OperativeIndexer Mac virus (Free Guide)
OperativeIndexer Mac virus Removal Guide
What is OperativeIndexer Mac virus?
OperativeIndexer is a Mac virus that avoids detection by XProtect and Gatekeeper

OperativeIndexer is malware that targets Mac systems and their users. It comes from a sizable family of Adload, which has been used in hundreds of variations throughout the cybercrime scene for at least five years. There are many characteristics that are considered dangerous about it, even though the virus' primary role is to operate as adware that subjects users to a range of advertisements and generates income for bad actors in this way.
Users don't intentionally let the OperativeIndexer virus enter their systems, even though this is exactly what happens. People frequently install malware because they are unaware of how it is spread. Fake Flash Player updates and cracked or repacked software packages are to blame for this. In both situations, users input their Apple ID thinking they are installing something else and consent to it.
As soon as the virus is settled, it begins to change the way Macs operate. The first sign that regular users would notice is the changed browser settings and the extension of the same name installed on Safari, Chrome, or another browser – it uses a magnifying glass icon on a gray, teal, or green background. Those affected may notice that searches lead to suspicious providers such as Safe Finder, and their browser sessions are filled with ads.
| Name | OperativeIndexer |
| Type | Mac virus, adware, browser hijacker |
| Malware family | Adload |
| Distribution | Malware can be downloaded along with pirated software installers or via fake Flash Player updates |
| Symptoms | A new extension is downloaded to the browser, along with a matching app; search and browsing preferences are changed to use a different search engine; new user profiles and login items are created on the account; intrusive advertising and redirects |
| Removal | Mac malware can be eliminated with the aid of robust security tools, such as SpyHunter 5Combo Cleaner. A manual option is also available; however, it is not recommended for novice users |
| Optimization | By clearing your web browser caches and data, you can prevent third parties from tracking you. Use FortectIntego to do this optimally |
Distribution
One of the most potent and prevalent types of Mac malware is called Adload. Since it was first identified in 2017, its creators have continued to release additional iterations, several of which have previously been discussed here – LinkRoot, UnitDisplay, and NanoProtocol are just a few examples.
The overwhelming majority of people who get this malware do so after being fooled by a fake Flash Player Update.[1] Flash Player is a well-known program that has been used to play multimedia material online and has become very established over the years. With the help of this popularity, crooks can use fake messages that urge people to install it, even though they would be installing malicious software instead. The plugin has been discontinued by its developer for a few years now, so keep in mind that all the requests to download it are fake.
Alternatively, some people might install OperativeIndexer along with pirated software from dubious websites. Illegal software distributors are known to be spreading all sorts of malicious links and malware on their websites, so it is recommended to stay away from them in the first place.

Operation
The OperativeIndexer malware enters the system and quickly installs a number of components, completely bypassing the built-in Mac security. This enables malware to penetrate the system effectively and take control of certain of its components. For instance, users who have been infected could discover that a browser add-on has been added to their hijacked[2] version of Safari, Chrome, or another web browser. As a result, users will see plenty of advertisements and encounter browser redirection to dangerous websites.
The effects of the malware infection can be severe, and not only in terms of disrupted surfing. It may potentially be able to monitor personal user information, install additional versions of itself without user consent, and expose users to harmful content online. Besides, Adload may be associated with serious threats like Shlayer Trojan or Crescent Core – other malware that are well known to cybersecurity experts analyzing Mac infections.
Additionally, malware introduces a man-in-the-middle[3] proxy, allowing traffic to be diverted through cybercriminals' servers – another kind of traffic monetization that exposes visitors to potentially malicious websites and advertisements.
Get rid of the infection effectively
Since Mac's defenses are relatively useless when it comes to most Adload versions, there is another way out here – using third-party software like SpyHunter 5Combo Cleaner or Malwarebytes. Anti-malware can quickly and easily find all the malicious components at once and get rid of them easily for you. If you insist on eliminating the virus manually, you can use the instructions below, although keep in mind that, if incorrectly removed, the virus may come back. Also, if you choose the automatic option, please remember to clean your browsers as well – either by using FortectIntego or checking the manual steps below.
