How to remove browser plugins
Browser plugins can be useful, although you shouldn't trust all of them

A browser plugin (or a browser plug-in) is a computer application that expands a web browser’s functionality by adding extra features to it. It is installed within the browser environment, so it rarely alters system files, although it does depend on what the app is equipped with and how it is engineered.
A plugin is usually a small unit of software produced to allow users to customize their web browsing experience based on their preferences. While in many cases, they are used to add certain features, some of them are used to remove elements within the browsing environment. For example, ad-blockers are excellent tools to prevent intrusive ads from showing up on most websites.
Just as with any program that can be installed on the system, browser plugins can also result in a negative user experience, mainly due to marketing and ads they may bring. Besides, data tracking of such potentially unwanted applications is also relatively common. Reading Privacy Policy and EULA can often inform users whether the add-on has some type of unwanted features they rather not deal with.
Since there are almost 200 thousand add-ons on Google Web Store alone, deciding which ones should be trusted and which ones shouldn't might not always be an easy thing to do. Some add-ons require permissions to be established within the web browser environment in order to operate, and some of them can ask for a lot, e.g., permission to read and change all the information on users' visited websites.
Some of such apps are invisible to users, as they run in the background and do not have any graphical interface. However, most of them cannot be missed. Some of their functions can be malicious. Browser plugins are divided into two categories:
- Potentially dangerous or malicious.
- Useful add-ons that enhance user experience.
Malicious versions of browser plugins are very similar to spyware, adware, and browser hijackers and often have some of their functions. They can be installed without the user's consent and then fail to provide an uninstall feature. Some versions of malicious apps are integrated into legitimate toolbars and other additional tools, which often help them trick PC users into ignoring their existence and leaving them in the system.
Legitimate browser plugins are not only harmless but also very useful. The perfect examples of legitimate ones are popular apps like Google Toolbar, MSN Search Toolbar, Ad-block, Macromedia Flash, or Adobe Acrobat Reader.
Differences between legitimate and malicious browser plugins
Legitimate browser plugins act as they should and can help people by adding specific features to an existing computer program (web browser). However, installing a malicious app can cause these unwanted and dangerous activities:
- The appearance of additional web browser plugins and toolbars on the system. Typically, they are filled with particular, mostly dangerous, features.
- Changes in the default search engine and the home page without asking any user's permission.
- Installation of additional web browser buttons and completely altered bookmarks/favorites list.
- The appearance of numerous links, banners and similar content in various Internet resources.
- Web browser redirects to a predefined website whenever the user enters his/hers desired address. Redirects can also be caused by showing commercial pop-up ads.
- The loss of non-personally identifiable data. The malicious web browser plugin can track users' browsing habits, gather information about their interests, mostly visited addresses, and other activities. Collected data is sent to a remote server.
- Serious problems related to overall stability and performance of the web browser.
To sum up, most examples of malicious web browser plugins complicate users' web surfing activity. They can redirect them to undesirable websites, display many annoying commercial advertisements, block access to certain Internet resources, and so on. Although such behavior is not harmful, the user may be unable to find the required information.
Besides, some versions of malicious browser plugins affect the system and software that is installed on it. They cause web browser instability issues, frequent errors, and overall performance problems. Some reputable applications and legitimate browser add-ons may also be affected by such activity. Malicious browser plugins can affect Internet Explorer, Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Safari, and other known web browsers.
Installing a malicious version of browser plugin on computer
Malicious versions of browser plugins do not spread like regular viruses. They do not rely on Trojan horses and similar malware when they seek to infiltrate the system. However, they can also appear on your computer out of nowhere. This can be implemented with the help of four major ways:
- Some vendors of malicious browser plugins deceive users by presenting their products as very helpful and reliable tools, for example, a powerful web search service or a reliable pop-up blocker. Users download and install such plugins thinking that they seek to improve their browsing experience. However, practically all of them appear to be not only completely useless but also potentially dangerous.
- There are lots of free programs that are bundled with malicious browser plugins. They are presented as useful additions to the software. Uninstalling the host application not always removes bundled threat.
- Adware, browser hijackers, and similar PUPs can be used for promoting third-party browser plugins. They can be silently installed on the system and then used for malicious activity.
- Some part of dangerous browser plugins can get into the system using Internet Explorer ActiveX controls or by exploiting certain web browser vulnerabilities. Their vendors rely on hazardous websites filled with malicious code or unsafe pop-ups. Whenever the user visits such a site or clicks on such a pop-up ad, a malicious script is instantly installed on the system. The user cannot notice anything suspicious, as a threat does not display any setup wizards, dialogs, or warnings.

The most popular examples of malicious browser plugins
There are lots of different browser plugins that are considered malicious. The following examples illustrate how harmful these threats can be.
Total Dating Guide is one of the trickiest browser plugins that claims to be capable of improving people's browsing sessions. It can easily appear on your computer without downloading it as it has been actively spreading in a bundle with freeware and shareware. Once this toolbar enters the system, it offers a web search service and “useful” navigation buttons to such pages as Weather, Entertainment, or News. However, its ad-supported version can also modify your search results and display undesirable commercial advertisements.
Boggles.co is a third-party web browser plugin compatible with Internet Explorer, Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, and other web browsers. The program claims to be a reliable search site, but all that it does is recording the most visited websites, logging the users' search sessions, and collecting information about their computer and installed software. Gathered data is sent to a remote web server. Boggles.co can update itself via the Internet without users' permission asked. The threat runs on every Windows startup.
Istbar is a suspicious browser plugin designed to redirect people to unwanted and sometimes even dangerous websites. This web browser plugin has been actively used to promote Internet sites filled with adult-oriented content and similar dangerous content. In most cases, it spreads around as an optional component of third-party software, so it can be installed without noticing that. It does not have the uninstall feature.
Removing the malicious browser plugin from the system
Malicious versions of browser plugins are quite similar to malware and similar threats. They can infiltrate a computer without the user's approval, they can install related software, collect various information and cause unwanted activity on it. In most cases, the malicious browser plugin cannot be removed with the help of the manual removal option.
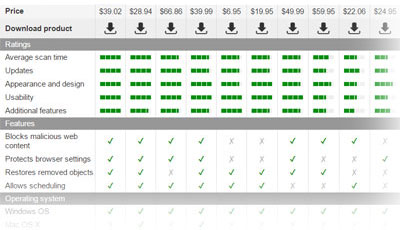
To remove suspicious versions of browser plugins, we recommend using reputable anti-spyware tools. These programs similarly scan the system as antivirus software does and then report malicious files. However, they have special parasite signature databases that allow them to detect and eliminate most security and privacy risks. In addition, they include real-time monitors that prevent the installation of additional viruses.
In some cases, even a spyware remover can fail to get rid of a particular parasite because of its updated database. Such a trick has been actively used by most malware developers. In this case, manual removal is recommended.
Latest browser plugins added to the database
Removal of YTube AdSkipper adware
Uninstalling Massive Engine.exe virus
Delete Controller browser extension
Information updated: 2021-06-03