Djvu ransomware virus. 36 variants listed
Djvu virus Removal Guide
What is Djvu ransomware?
Djvu ransomware – a malware family of over 350 members that expands weekly
Djvu is a crypto-malware variant that belongs to one of the most prominent ransomware families – STOP. The infections started spreading around in December 2018, and the success of the strain encouraged its developers to expand their operations and release sub-variants regularly. As soon as malware infects the host machine, it applies a proper AES[1] or RSA encryption algorithm (depending on the variant) to lock up pictures, videos, music, document, and other files.
Users can immediately spot the infection as all their files are appended with particular extensions that indicate the name of the virus, in most cases. To achieve a prompt result, the virus modifies various system files and deletes Shadow Volume Copies to prevent recovery, alters Windows registry entries and other system files to interfere with particular data recovery and security functions. It is also known that the virus created all alters host files to keep users from security sites and AV tool providers.
Note that numerous expert teams are working really hard on closing the virus, so you can store encrypted files and other data related to the cryptovirus on your computer and wait for the decryption tool. It is especially difficult and takes time, so rely on malware removal, do not expect to get your files back easily. This is a known family that keeps on releasing new versions every few weeks. The recent times show extremely active criminals because new versions come out pretty much every week. The most recent ones being Pahd, Paas, Ehiz, and Nusm, which share many similarities with the other ones released the same year.
Researches have disabled the previously known decryption tool STOPDecrypter that worked for many variants before August 2019. Some of the versions can be decrypted still but the fact that can indicate whether or not your files can get decrypted is online or offline keys. Victims' IDs get generated for each victim, so when online keys are used those IDs are unique for each person and the device. This means that there are tons of different decryption keys too.
When offline IDs are used, there are many similar IDs because there is no connection to the remote server and each version with the same file extension on encoded files has the same identification key. If you see t1 at the end of your ID in the ransom note, you may have the opportunity to get those files restored, but there are no Djvu decryption tools besides Emsisoft decrypter that works with offline keys only.
| Name | Djvu |
|---|---|
| Category | Ransomware |
| Appendixes | There are over 300 different file markers that the virus uses. Since 2019, malware applies a combination of four random letters as extensions to the encrypted files |
| Ransom message | Earlier versions used _openme.txt files; currently, _readme.txt ransom note name is used |
| Ransom | $490 to be increased to $980 after 72 hours |
| Recent versions | The list coves over 350 with the last versions being: .cool, .palq, .stax, .irfk, .qdla, .qmak, .futm, .utjg, .iisa, .pqgs, .yqal, .hudf, .xcmb, .miia, .vgkf, .zaqi, .maak, .qqqe, .qqqr, .bbbw, .bbbr, .maiv, .cuag, .eucy, .ooii, .kqgs, .xcvf, .bbnm, .egfg, .byya, .kruu, .ifla, .errz, .dfwe, .fefg, .fdcv, .nnuz, .qlln, .zpps |
| Contact | Hackers use several emails over the years; the most recent ones are helpmanager@airmail.cc and helpteam@mail.ch |
| System modification | The virus deletes shadow volume copies, modifies the registry, starts/stops various processes, modifies Windows “hosts” file, inserts data-stealing modules, etc. |
| Distribution techniques | Malware is mostly distributed via software cracks and pirated program installers on torrent and crack websites |
| Virus removal | Use anti-malware software, such as SpyHunter 5Combo Cleaner, Malwarebytes |
| Decryptable? | Some versions are decryptable. You can try this decryption tool to check if your versions are older or use the offline IDs. In some cases, recovery software might be useful |
| Repair process | FortectIntego program is required to fight malicious files and fix virus damage completely |
While, initially, it was not much known about this strain's distribution, researchers spotted that victims let the virus into their systems after downloading and executing the so-called software cracks or keygens. These tools allow users to use the paid software for free, although they are often laden with malware. These cracks and cheats are typically available on torrent sites and remain the main attack vector, especially for the last versions.
As soon as the encryption process is complete, users are introduced with a ransom note called _readme.txt or _openme.txt. The message from hackers claims that victims have to pay up for the file recovery tool that they would allegedly provide as soon as the payment (as a general rule, $980/$490 in BTC is asked) is processed.