Remove the main app components
Malware would launch background processes as soon as it was installed to continue operating. Therefore, you should check Activity Monitor and end any dependent processes before moving further with the primary app's uninstallation.
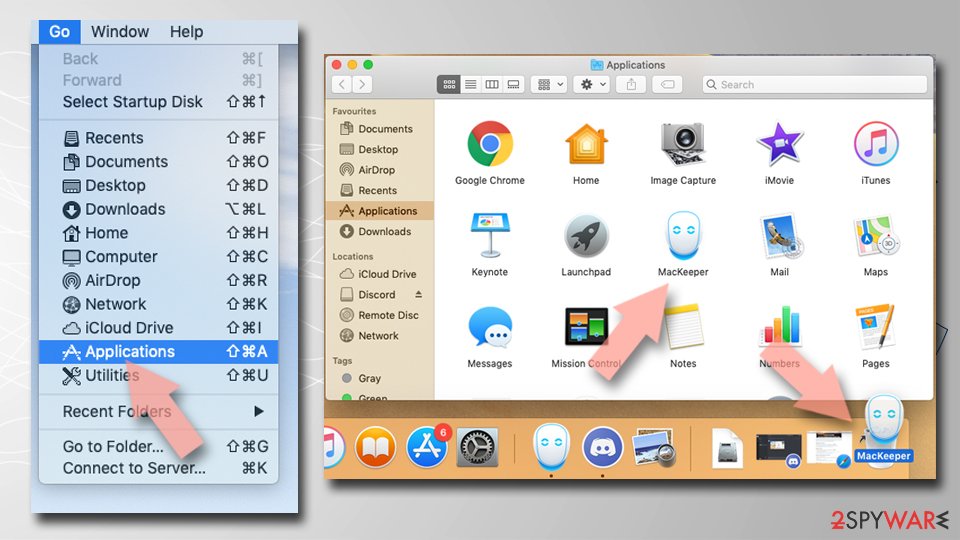
- Open Applications folder
- Select Utilities
- Double-click Activity Monitor
- Here, look for suspicious processes related to the virus and use the Force Quit command to shut them down
- Go back to the Applications folder
- Find the malicious app in the list and move it to Trash.
While Profiles take care of various account settings, Login items are in charge of running the malicious program as soon as the machine turns on. To remove these malware-related components, do the following:
- Go to Preferences and pick Accounts.
- Click Login items and delete everything suspicious.
- Next, pick System Preferences > Users & Groups.
- Find Profiles and remove unwanted profiles from the list.
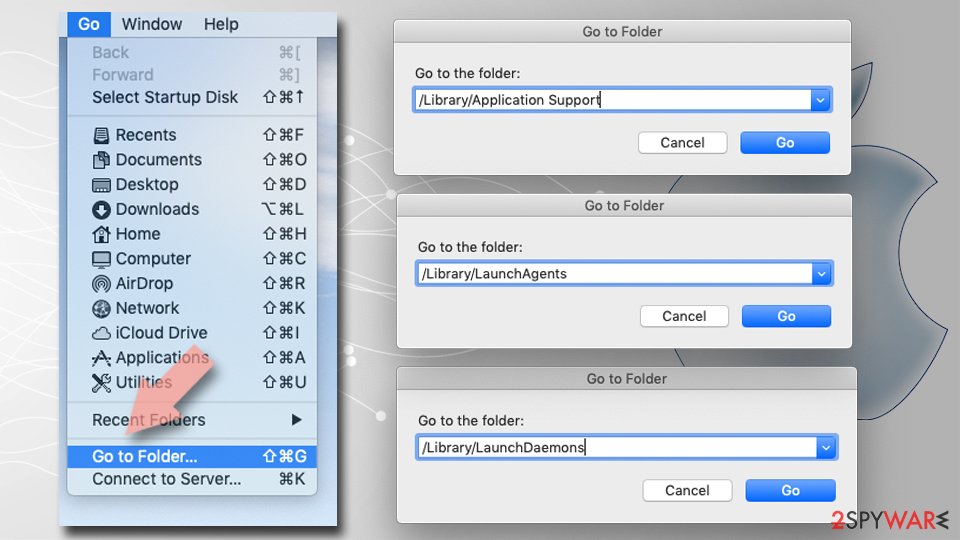
Finally, you need to remove any Launch Daemons and other configuration files that malware may have left behind.
