Christmas virus (Removal Guide) - Free Instructions
Christmas virus Removal Guide
What is Christmas virus?
Christmas virus is a set of cyber infections that are related to festive period

Christmas virus is a term used to describe multiple different cyber threats that are related to Christmas. Therefore, the array of infections can vary, including worms, ransomware, trojans, as well as social engineering[1] attacks via emails and social networks. The variety of viruses have a different goal, but, nevertheless, most of them are malicious and should be avoided at all costs. The majority of Christmas viruses are spread with the help of spam emails, although other propagation methods, like fake updates, can be used as well. In this article, we will go through most common Christmas-themed malware and ways to avoid it.
| Summary | |
| Name | Christmas virus |
| Type | Malware |
| Sub-types | Ransomware, worm, trojan, scam, etc. |
| Infiltration | Spam emails, although can use brute-force attacks, fake updates, malicious executables, etc. |
| Symptoms | Vary, depending on the infection |
| Elimination | Use anti-malware software like FortectIntego or SpyHunter 5Combo Cleaner |
Because the term describes multiple different infections, there are different ways of dealing with it. However, the best way to remove Christmas virus is by employing reputable security software that can detect and clean the system from malicious software. We highly recommend using FortectIntego or SpyHunter 5Combo Cleaner for the job, although any other powerful anti-malware tool should do the job.
Some infections, such as ransomware, leave the devastation behind, even after victims remove Christmas virus. Ransomware locks up personal data and demands a ransom to be paid for its release. Thus, file recovery needs to be performed in order to get access to the encoded data.
Below are some of the examples of Christmas virus, and we hope that you will be able to protect your privacy and online security this Christmas with the help of this article!
Christmas-themed malware examples
Christmas Tree EXEC
The very first holiday season malware appeared back in 1987 when a German student who initially claimed that he only wanted to wish Season's Greetings to friends. The worm, written in Rexx language,[2] used to be sent to an inbox with the subject line “Let this exec run and enjoy yourself!”, and, once the victim typed CHRISTMAS as instructed, the virus sent drew a Christmas Tree as text graphics, and sent out its copies to everybody in the target's contact's file. Ultimately, the Christmas Tree EXEC worm managed to paralyze international networks, and some 350,000 machines were shut down by IBM.
WM97/Melissa-AG or Prilissa
Prilissa is one of the old Christmas viruses, that was first detected back in 1999. It is as well propagated with the help of spam emails with the subject line “Message from [username].” The malicious DOC file, once executed, infects the machine with malware that would trigger on 25th of December.
Prilissa opens pop-up windows, inserts randomly colored squares into the opened MS Word document, and attempts to wipe out the C: drive upon next reboot.
The Maldal virus
The Maldal virus was injected into victims' machines once they opened a Christmas.exe file. The phishing email came with “Happy New Year” subject line and seemed like a Season's Greetings electronic card, which most people fell for.
Once executed, the malware opened a window that displayed a Santa Claus with a reindeer, sliding on his skis with a message at the bottom:
From the heart, Happy new year!
Koobface worm
Koobface malware was targeting users of social networks like Facebook, Skype, Twitter, and redirected victims to a spoofed Santa-themed web page. Soon after the infiltration, it starts its malicious activity – it is capable of stealing login information of various accounts, as well as banking information, which can result in money loss for victims.
Additionally, Koobface forms a peer-to-peer botnet[3] that propagates the malware even further.
MerryChristmas ransomware