Some of the first Djvu ransomware variants are entirely decryptable with the STOPDecrypter – a decryption tool created by Michael Gillespie. Later variants, however, might not be as easy to crack. Nevertheless, later versions can sometimes be decoded if the encryption process was performed when the malware could not contact its C&C server or the host machine was disconnected from the internet. Regardless of which virus version you are affected by, paying the ransom is never recommended, as the possibility of being scammed prevails.
After spreading on the Internet for several weeks, the ransomware came back with the Djvus virus version. It is the same file-encrypting virus that uses unique encryption[2] algorithms to lock up important documents that are found on the infected PC. In this case, the hackers are using the RSA encryption algorithm.
Even though the decryption might be hard to perform even for the highly-experienced users (you cannot guess this key or find it on the Internet), there is no need for rushing to pay the criminals. Note that these people often try to scam their victims by providing them false promises. We suggest taking a look at some data recovery methods that we have provided below this article.
No matter which virus version you are dealing with, the ransom warning stays the same. As you can see from the message body, no particular details about the money are given in the ransom note. However, victims have reported that they were asked to pay from $350 to $500 for the decryption of encrypted data:
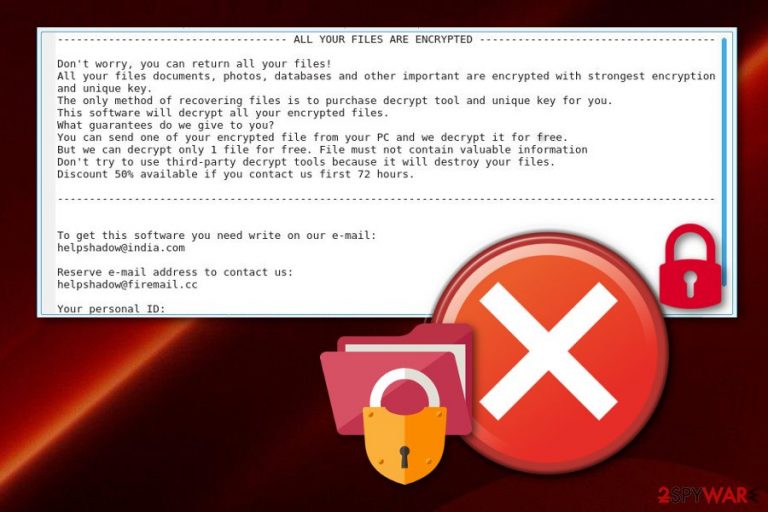
———————— ALL YOUR FILES ARE ENCRYPTED ————————
Don't worry, you can return all your files!
All your files documents, photos, databases and other important are encrypted with strongest encryption and unique key.
The only method of recovering files is to purchase decrypt tool and unique key for you.
This software will decrypt all your encrypted files.
What guarantees do we give to you?
You can send one of your encrypted file from your PC and we decrypt it for free.
But we can decrypt only 1 file for free. File must not contain valuable information
Don't try to use third-party decrypt tools because it will destroy your files.
Discount 50% available if you contact us first 72 hours.——————————————————————————————————-
To get this software you need write on our e-mail:
helpshadow@india.comReserve e-mail address to contact us:
helpshadow@firemail.ccYour personal ID:
Crooks who spread ransomware are exclusively asking for cryptocurrency as a payment for a decryption tool. The most popular demanded currency is Bitcoin,[3] as it is commonly used worldwide. Hackers urge this type of ransom because cryptocurrency transfers do not require any specific personal details, and because of that, the process remains completely untrackable. This lets the crooks scam victims easily without the risk of getting caught.
If you are seeking to recover your encrypted data, remove ransomware infection first before that. If you do not proceed with these actions in the right order, your files might be encrypted again after the next computer boot as the cyber threat will still remain in the computer system. Next time, make sure you take care of your data's safety properly. A piece of advice would be to store it on a remote server or device which is accessible only for you. This way, no other person will be able to reach that data.