- Select Go > Go to Folder.
- Enter /Library/Application Support and click Go or press Enter.
- In the Application Support folder, look for any dubious entries and then delete them.
- Now enter /Library/LaunchAgents and /Library/LaunchDaemons folders the same way and delete all the related .plist files.
Take care of your browser
If you have chosen a manual method of removal, you should take care of the OperativeIndexer extension, which is attached to your web browser. Keep in mind that it's used to read personal information such as account details or passwords, so make sure you don't leave it behind. If this step is not possible, proceed with the next one.
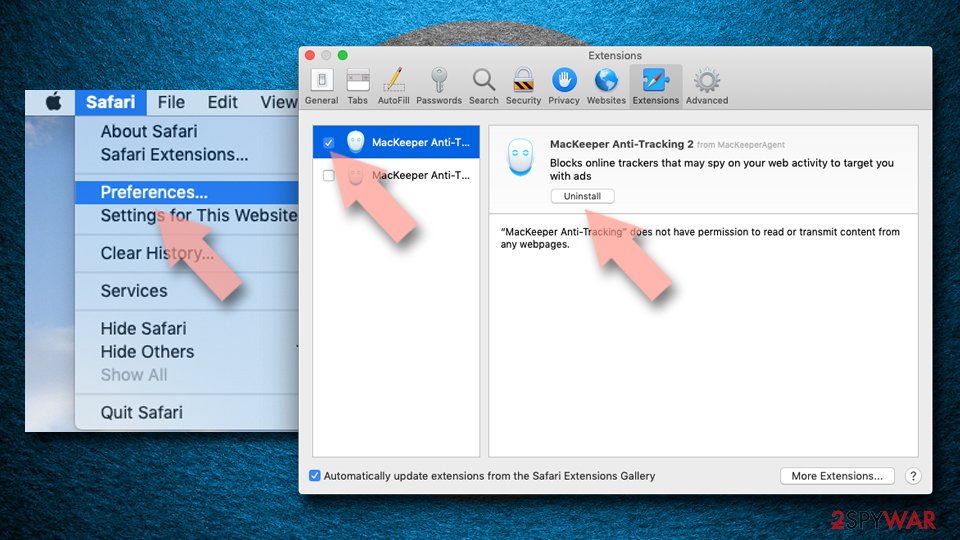
Safari
- Click Safari > Preferences…
- In the new window, pick Extensions.
- Select the unwanted extension and select Uninstall.
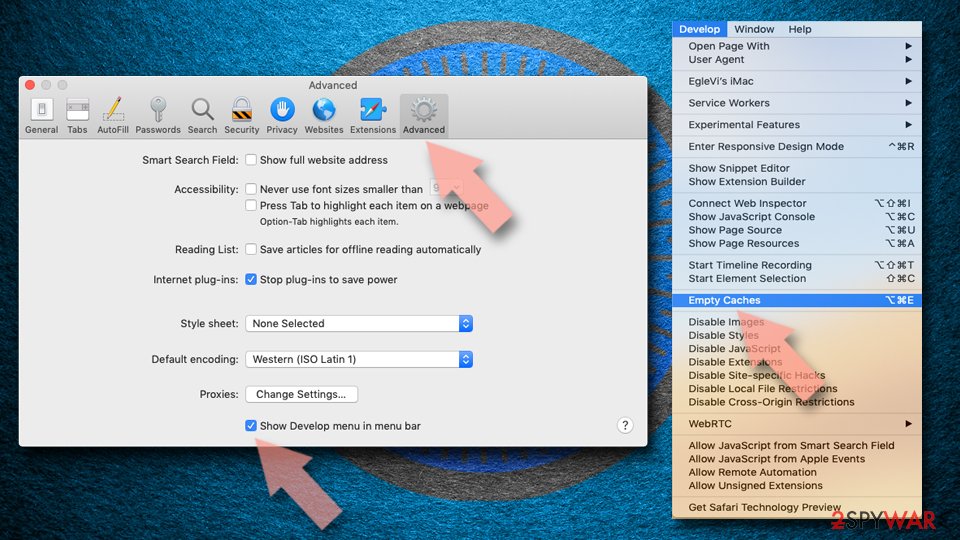
If you were unable to remove malware from your web browser, you might reset it as we describe below. You won't lose your bookmarks or other settings.