MerryChristmas ransomware is a file locking virus, as well as data stealing malware[4] that first appeared in January 2017. While it is strange that malware with such name appeared in January, it is believed that it is of Orthodox origin, as Christmas is celebrated on 7th of January.
The virus was distributed with the help of spam campaign – one came from the alleged Federal Trade Commission, while the other one pretended to be a notice from the court. The email embedded a hyperlink that downloaded a zip file disguised as a PDF document.
As soon as the machine gets infected, all personal videos, music, pictures and similar files are encoded, and an appendix is added. Additionally, users can view a ransom note that shows Santa Claus from Futurama and displays a timer. Allegedly, after it expires and no payment in Bitcoin will be transferred, all the data on the machine will be erased. Nevertheless, users should not pay the ransom and instead use official decryptor that is available to download on our main article page.
Stay away from Christmas gift and similar scams
Low profile cyber criminals and people who want an easy profit often rely on scams. The following are most prominent Christmas virus scams that should not be overlooked this Christmas.
Christmas Day Bonus Gift email virus
Christmas Day Bonus Gift email virus is a spam email campaign that aims to distribute a data-stealing trojan Ursnif.
Users receive an email into their inboxes that claims that they are entitled to a Christmas bonus. In order to claim it, they are meant to click on a provided link. As soon as they click on the link, they are led to a Google doc, which is an executable file. Once executed, it will install Ursnif trojan that can record keystrokes, system information, and other sensitive data.
The Secret Sister Gift Exchange scam
This Christmas scam has been active since 2015,[5] and it seems like it is not going away three years later. The hoax is prevalent on social media platforms like Facebook or Twitter. It operates a “pyramid scheme.” It promises that you will be able to receive 36 gifts in exchange for just one. While it sounds too good to be true, it really is.
In reality, it is merely a scam that asks victims to send $10 via the spoofed website. Do not participate in The Secret Sister Gift exchange scam, and rather buy presents who you actually care about this festive season.