Performing malware removal requires a lot of attention. That is why you need to leave the process for reliable anti-malware computer software. However, we suggest using a program such as FortectIntego to detect all malware-related content that might create issues in the PC system. If all hazardous components are successfully removed, the ransomware virus should not return to your computer after the process.
One more thing you need to know about this files virus: this file locker can inject malicious components anywhere in the system. Furthermore, it can clean paths for other malware to distribute easily, delete Shadow Volume Copies of encrypted documents, and add unwanted content to the Windows Registry.[4] Once you spot this threat, make sure you get rid of it ASAP.
To recover the encrypted files, try the STOPDecrypter from DemonSlay335. According to the researcher, the program is not ready to recover all encrypted files. At the moment, it works only for this personal ID: 6se9RaIxXF9m70zWmx7nL3bVRp691w4SNY8UCir0, which is generated while your computer is off. Take into account that if you try to add invented numbers can result in a complete loss of your encrypted data.
Ransomware infection process explained
Djvu ransomware infection progression is multi-stage, and there are several steps that it performs as soon as it is able to get into the machine's system. The primary executable installs into the LocalAppData[5] and then downloads several additional files: 1.exe, 2.exe, 3.exe, and pdatewin.exe. All of these executables serve different functions:
- 1.exe is used to disable various features and functionalities within Windows Defender. Additionally, the file launches a PowerShell script called Script.ps1 which disables Defender's real-time protection feature;
- 2.exe modifies Windows' HOSTS file by adding multiple security site URLs, preventing users from navigating there and seeking for help;
- 3.exe's functionality is not yet identified.
After these processes are complete, malware will contact the C2 server, providing hackers with the unique ID that is based on the victims' MAC address.[6] The remote server then responds with the encryption key used to encode all personal files. During data encryption, the virus launches a fake Windows Update window (spawned by pdatewin.exe) so that the victim would not suspect anything.
Finally, it will append the appropriate file extension, depending on the virus version. For example, a file called picture.jpg will be turned into picture.jpg.ytbn and will become inaccessible for users. Additionally, a ransom note is inserted into each of the affected folders.
Once the encryption process is complete, malware will create a scheduled task called Time Trigger Task that will periodically encrypt newly-added files.
Djvu virus versions
The notorious malware strain was first spotted on the internet at the late end of 2018. Since then, there have been many changes that happened to ransomware as a whole. Initially, cybercriminals were using seemingly random extensions that were appended to each of the locked files.
Since August 2019, when malware started using the more improved RSA encryption method, extensions also shifted and now use a combination of random four characters. It seems like the attackers are not going to change this method any time soon, although email addresses, as it is common within ransomware business operations, are changing regularly.
Djvus virus
This ransomware version came out right before the New Year. While virus developers haven't changed the virus much, we can see that the email address is nowrestoredjvu@firemail.cc. In addition, the virus is still offering 50% discount for those who contact its developers within 72 hours. Unfortunately, people have reported numerous cases when they found this virus on their computer system, cloud services, and even hard drives which were connected to the compromised system without much thinking. While some versions of STOP ransomware can be decrypted, unfortunately, this is not applied to the this virus.
Djvuu virus
This variant was discovered back in December 2018. As the name suggests, it is appending the previously mentioned extension to affect users' personal data. The ransom note displayed in a text file is still named _openme.txt and displays the message encouraging victims to contact these criminals via email and contact addresses: restoredjvu@india.com and restoredjvu@firemail.cc. This version is not decryptable, so you should use your files' backups to recover encrypted data. The virus is using RSA encryption method to make files useless. The private keys are stored on hackers' servers.