Safari
- Click Safari > Preferences…
- Go to the Advanced tab.
- Tick the Show Develop menu in the menu bar.
- From the menu bar, click Develop, and then select Empty Caches.
If you successfully removed the extension traditionally, you should also clear your browser caches to stop any more data from being tracked.
- Click Safari > Clear History…
- From the drop-down menu under Clear, pick all history.
- Confirm with Clear History.

Getting rid of OperativeIndexer Mac virus. Follow these steps
Remove from Google Chrome
Delete malicious extensions from Google Chrome:
- Open Google Chrome, click on the Menu (three vertical dots at the top-right corner) and select More tools > Extensions.
- In the newly opened window, you will see all the installed extensions. Uninstall all the suspicious plugins that might be related to the unwanted program by clicking Remove.
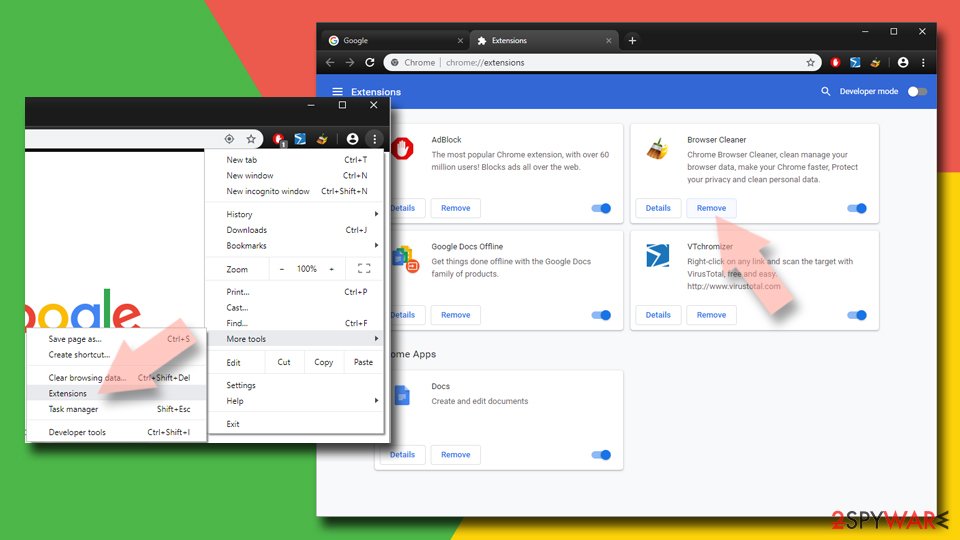
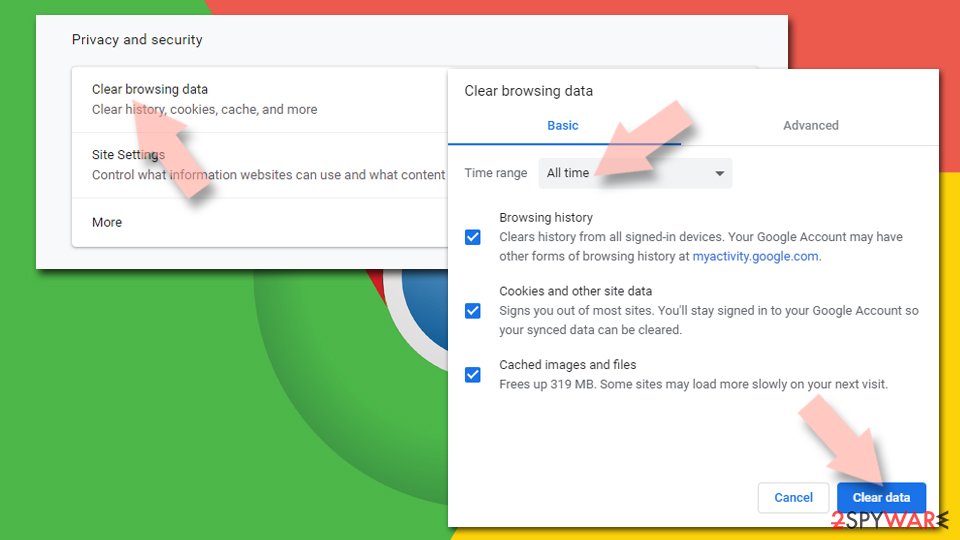
Clear cache and web data from Chrome:
- Click on Menu and pick Settings.