Amazon scams
Amazon scams, such as Amazon Gift Card, Amazon Membership Rewards, Congratulations Amazon User and many others, are designed to trick people into either providing sensitive information that can be used for marketing purposes, or installing bogus software, subscribing for useless services, and such. Ultimately, users end up wasting money and simply being scammed by cyber crooks.
The most recent Amazon scam which you might encounter while shopping for presents is masked as an email coming from the industry giant itself. Allegedly, users are informed that a Prime membership was purchased, and, in order to cancel it, they have to log in using their Amazon account credentials. As evident, bad actors' goal is to get access to the official account.
Extortion scams
Extortion scams have been extremely prevalent since mid-2018, and the number of users reporting these incidents increased drastically. Initially, sextortion scams were employed for blackmail. The crooks claim that they injected malware into the targeted computer, which allowed them to record users via the camera while they were watching porn online.
Crooks typically use information that was obtained from previous data breaches (such as email address and password) to make the hoax email more believable. Malicious actors ask users to pay a certain amount of Bitcoin, or else the recorded shameful videos would be sent to victims' friends and family.
The most recent scam evolves bomb threats and asks users to pay as much as $20,000 in order to save hundreds of people from bomb's detonation.[6]
Christmas virus distribution methods
As evident, the main culprit in Christmas virus distribution is the fake emails. Users are sometimes redirected to a malicious website via a hyperlink or click on an attachment that holds macro scripts. We suggest you follow these simple tips if you want to avoid being tricked by a phishing email:
- Do not jump into the email contents straight away. First, example the email address of the sender, as well as the subject line. These two simple checks might straight away disclose the deception. For example, an email from customer.support@amazonn.com might be easily interpreted as an original one.
- The contents of the email might look very legit, with correct logos and formatting. However, make sure you carefully read through it and make some conclusions. You can ask yourself these questions: “why did this company send me an email? was I expecting it?.” In some cases, you will answer yes, but then you should proceed with the more advanced examination.
- Phishing emails usually contain a link or n attachment that might be disguised as a .pdf, .doc, .txt, .html, and other documents. Before opening them, make sure you scan them using reputable security software.
- When it comes clicking on hyperlinks, hover your mouse over it and see where it is actually bringing you.
- Call the company that is trying to contact you or go to the official website, and use the email address provided there.
All in all, experts advise users to be vigilant, and always go by the rule “If it is too good to be true, it probably is.”
Get rid of Christmas virus and protect yourself from cyber infections in the future
In most cases, scamming attempts can be noticed straight away, as fake messages are usually littered with grammar and spelling mistakes, or terrible formatting. However, some hoax messages sent via Facebook or other platforms might seem legitimate, and some people might fall for the trick. To avoid such consequences, we suggest you search online for the information. Simply copy the first line of the email or message and search for it. There will be plenty of blogs, forums posts, articles, and similar data regarding the threat.
Do not forget that scam messages often trick users into installing viruses. In such a case, Christmas virus removal must be performed. However, because Christmas malware can be related to so many different threats, it's elimination instructions can differ. Nevertheless, the most optimal solution would be scanning your machine with security software like FortectIntego, SpyHunter 5Combo Cleaner, or Malwarebytes. The scans will find any malicious files embedded into the system and safely eliminate them.
In some cases, you can remove the Christmas virus manually. In case you installed bloatware[7] like Power System Care, MyShopcoupon, Safe PC Cleaner, and similar, you can get rid of all the files manually via the Control Panel (Windows) or Applications folder (macOS). Additionally, you might have to reset each of the affected browsers, such as Google Chrome, Internet Explorer, Mozilla Firefox, Safari, Opera, or others.
Nevertheless, if you are dealing with a severe Christmas virus infection, you should enter Safe Mode with Networking in case malware is interfering with AV engine's operation. Follow the instructions below.
Getting rid of Christmas virus. Follow these steps
Manual removal using Safe Mode
To remove Christmas virus from your machine safely, enter Safe Mode with Networking on your Windows device:
Important! →
Manual removal guide might be too complicated for regular computer users. It requires advanced IT knowledge to be performed correctly (if vital system files are removed or damaged, it might result in full Windows compromise), and it also might take hours to complete. Therefore, we highly advise using the automatic method provided above instead.
Step 1. Access Safe Mode with Networking
Manual malware removal should be best performed in the Safe Mode environment.
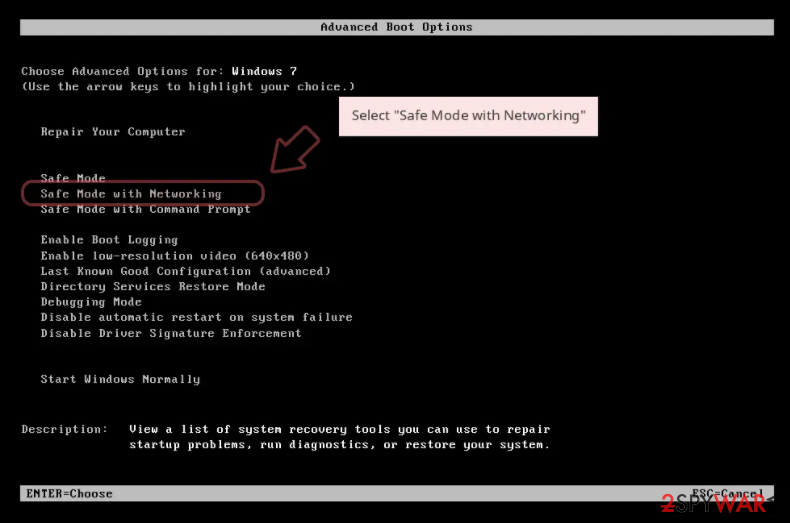
Windows 7 / Vista / XP
- Click Start > Shutdown > Restart > OK.
- When your computer becomes active, start pressing F8 button (if that does not work, try F2, F12, Del, etc. – it all depends on your motherboard model) multiple times until you see the Advanced Boot Options window.
- Select Safe Mode with Networking from the list.

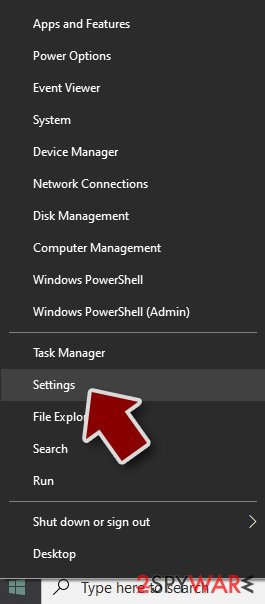
Windows 10 / Windows 8
- Right-click on Start button and select Settings.

