off Platform functionality which would stop third-party apps and websites integration:
- Login to your Facebook account and click this little triangle on your right;
- Click Settings to open General Account Settings window;
- Look on your left and select Apps;
- Click Edit button on Apps, Websites and Plugins option;
- Select Disable to protect your account from unauthorized access of third party apps.
Change your Facebook password
If your account was hacked or accessed by unknown individuals, make sure you immediately reset your password:
- Click on the small triangle icon at the top-right corner of your Facebook page
- Select Settings & Privacy
- On the left, pick Security and Login
- Select Change password on the right side
- Type in the current password and then type in the new one
- Click Save Changes.
Reset all the affected browsers to remove the Facebook virus
Typically, adware or other potentially unwanted programs might change web browser settings. Such a browser will still redirect you to spoofing, scam, and phishing sites. Additionally, some malware might steal cookie information. Therefore, make sure you reset your web browsers and eliminate the possibility of hackers keep harvesting the crucial data.
Google Chrome
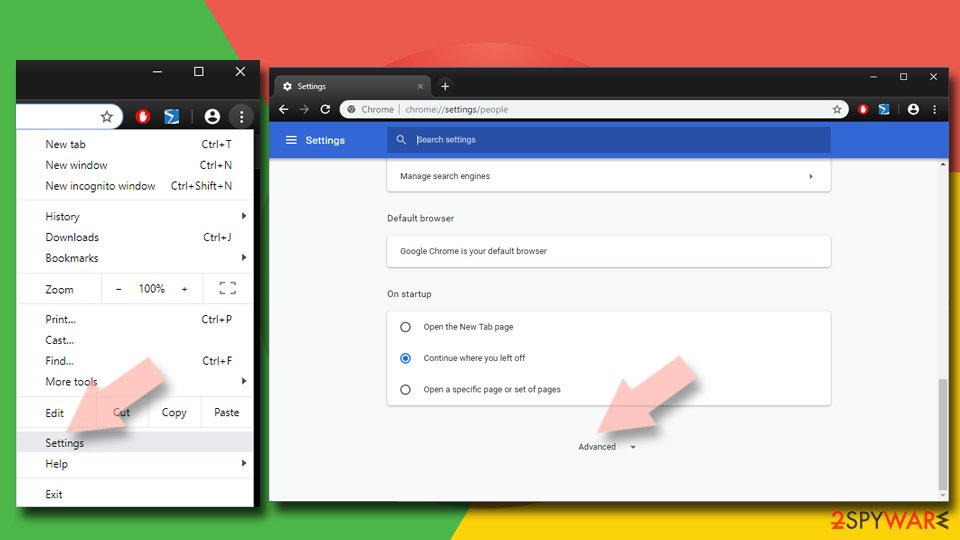
- Go to Google Chrome and click on the menu (three vertical dots at the top-right corner) and select Settings.
- Scroll down and pick Advanced.

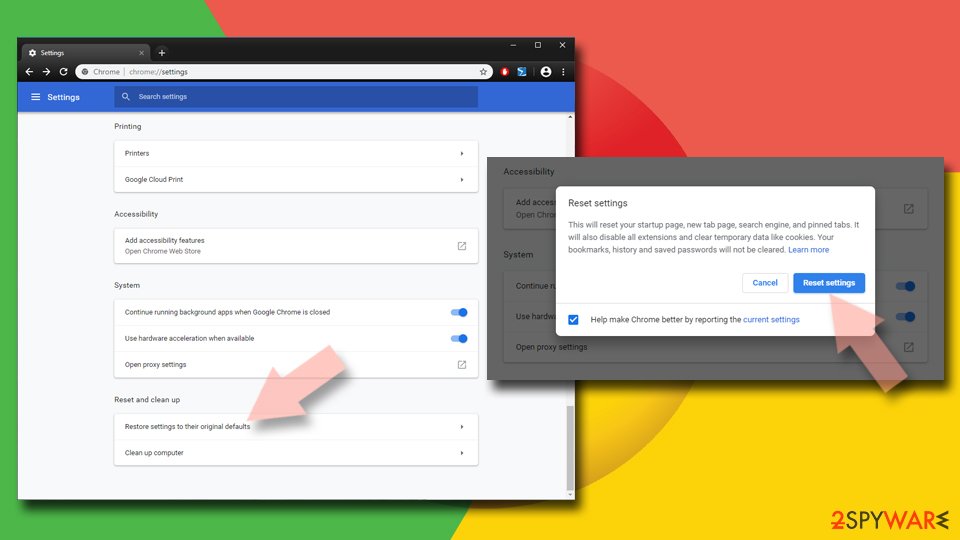
- Next, find Reset and clean up section.
- Now click on Restore settings to their original defaults.
- To confirm the action, click on Reset settings and complete Facebook virus removal.

Mozilla Firefox
- Open Mozilla Firefox and click on the menu.
- Go to Help and then select Troubleshooting Information.
- In the Give Firefox a tune up section, click on Refresh Firefox…
- Finally, confirm the action by pressing on Refresh Firefox.
Safari
- Select Safari and then click on Preferences…
- Go to Advanced tab.
- Tick the Show Develop menu in menu bar.
- Go to the menu bar and click on Develop, and then pick Empty Cache.
Internet Explorer
- Click on Gear icon and select Internet options.
- Pick Advanced tab.
- Select Reset.
- In the new window, check Delete personal settings and click on Reset.
MS Edge
- Select Menu (three horizontal dots at the top-right) and click on Privacy & security.
- Pick Choose what to clear located under Clear browsing data.
- Select everything and click Clear.
- Now press Ctrl + Shift + Esc on your keyboard to open Task Manager.
- Click on More details arrow at the bottom of the window.
- Select Details tab.
- Find all MS Edge entries, right-click and select End task.
Scan your computer with security software:
A full system scan is recommended to prevent further damage to Facebook-related threats. By running a full scan with SpyHunter 5Combo Cleaner or similar software, you will ensure the removal of trojans, ransomware-type viruses, and similar malware that has been spread with the help of this virus. Note that FortectIntego is an excellent tool that can fix virus damage and keep your privacy at bay with various security and maintenance features, so we highly recommend it.
Delete all Facebook virus-related files and components by following the detailed instructions below.
Getting rid of Facebook virus. Follow these steps
Uninstall from Android
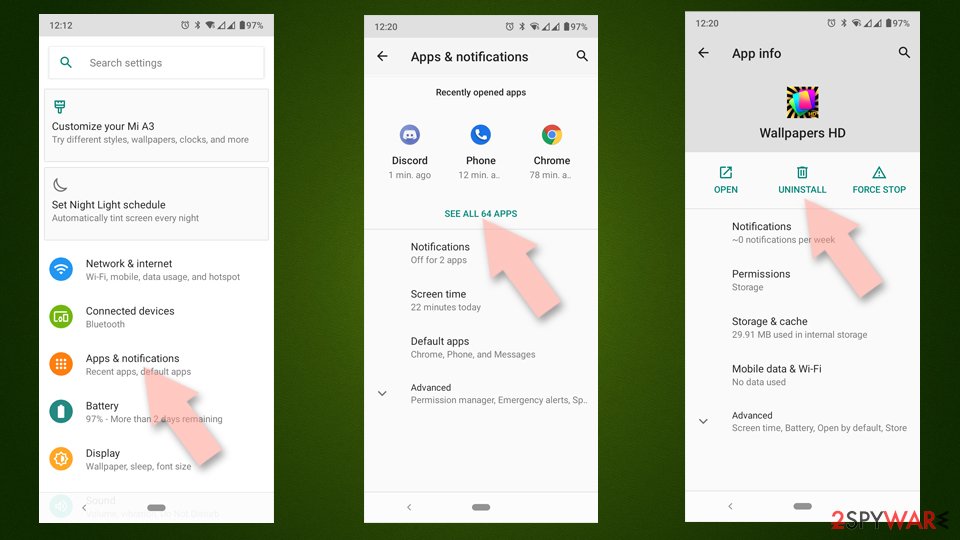
Uninstall unwanted programs from Android device:
- Go to Settings -> Apps/Applications.
- Expand the full list of the installed apps.
- Scroll through the list and tap on a suspicious application once.
- Tap on it and select Uninstall.