- Under Privacy and security, select Clear browsing data.
- Select Browsing history, Cookies and other site data, as well as Cached images and files.
- Click Clear data.
Change your homepage:
- Click menu and choose Settings.
- Look for a suspicious site in the On startup section.
- Click on Open a specific or set of pages and click on three dots to find the Remove option.
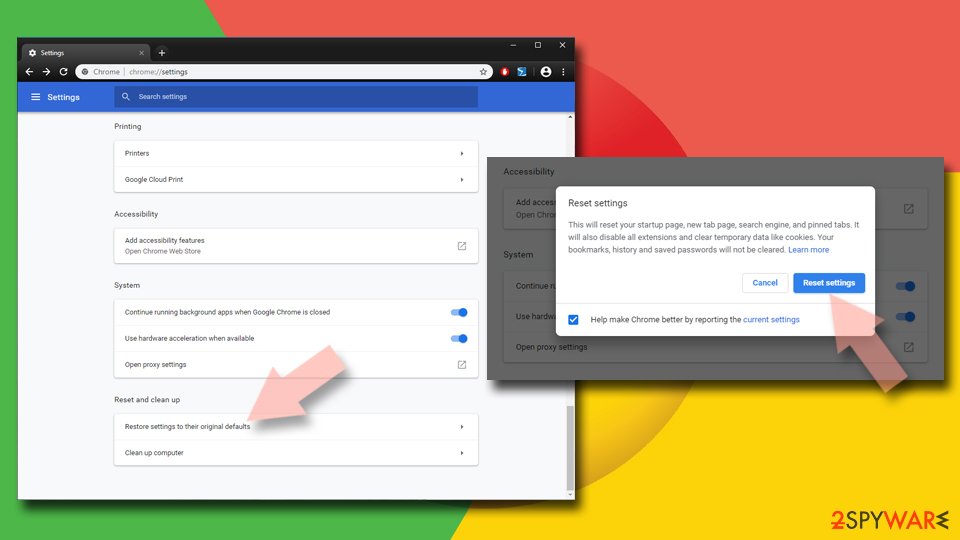
Reset Google Chrome:
If the previous methods did not help you, reset Google Chrome to eliminate all the unwanted components:
- Click on Menu and select Settings.
- In the Settings, scroll down and click Advanced.
- Scroll down and locate Reset and clean up section.
- Now click Restore settings to their original defaults.
- Confirm with Reset settings.
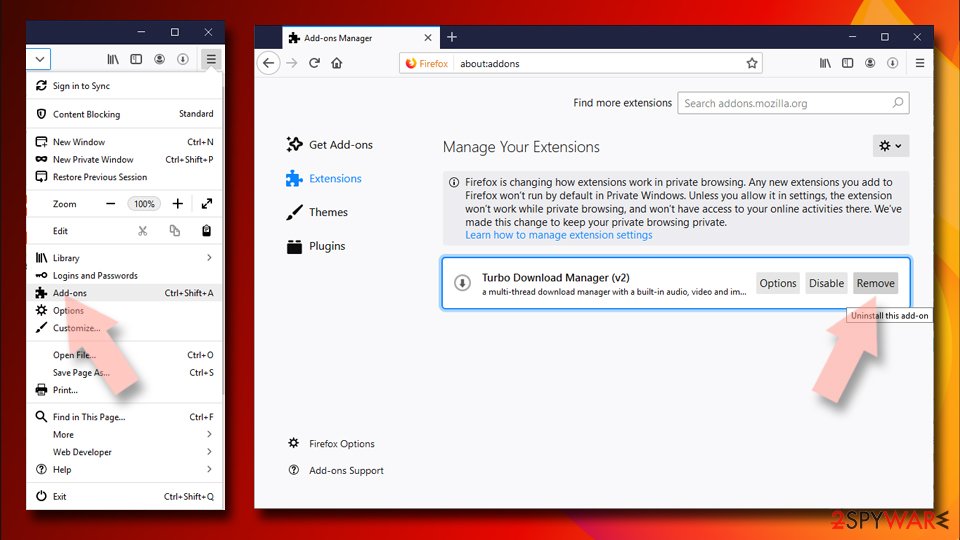
Remove from Mozilla Firefox (FF)
Remove dangerous extensions:
- Open Mozilla Firefox browser and click on the Menu (three horizontal lines at the top-right of the window).