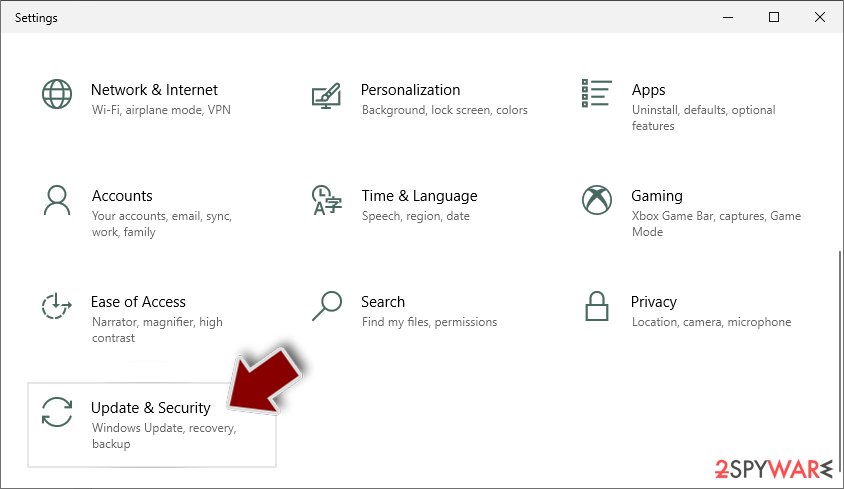
- Scroll down to pick Update & Security.

- On the left side of the window, pick Recovery.
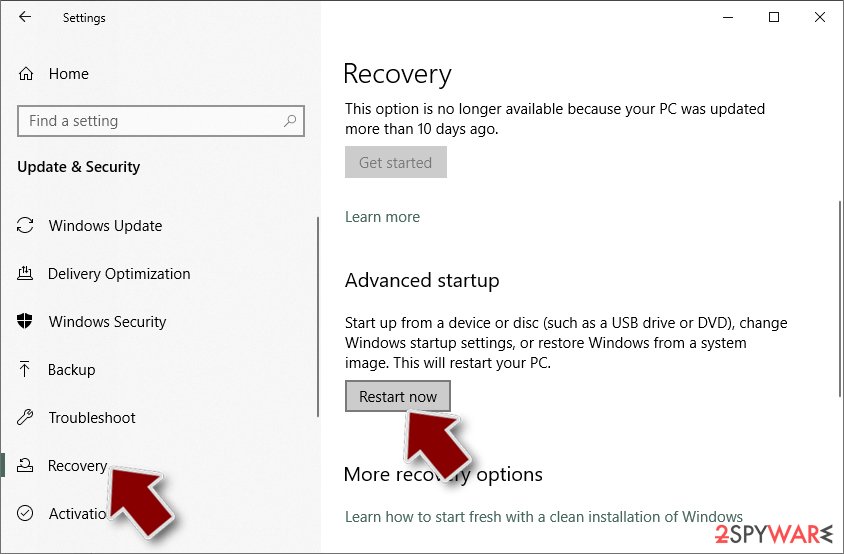
- Now scroll down to find Advanced Startup section.
- Click Restart now.

- Select Troubleshoot.

- Go to Advanced options.

- Select Startup Settings.

- Press Restart.
- Now press 5 or click 5) Enable Safe Mode with Networking.

Step 2. Shut down suspicious processes
Windows Task Manager is a useful tool that shows all the processes running in the background. If malware is running a process, you need to shut it down:
- Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc on your keyboard to open Windows Task Manager.
- Click on More details.