- Reboot the device.
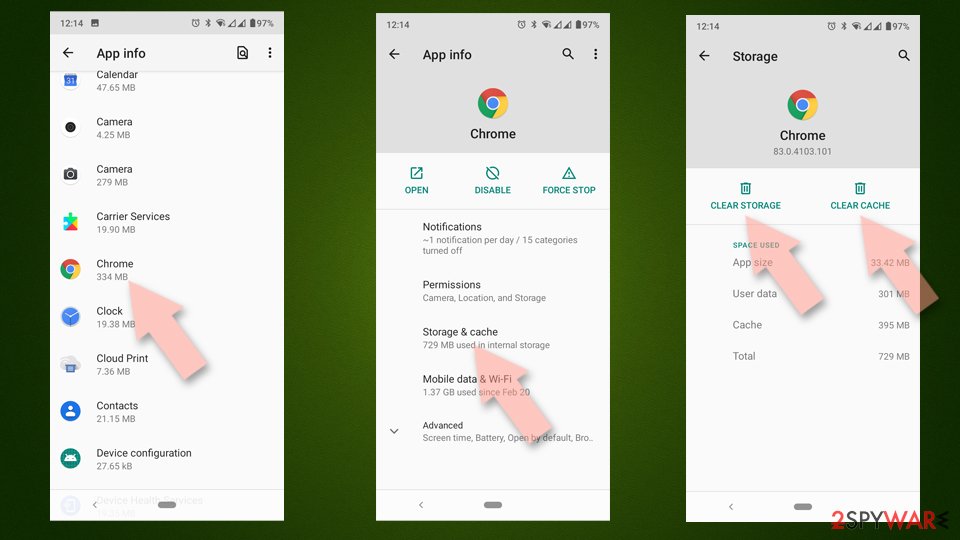
Clear Storage and data files on Android from Google Chrome or other apps:
- Go to Settings > Apps/Applications.
- Expand the full list of the installed apps.
- Tap on Chrome and select Storage & cache.
- Clear storage and clear cache of the app.

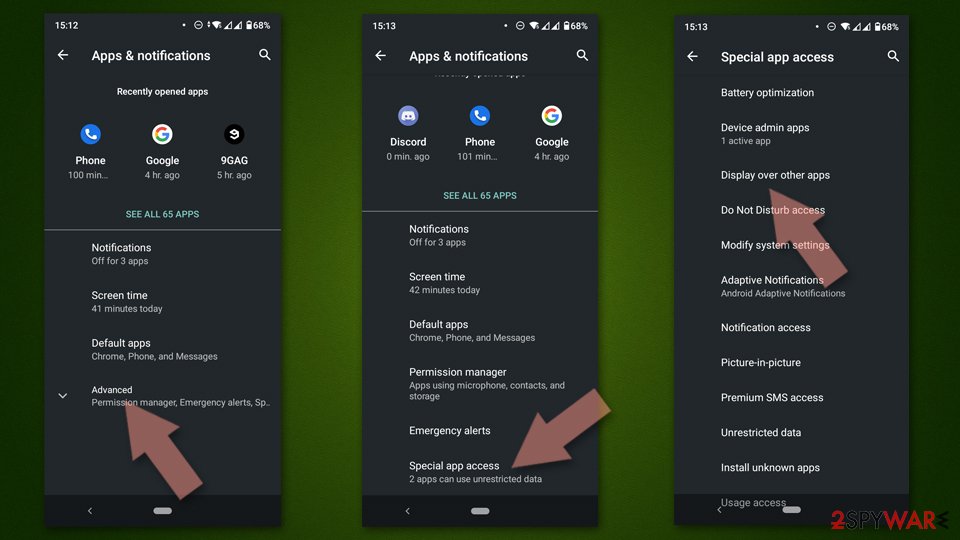
If you are seeing ads on top of other apps but are not sure what is causing it, perform the following steps:
- Go to Apps/Applications.
- Tap Advanced.
- Select Special App access.
- Tap on Display over other apps.