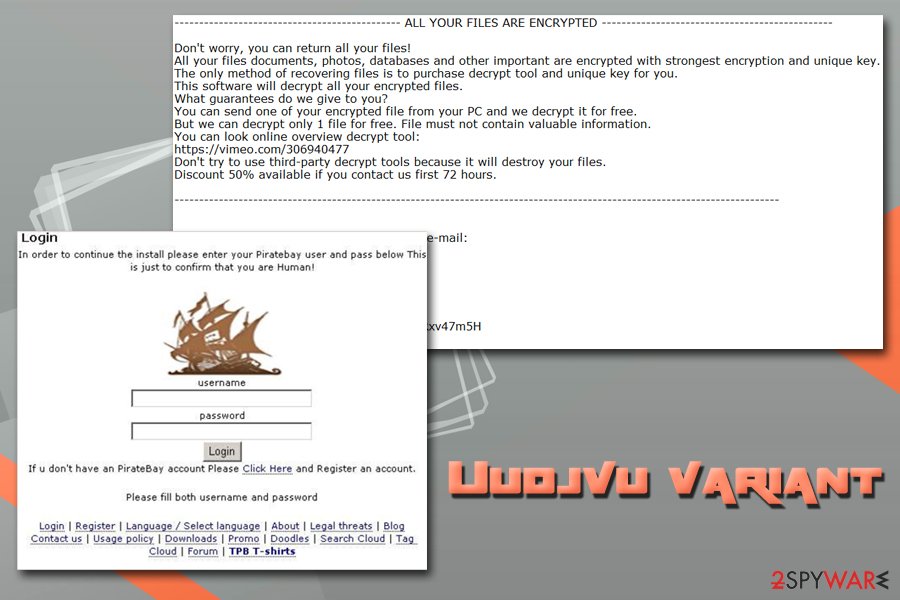
Uudjvu ransomware
Uudjvu ransomware is a slightly different version of the same virus that appears on the targeted system by using the common PirateBay setup window and this way attempts to steal user's credentials from various accounts to use them in later scams. Developers created this variant without a ransom demand but files on the computer still get encrypted by using AES and RSA mix. The affected part of the files is marked with .uudjvu file appendix. We don't recommend contacting hackers for their ransomware demands as you can be left with more damage on your computer. Remove the virus at first and then continue with the recovery of your files. Use backups or third-party software in this stage.
Djvuq ransomware
Djvuq ransomware is one of the versions that are more similar to the initial virus. It also encrypts files using the algorithm and marks encoded photos, documents, or even archives with .djvuq at the end. Ransom note, in this case, also gets placed in the _openme.txt file with the discount deal on the ransom and previously used contact emails restoredjvu@india.com and restoredjvu@firemail.cc.
Udjvuq ransomware
This ransomware also appeared in December 2018 following previous identical versions. Cybercriminals behind the threat still focus on the encryption and file marking process with extortion purposes. However, ransom note states about the only way to recover the files – pay up. According to developers, other decryption tools cannot give you the needed results, so they give you a half-off for the ransom if you contact them in the first 72h. These details alongside the same email addresses are delivered in the file _openme.txt.
Tfude ransomware
Tfude ransomware is one of the numerous versions of this strain. Being split into several versions as well (.tfude, .tfudeq, .tfudet), the virus is actively trying to overcome computers' protection and install its malicious executable. Once active, malware encrypts files and drops _openme.txt ransom note. Unfortunately, even if your computer is offline, the virus can still continue the encryption of your files.
Additionally, cybercriminals are asking to use pdfhelp@india.com or pdfhelp@firemail.cc email addresses to reach them for files' decryption. However, making any contact with these criminals can result in money loss. If your personal ID consists of these numbers, you should be capable of using the decryptor given at the end of this post: 6se9RaIxXF9m70zWmx7nL3bVRp691w4SNY8UCir0
Pdff ransomware
Pdff ransomware also uses AES encryption algorithm to encrypt files and was first spotted in January 2019 attacking computer users from the Middle-East. Nevertheless, the ransom note _openme.txt remains to be written in the English language and contains almost identical text that is typical for this virus infection.
However, this time crooks ask users to contact them with the help of pdfhelp@india.com and pdfhelp@firemail.cc email addresses. Another difference from the previous variants seems to be the file extension that is added – .pdff. While this version is not decryptable yet, we suggest you remove Pdff ransomware and use alternative file recovery methods.
Tro ransomware
Tro ransomware was observed on the web just a day after Pdff ransomware came out. It was spotted being distributed with the help of cracks, keygens, or bundled software that includes adware applications.