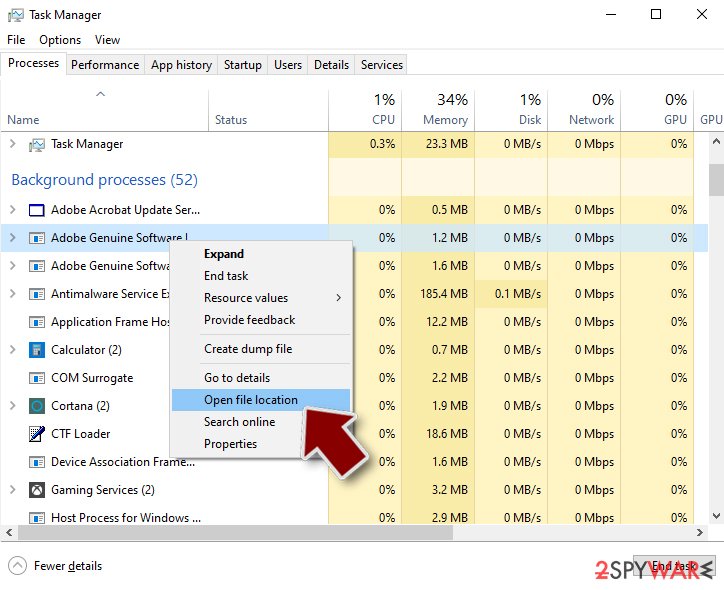
- Scroll down to Background processes section, and look for anything suspicious.
- Right-click and select Open file location.

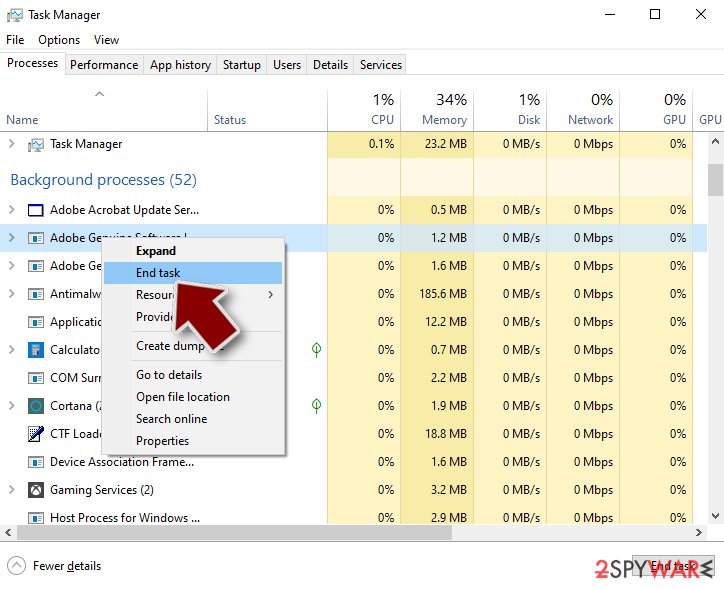
- Go back to the process, right-click and pick End Task.

- Delete the contents of the malicious folder.
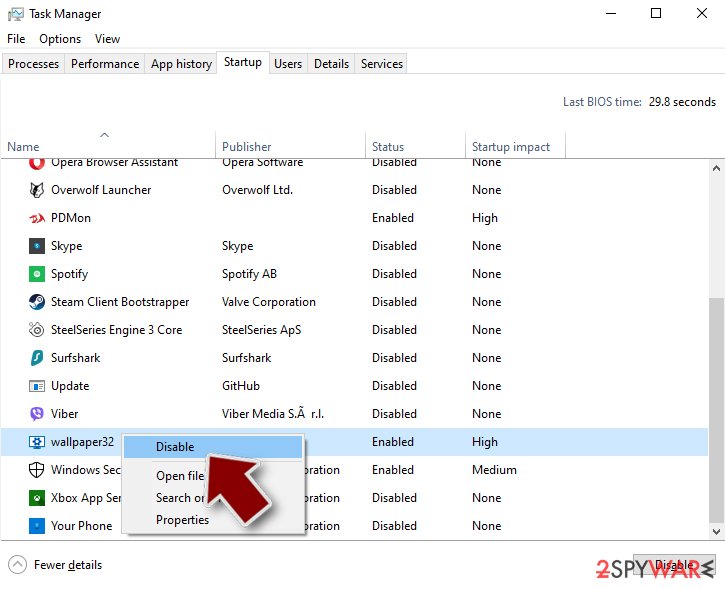
Step 3. Check program Startup
- Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc on your keyboard to open Windows Task Manager.
- Go to Startup tab.
- Right-click on the suspicious program and pick Disable.