- Eliminate apps with these access rights enabled.
Scan your system with anti-malware
If you are a victim of ransomware, you should employ anti-malware software for its removal. Some ransomware can self-destruct after the file encryption process is finished. Even in such cases, malware might leave various data-stealing modules or could operate in conjunction with other malicious programs on your device.
SpyHunter 5Combo Cleaner or Malwarebytes can detect and eliminate all ransomware-related files, additional modules, along with other viruses that could be hiding on your system. The security software is really easy to use and does not require any prior IT knowledge to succeed in the malware removal process.
Repair damaged system components
Once a computer is infected with malware, its system is changed to operate differently. For example, an infection can alter the Windows registry database, damage vital bootup and other sections, delete or corrupt DLL files, etc. Once a system file is damaged by malware, antivirus software is not capable of doing anything about it, leaving it just the way it is. Consequently, users might experience performance, stability, and usability issues, to the point where a full Windows reinstall is required.
Therefore, we highly recommend using a one-of-a-kind, patented technology of FortectIntego repair. Not only can it fix virus damage after the infection, but it is also capable of removing malware that has already broken into the system thanks to several engines used by the program. Besides, the application is also capable of fixing various Windows-related issues that are not caused by malware infections, for example, Blue Screen errors, freezes, registry errors, damaged DLLs, etc.
- Download the application by clicking on the link above
- Click on the ReimageRepair.exe

- If User Account Control (UAC) shows up, select Yes
- Press Install and wait till the program finishes the installation process

- The analysis of your machine will begin immediately

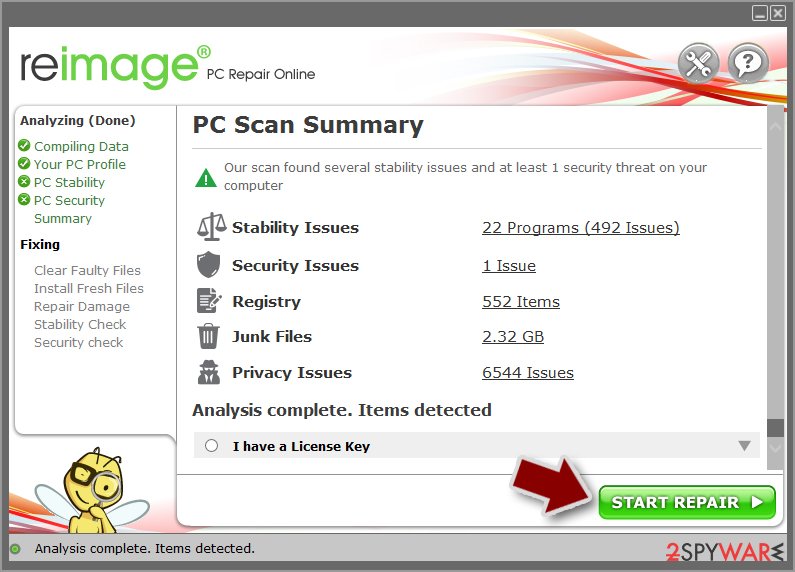
- Once complete, check the results – they will be listed in the Summary
- You can now click on each of the issues and fix them manually
- If you see many problems that you find difficult to fix, we recommend you purchase the license and fix them automatically.