- Select Add-ons.
- In here, select unwanted plugin and click Remove.
Reset the homepage:
- Click three horizontal lines at the top right corner to open the menu.
- Choose Options.
- Under Home options, enter your preferred site that will open every time you newly open the Mozilla Firefox.
Clear cookies and site data:
- Click Menu and pick Settings.
- Go to Privacy & Security section.
- Scroll down to locate Cookies and Site Data.
- Click on Clear Data…
- Select Cookies and Site Data, as well as Cached Web Content and press Clear.
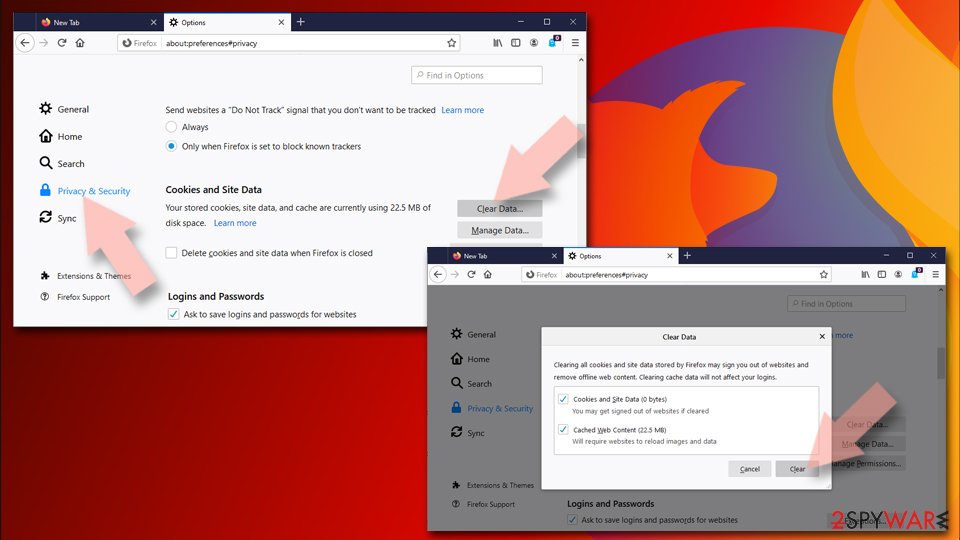
Reset Mozilla Firefox
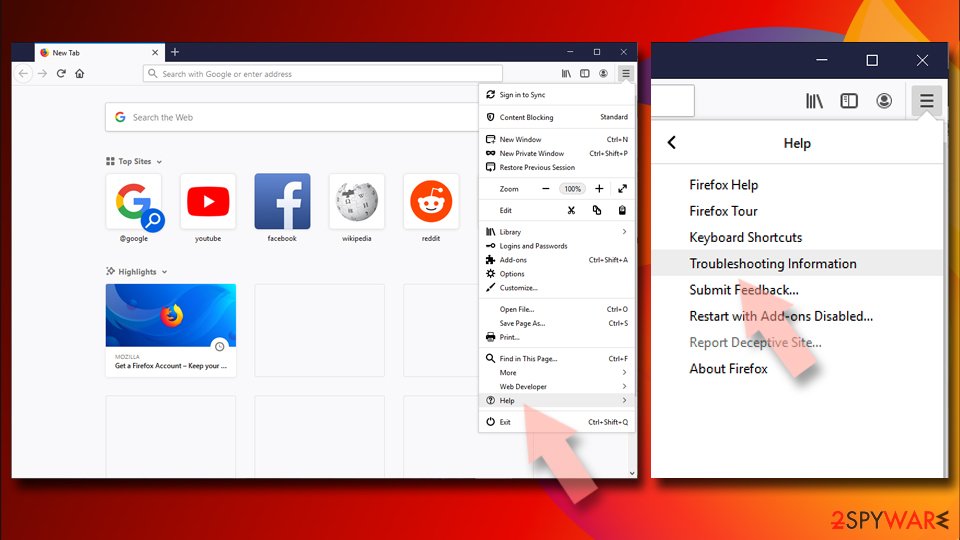
If clearing the browser as explained above did not help, reset Mozilla Firefox:
- Open Mozilla Firefox browser and click the Menu.