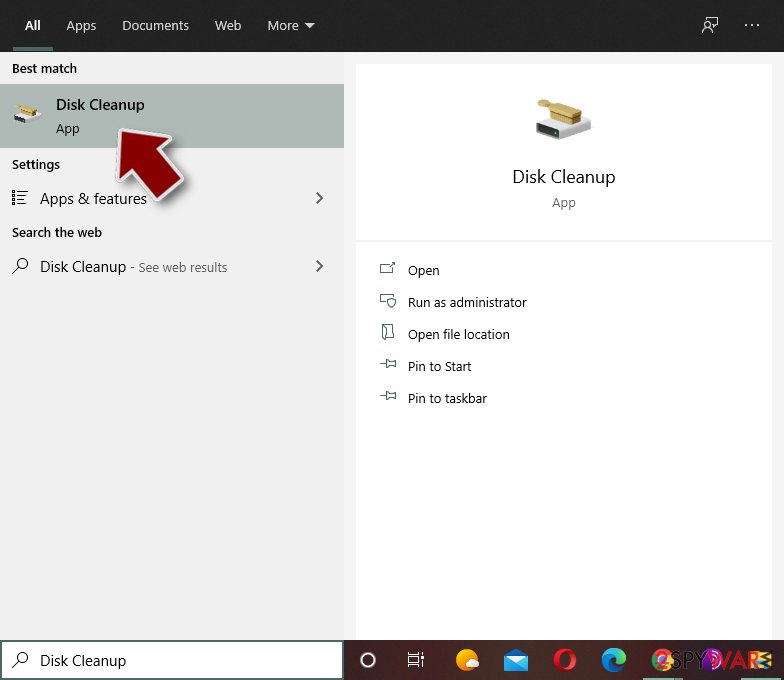
Step 4. Delete virus files
Malware-related files can be found in various places within your computer. Here are instructions that could help you find them:
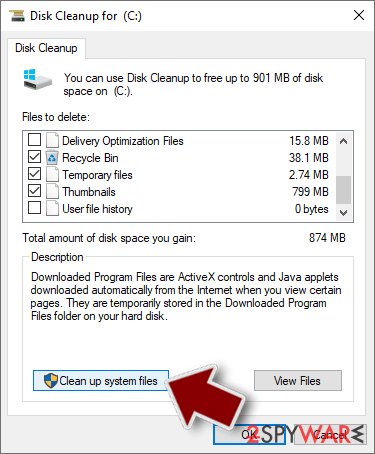
- Type in Disk Cleanup in Windows search and press Enter.

- Select the drive you want to clean (C: is your main drive by default and is likely to be the one that has malicious files in).
- Scroll through the Files to delete list and select the following:
Temporary Internet Files
Downloads
Recycle Bin
Temporary files - Pick Clean up system files.