By employing FortectIntego, you would not have to worry about future computer issues, as most of them could be fixed quickly by performing a full system scan at any time. Most importantly, you could avoid the tedious process of Windows reinstallation in case things go very wrong due to one reason or another.
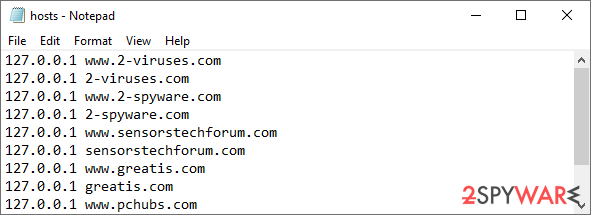
Restore Windows "hosts" file to its original state
Some ransomware might modify Windows hosts file in order to prevent users from accessing certain websites online. For example, Djvu ransomware variants add dozens of entries containing URLs of security-related websites, such as 2-spyware.com. Each of the entries means that users will not be able to access the listed web addresses and will receive an error instead.
Here's an example of “hosts” file entries that were injected by ransomware:
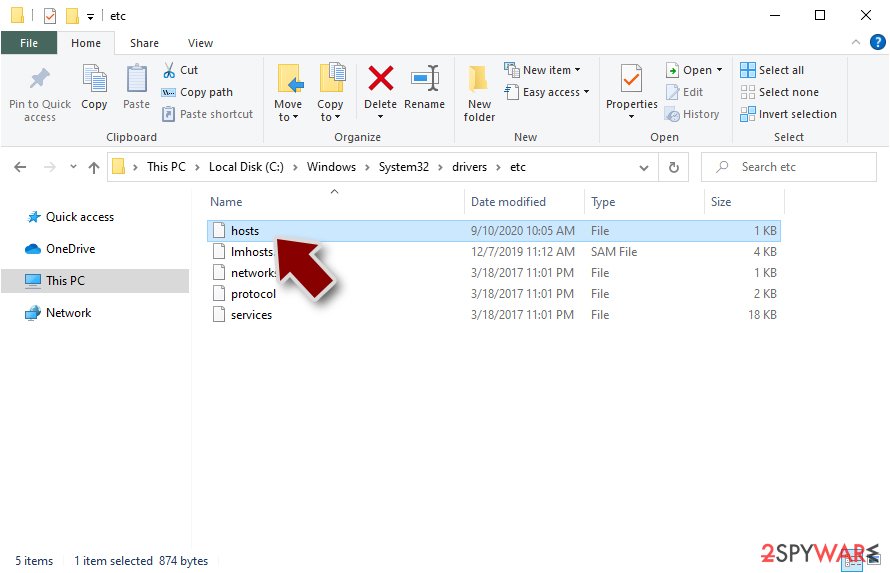
In order to restore your ability to access all websites without restrictions, you should either delete the file (Windows will automatically recreate it) or remove all the malware-created entries. If you have never touched the “hosts” file before, you should simply delete it by marking it and pressing Shift + Del on your keyboard. For that, navigate to the following location:
C:\\Windows\\System32\\drivers\\etc\\
Restore files using data recovery software
Since many users do not prepare proper data backups prior to being attacked by ransomware, they might often lose access to their files permanently. Paying criminals is also very risky, as they might not fulfill the promises and never send back the required decryption tool.
While this might sound terrible, not all is lost – data recovery software might be able to help you in some situations (it highly depends on the encryption algorithm used, whether ransomware managed to complete the programmed tasks, etc.). Since there are thousands of different ransomware strains, it is immediately impossible to tell whether third-party software will work for you.
Therefore, we suggest trying regardless of which ransomware attacked your computer. Before you begin, several pointers are important while dealing with this situation:
- Since the encrypted data on your computer might permanently be damaged by security or data recovery software, you should first make backups of it – use a USB flash drive or another storage.
- Only attempt to recover your files using this method after you perform a scan with anti-malware software.
Install data recovery software
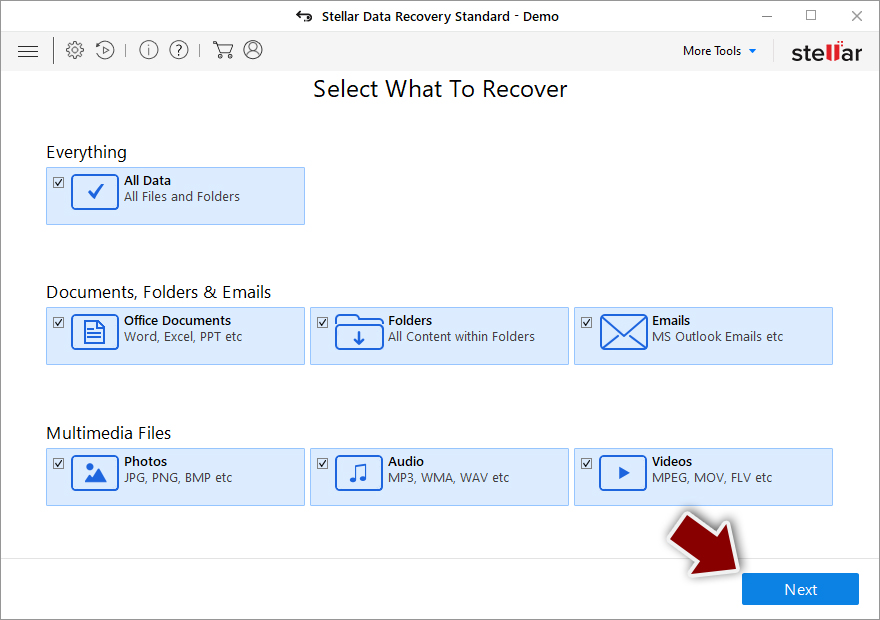
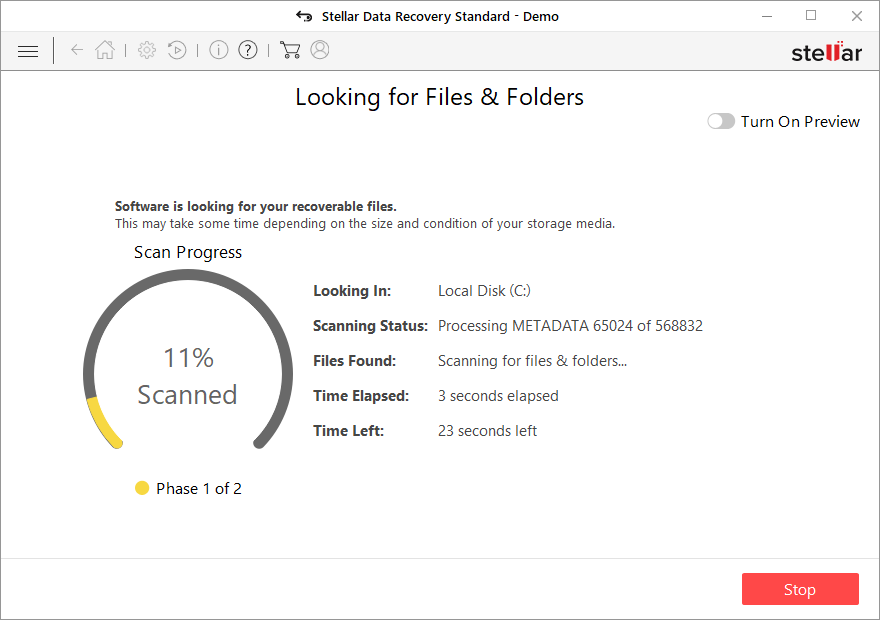
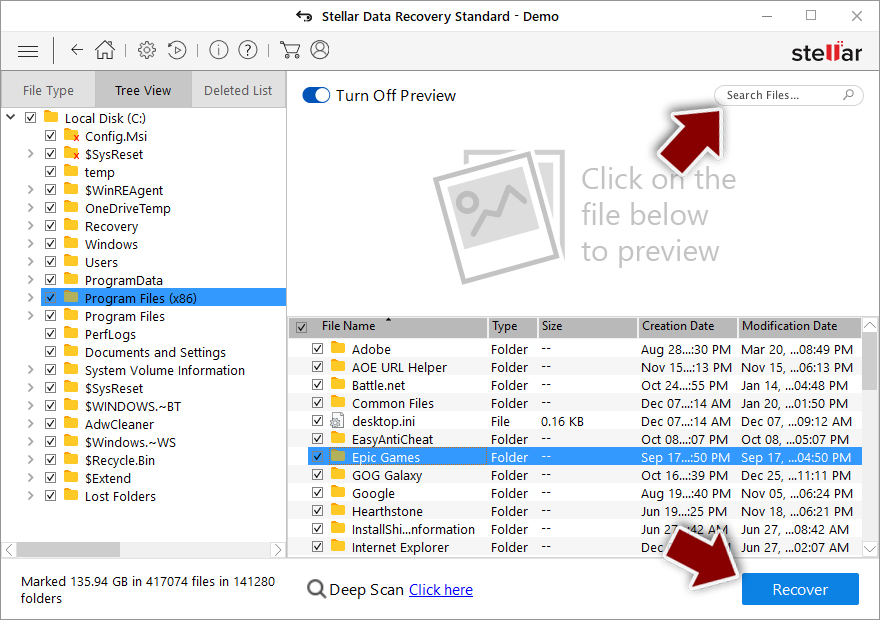
- Download Data Recovery Pro.
- Double-click the installer to launch it.

- Follow on-screen instructions to install the software.

- As soon as you press Finish, you can use the app.
- Select Everything or pick individual folders where you want the files to be recovered from.

- Press Next.
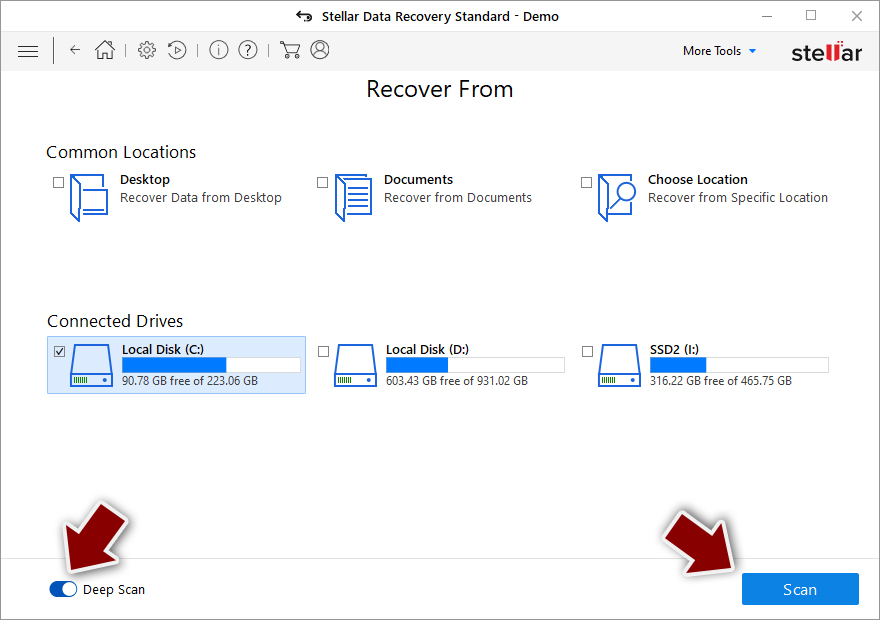
- At the bottom, enable Deep scan and pick which Disks you want to be scanned.