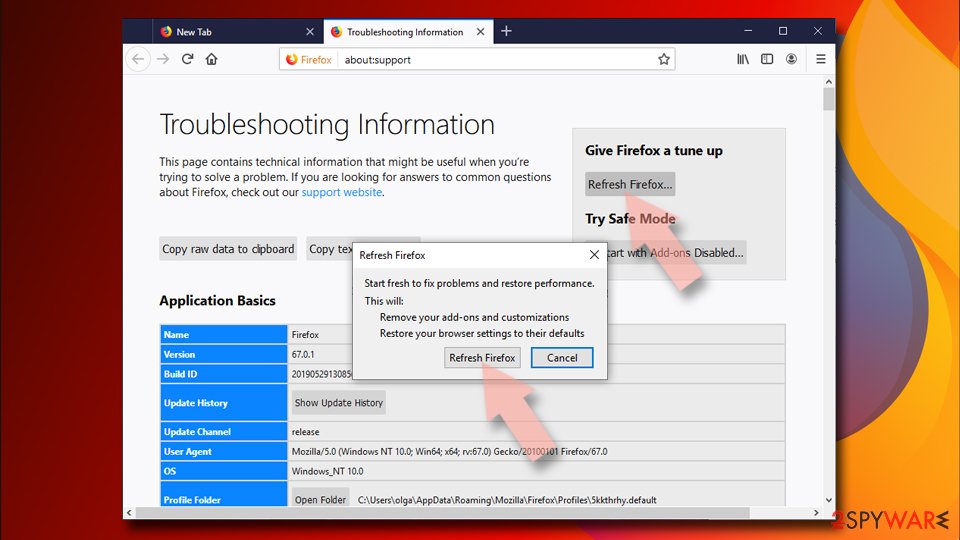
- Go to Help and then choose Troubleshooting Information.
- Under Give Firefox a tune up section, click on Refresh Firefox…
- Once the pop-up shows up, confirm the action by pressing on Refresh Firefox.
How to prevent from getting adware
Stream videos without limitations, no matter where you are
There are multiple parties that could find out almost anything about you by checking your online activity. While this is highly unlikely, advertisers and tech companies are constantly tracking you online. The first step to privacy should be a secure browser that focuses on tracker reduction to a minimum.
Even if you employ a secure browser, you will not be able to access websites that are restricted due to local government laws or other reasons. In other words, you may not be able to stream Disney+ or US-based Netflix in some countries. To bypass these restrictions, you can employ a powerful Private Internet Access VPN, which provides dedicated servers for torrenting and streaming, not slowing you down in the process.
Data backups are important – recover your lost files
Ransomware is one of the biggest threats to personal data. Once it is executed on a machine, it launches a sophisticated encryption algorithm that locks all your files, although it does not destroy them. The most common misconception is that anti-malware software can return files to their previous states. This is not true, however, and data remains locked after the malicious payload is deleted.
While regular data backups are the only secure method to recover your files after a ransomware attack, tools such as Data Recovery Pro can also be effective and restore at least some of your lost data.
- ^ Graham Cluley. Fake Adobe update really *does* update Flash (while also installing cryptominer). Tripwire. The State of Security blog.
- ^ What Is Browser Hijacking?. Kaspersky. Cybersecurity research.
- ^ Man-in-the-middle attack. Wikipedia. The free encyclopedia.