- You can also look for other malicious files hidden in the following folders (type these entries in Windows Search and press Enter):
%AppData%
%LocalAppData%
%ProgramData%
%WinDir%
After you are finished, reboot the PC in normal mode.
Remove Christmas using System Restore
System Restore is also a very useful feature that might get rid of the Christmas virus:
-
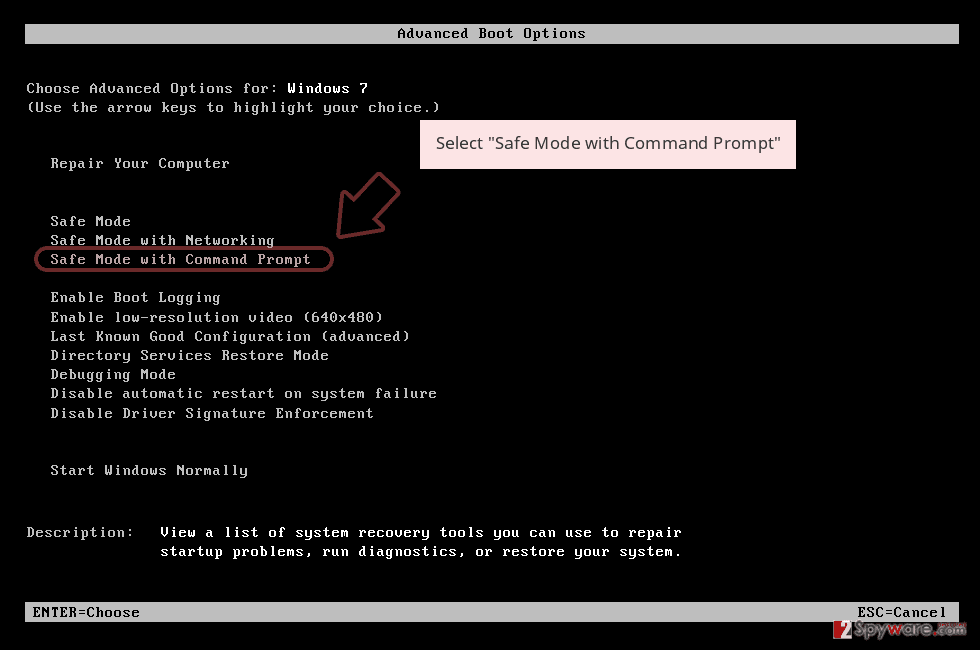
Step 1: Reboot your computer to Safe Mode with Command Prompt
Windows 7 / Vista / XP- Click Start → Shutdown → Restart → OK.
- When your computer becomes active, start pressing F8 multiple times until you see the Advanced Boot Options window.
-
Select Command Prompt from the list

Windows 10 / Windows 8- Press the Power button at the Windows login screen. Now press and hold Shift, which is on your keyboard, and click Restart..
- Now select Troubleshoot → Advanced options → Startup Settings and finally press Restart.
-
Once your computer becomes active, select Enable Safe Mode with Command Prompt in Startup Settings window.

-
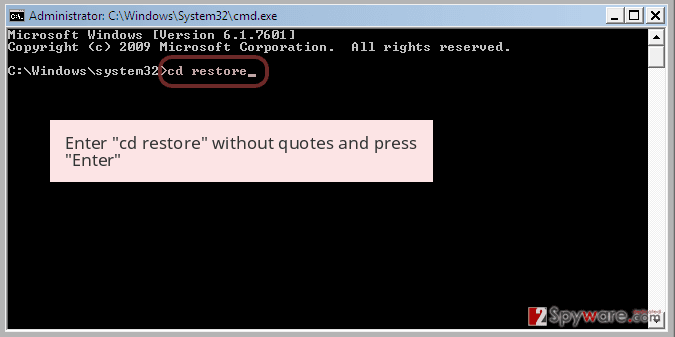
Step 2: Restore your system files and settings
-
Once the Command Prompt window shows up, enter cd restore and click Enter.

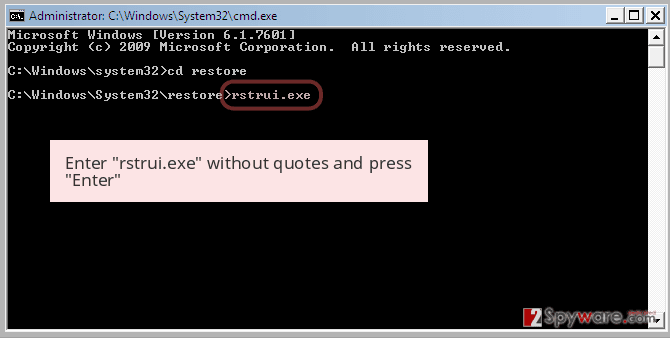
-
Now type rstrui.exe and press Enter again..