- Press Scan and wait till it is complete.

- You can now pick which folders/files to recover – don't forget you also have the option to search by the file name!
- Press Recover to retrieve your files.

Report the incident to your local authorities
Ransomware is a huge business that is highly illegal, and authorities are very involved in catching malware operators. To have increased chances of identifying the culprits, the agencies need information. Therefore, by reporting the crime, you could help with stopping the cybercriminal activities and catching the threat actors. Make sure you include all the possible details, including how did you notice the attack, when it happened, etc. Additionally, providing documents such as ransom notes, examples of encrypted files, or malware executables would also be beneficial.
Law enforcement agencies typically deal with online fraud and cybercrime, although it depends on where you live. Here is the list of local authority groups that handle incidents like ransomware attacks, sorted by country:
- USA – Internet Crime Complaint Center IC3
- United Kingdom – ActionFraud
- Canada – Canadian Anti-Fraud Centre
- Australia – ScamWatch
- New Zealand – ConsumerProtection
- Germany – Polizei
- France – Ministère de l'Intérieur
If your country is not listed above, you should contact the local police department or communications center.
Manual removal using Safe Mode
Important! →
Manual removal guide might be too complicated for regular computer users. It requires advanced IT knowledge to be performed correctly (if vital system files are removed or damaged, it might result in full Windows compromise), and it also might take hours to complete. Therefore, we highly advise using the automatic method provided above instead.
Step 1. Access Safe Mode with Networking
Manual malware removal should be best performed in the Safe Mode environment.
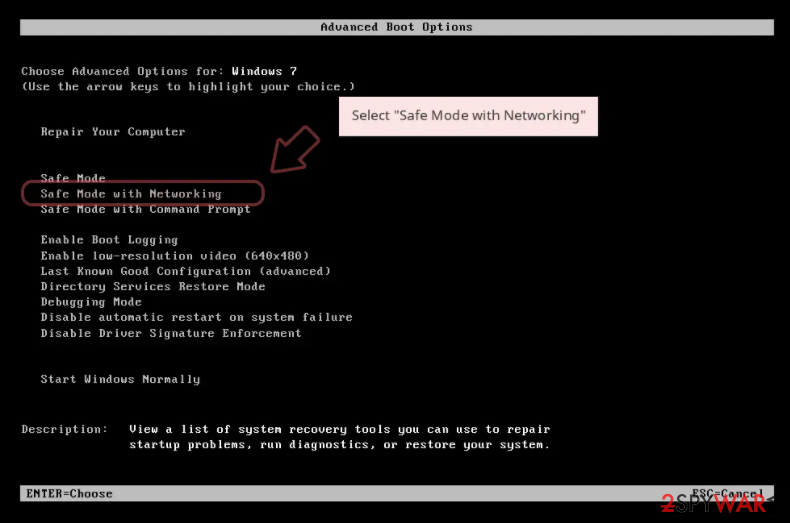
Windows 7 / Vista / XP
- Click Start > Shutdown > Restart > OK.
- When your computer becomes active, start pressing F8 button (if that does not work, try F2, F12, Del, etc. – it all depends on your motherboard model) multiple times until you see the Advanced Boot Options window.
- Select Safe Mode with Networking from the list.

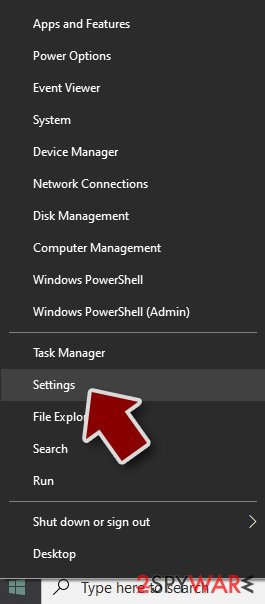
Windows 10 / Windows 8
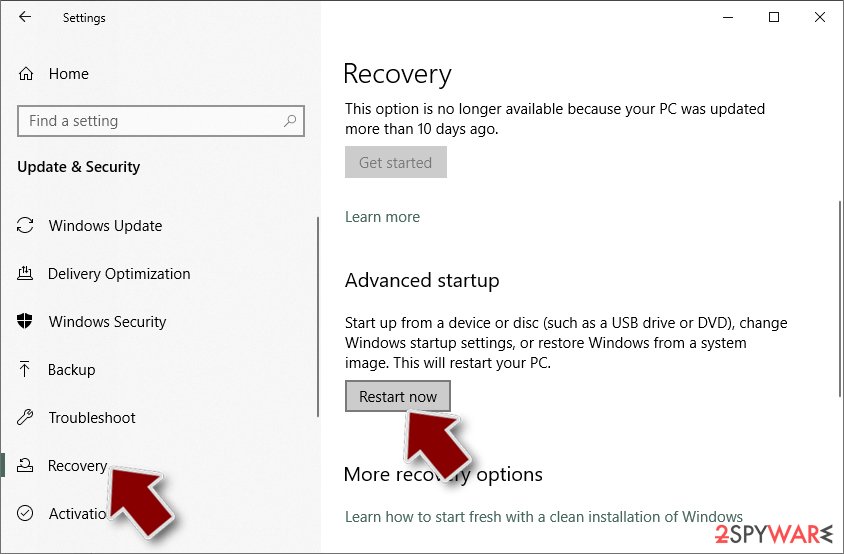
- Right-click on Start button and select Settings.

- Scroll down to pick Update & Security.

- On the left side of the window, pick Recovery.
- Now scroll down to find Advanced Startup section.
- Click Restart now.

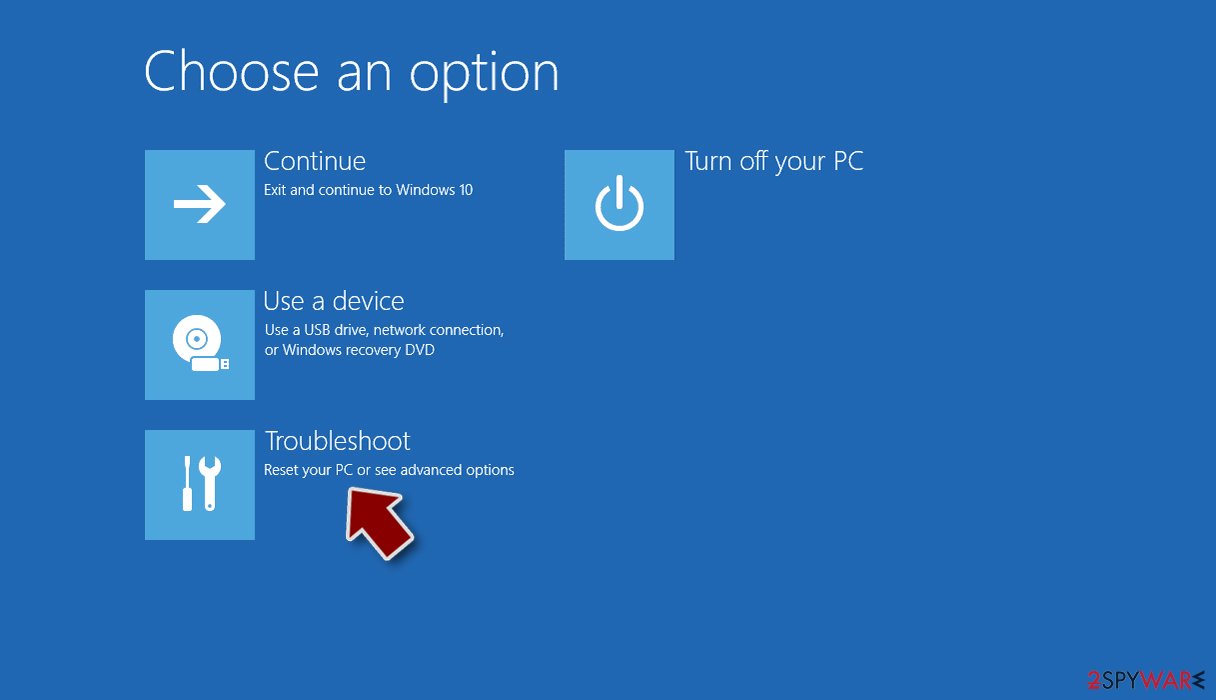
- Select Troubleshoot.

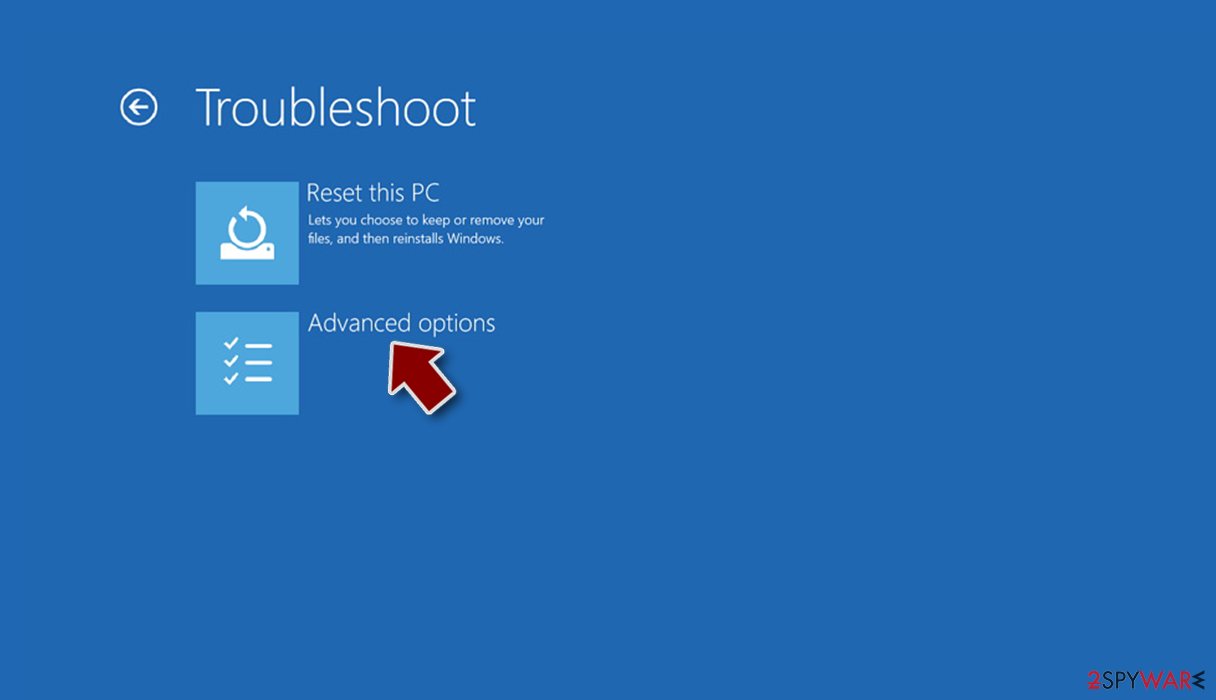
- Go to Advanced options.

- Select Startup Settings.