-
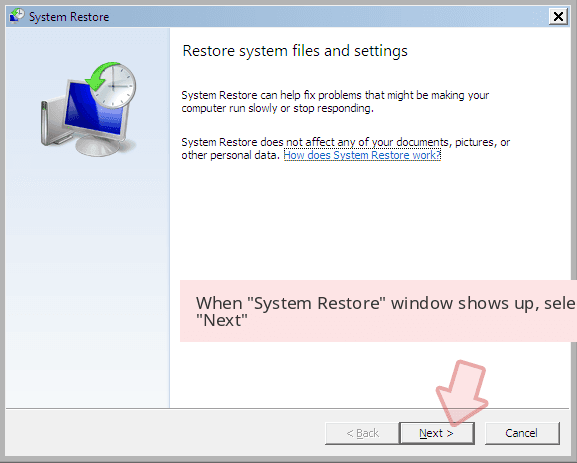
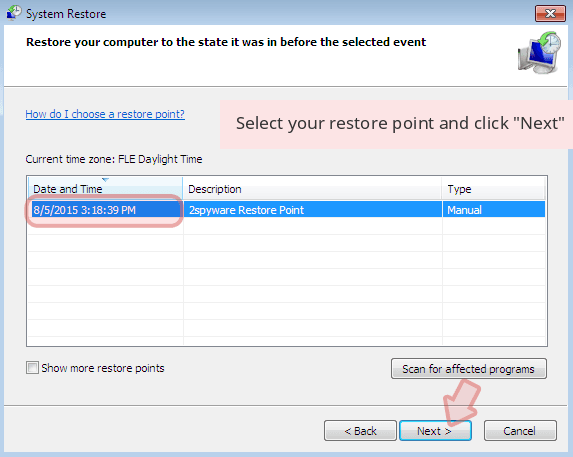
When a new window shows up, click Next and select your restore point that is prior the infiltration of Christmas. After doing that, click Next.


-
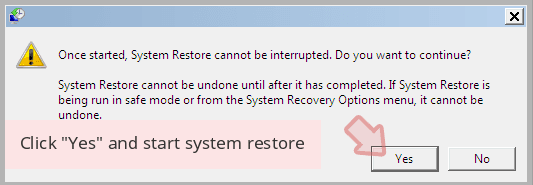
Now click Yes to start system restore.

-
Once the Command Prompt window shows up, enter cd restore and click Enter.
Finally, you should always think about the protection of crypto-ransomwares. In order to protect your computer from Christmas and other ransomwares, use a reputable anti-spyware, such as FortectIntego, SpyHunter 5Combo Cleaner or Malwarebytes
How to prevent from getting viruses
Stream videos without limitations, no matter where you are
There are multiple parties that could find out almost anything about you by checking your online activity. While this is highly unlikely, advertisers and tech companies are constantly tracking you online. The first step to privacy should be a secure browser that focuses on tracker reduction to a minimum.
Even if you employ a secure browser, you will not be able to access websites that are restricted due to local government laws or other reasons. In other words, you may not be able to stream Disney+ or US-based Netflix in some countries. To bypass these restrictions, you can employ a powerful Private Internet Access VPN, which provides dedicated servers for torrenting and streaming, not slowing you down in the process.
Data backups are important – recover your lost files
Ransomware is one of the biggest threats to personal data. Once it is executed on a machine, it launches a sophisticated encryption algorithm that locks all your files, although it does not destroy them. The most common misconception is that anti-malware software can return files to their previous states. This is not true, however, and data remains locked after the malicious payload is deleted.
While regular data backups are the only secure method to recover your files after a ransomware attack, tools such as Data Recovery Pro can also be effective and restore at least some of your lost data.
- ^ What is Social Engineering?. Webroot. Smarter Cybersecurity.
- ^ Rexx. Wikipedia. The free encyclopedia.
- ^ Margaret Rouse. Peer-to-peer botnet (P2P botnet). WhatIs. IT website.
- ^ Data Stealing Malware. Securebox. Data-protecting software.
- ^ Doug Bolton. Secret Sister Exchange: . Independent. Online British newspaper.
- ^ Ugnius Kiguolis. A new Bitcoin scam: bomb threats wreak panic in the US. 2-spyware. Cybersecurity news and articles.
- ^ Preston Gralla. Bloatware: What it is and how to get rid of it. Computerworld. IT news, careers, business technology, reviews.