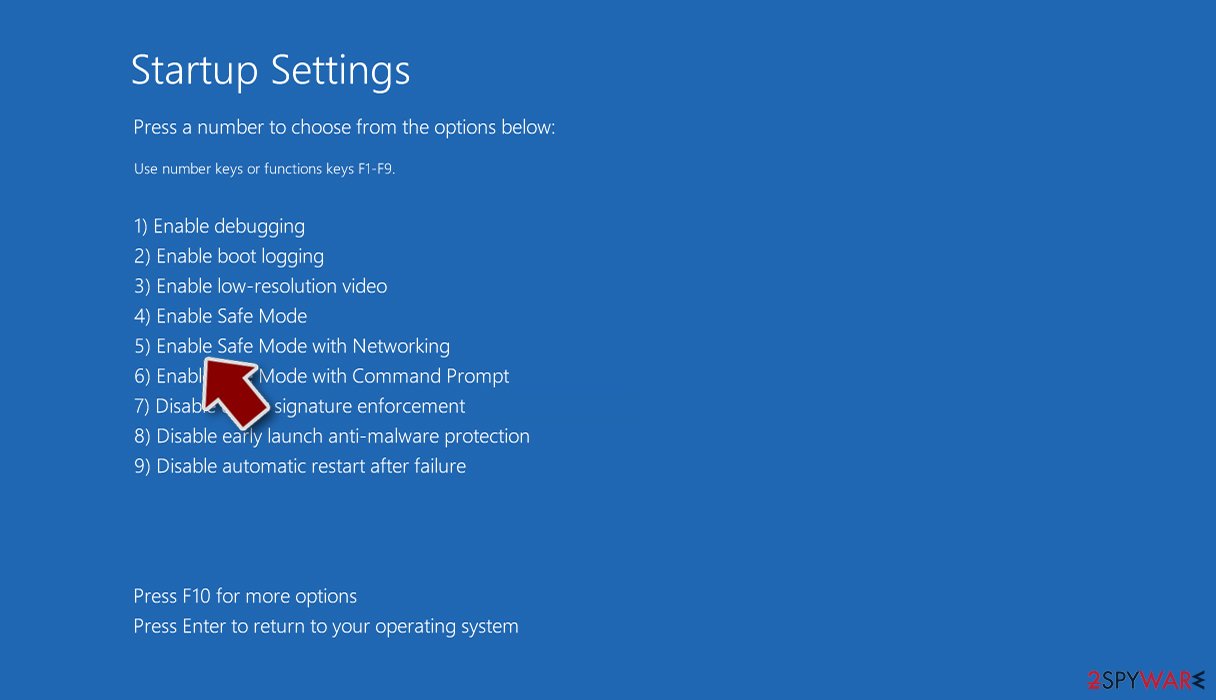
- Press Restart.
- Now press 5 or click 5) Enable Safe Mode with Networking.

Step 2. Shut down suspicious processes
Windows Task Manager is a useful tool that shows all the processes running in the background. If malware is running a process, you need to shut it down:
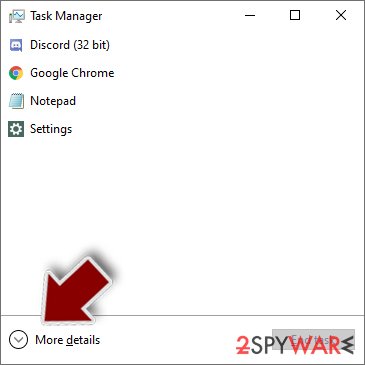
- Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc on your keyboard to open Windows Task Manager.
- Click on More details.

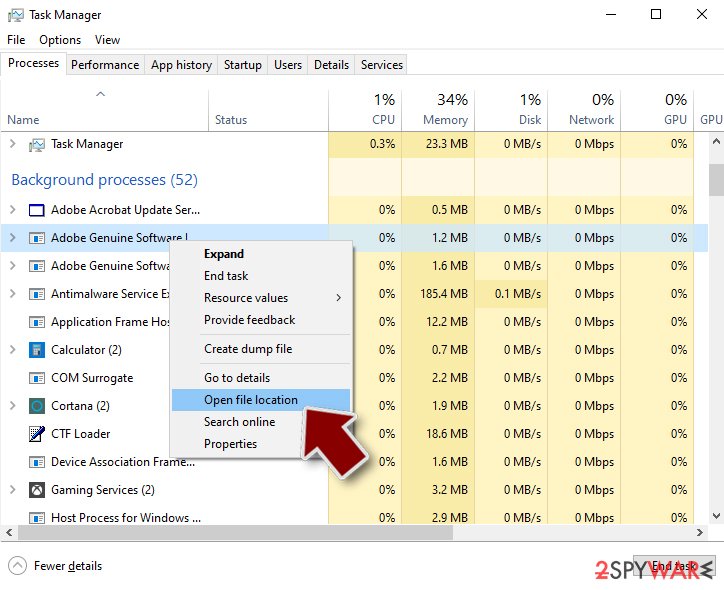
- Scroll down to Background processes section, and look for anything suspicious.
- Right-click and select Open file location.

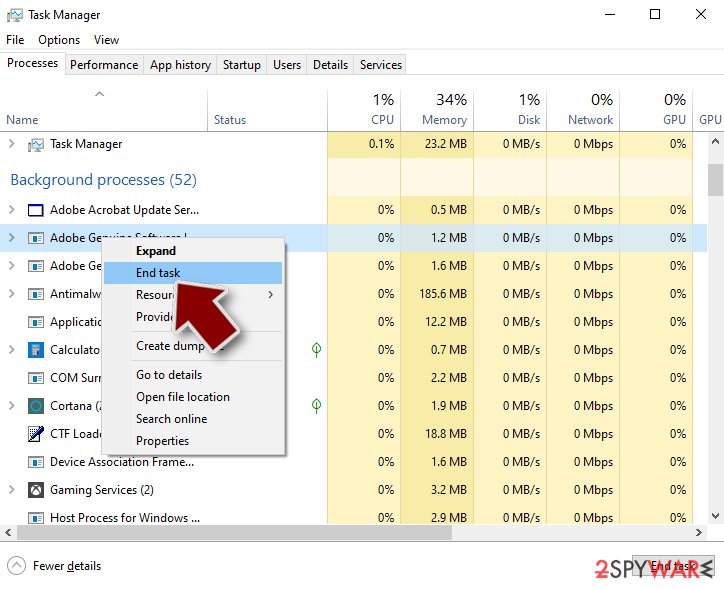
- Go back to the process, right-click and pick End Task.

- Delete the contents of the malicious folder.
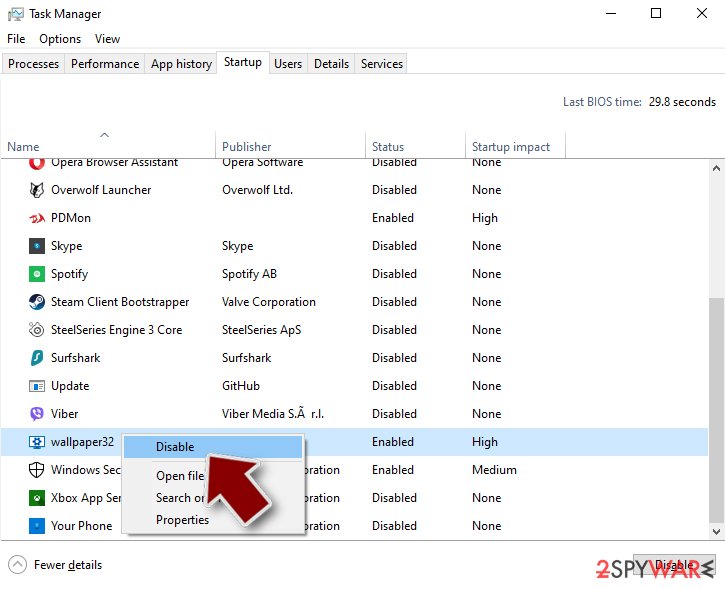
Step 3. Check program Startup
- Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc on your keyboard to open Windows Task Manager.
- Go to Startup tab.
- Right-click on the suspicious program and pick Disable.

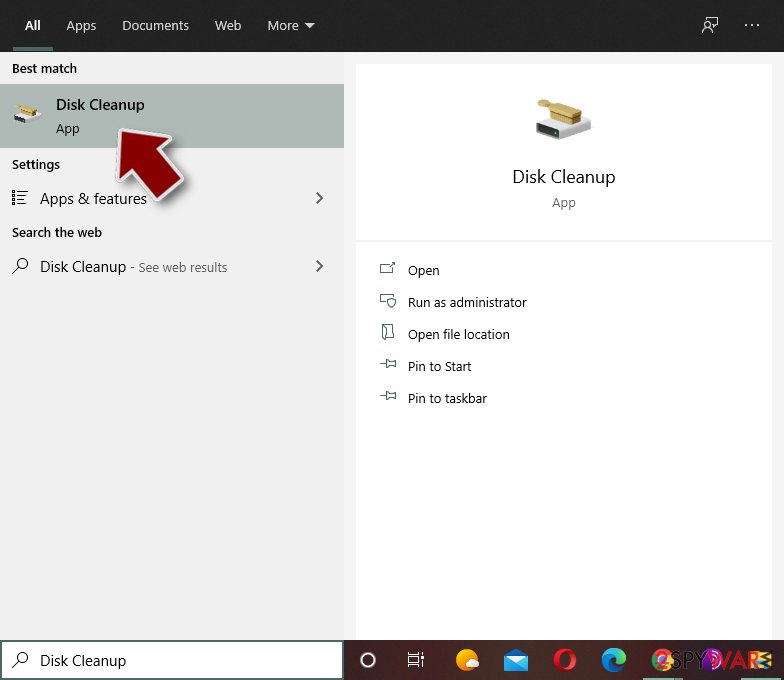
Step 4. Delete virus files
Malware-related files can be found in various places within your computer. Here are instructions that could help you find them:
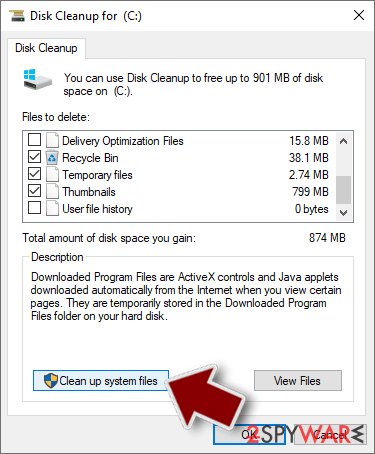
- Type in Disk Cleanup in Windows search and press Enter.

- Select the drive you want to clean (C: is your main drive by default and is likely to be the one that has malicious files in).
- Scroll through the Files to delete list and select the following:
Temporary Internet Files
Downloads
Recycle Bin
Temporary files - Pick Clean up system files.

- You can also look for other malicious files hidden in the following folders (type these entries in Windows Search and press Enter):
%AppData%
%LocalAppData%
%ProgramData%
%WinDir%
After you are finished, reboot the PC in normal mode.
How to prevent from getting malware
Access your website securely from any location
When you work on the domain, site, blog, or different project that requires constant management, content creation, or coding, you may need to connect to the server and content management service more often. The best solution for creating a tighter network could be a dedicated/fixed IP address.
If you make your IP address static and set to your device, you can connect to the CMS from any location and do not create any additional issues for the server or network manager that needs to monitor connections and activities. VPN software providers like Private Internet Access can help you with such settings and offer the option to control the online reputation and manage projects easily from any part of the world.
Recover files after data-affecting malware attacks
While much of the data can be accidentally deleted due to various reasons, malware is one of the main culprits that can cause loss of pictures, documents, videos, and other important files. More serious malware infections lead to significant data loss when your documents, system files, and images get encrypted. In particular, ransomware is is a type of malware that focuses on such functions, so your files become useless without an ability to access them.
Even though there is little to no possibility to recover after file-locking threats, some applications have features for data recovery in the system. In some cases, Data Recovery Pro can also help to recover at least some portion of your data after data-locking virus infection or general cyber infection.
- ^ Website spoofing. Wikipedia. The Free Encyclopedia.
- ^ What is Malicious Cryptocurrency Mining?. Zvelo blog.
- ^ Danny Palmer. What is malware? Everything you need to know about viruses, trojans and malicious software. Zdnet. Breaking news, analysis, and research.
- ^ Facebook Messenger video malware hoax makes a return to local accounts. Coconuts. Asian news website.
- ^ The detection of the malicious flash player.dmg. VirusTotal.
- ^ Olivia Morelli. Digmine Monero miner started spreading via Facebook Messenger. 2-spyware news.
- ^ Locky virus launched a new distribution campaign on Facebook. VirusActivity blog. The latest news about computer viruses.
- ^ Russell Brandom. There are hundreds of free iPhone scams on Facebook, Instagram, and YouTube. The Verge. Multimedia effort.
- ^ Kashmira Gander. Facebook 'Following me' hoax suggests users can reveal secret online followers. The Independent. UK and Worlwide News.
- ^ Martin Lewis video about scam. Twitter. The social network.
- ^ Ryanair post about scam. Facebook. The social network.
- ^ Tara Evans. Ryanair customers warned about new Facebook scam offering two free flights. The Sun. News, sport, celebrities and gossip.
- ^ Paul Ducklin. Why you shouldn’t forward the “Invitation FACEBOOK – Olympic Torch” chain letter. Sophos. Cybersecurity blog.
- ^ A new Facebook virus has already infected 800,000 users – here’s what you need to know. Digital Trends. Technology News and Product Reviews.
- ^ Dorien Vervoort. Zo geraak je van een Facebook-virus af. TechPulse. Elke dag de vinger aan de pols van de technologiewereld.
- ^ Nyheter. Virus sprids på Facebook – ser ut som Youtubelänk. Aftonbladet. Breaking Sweden news.