As soon as the virus enters the machine, it encrypts all the available data (skipping system files) with the help of a secure encryption algorithm and adds .tro file extension. This time it seems that the extension is the only difference compared to its previous versions, as the ransom note is called _openme.txt and the contact emails are pdfhelp@india.com and pdfhelp@firemail.cc.
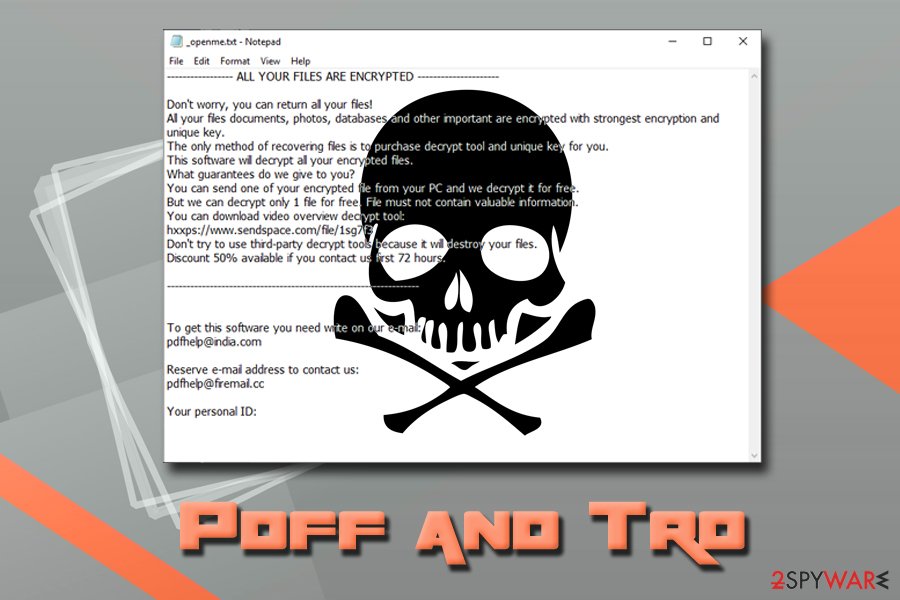
Adobe ransomware
.adobe file extension has first been introduced by an infamous Dharma ransomware. However, it was also adopted by other malware families. After some time, it was changed to .adobee. The virus is still using pdfhelp@firemail.cc as the default email address which should be used by victims to contact hackers for the ransom.
Unfortunately, no matter some of the previous versions can be recovered by using STOPDecrypter, .adobe hasn't been added to this tool's database yet. If infected, keep checking this post and hope that security researchers will soon find a cure for this malware.
Adobee ransomware
This one is familiar with the Adobe ransomware, however, with two e's (Adobee). It has the same operating principle. Once installed, the ransomware virus injects malicious content in the system and performs the encryption. After that, files appear with the .adobee appendix and are blocked from any access.
Additionally, Adobee ransomware, just like other virus versions, provides a ransom message named _openme.txt. The note shows up in the Notepad. Crooks urge for some money in order to receive the decryption tool. They provide pdfhelp@india.com and pdfhelp@ firemail.cc email addresses as a way to make contact.
Blower ransomware
Blower ransomware can enter the PC secretly just like others of its kind, for example, through infected hyperlinks, harmful attachments, etc. Once it is installed, rogue and harmful content is injected into the system and malicious activities such as data encryption are performed.
Blower is appending the .blower file extension to each encrypted file. This ransomware virus is capable of locking all kinds of data such as images, audio files, video, text documents, databases, excel sheets, PowerPoint, and others. Once the encryption is performed, crooks notify their users through a text message named _readme.txt. Two emails are provided in this message: blower@india.com, blower@firemail.cc. We suggest you avoid any contact with these cruel people.
Norvas ransomware
Norvas virus is a crypto-malware that is using the same _readme.txt ransom note to swindle the money from users worldwide. It is an easy task because before that the virus changes the code of target files and then appends the special extension called .norvas to every piece of data that was affected. In this case, files become useless and cannot be used as previously.
The developers of Norvas ransomware can be reached via vengisto@india.com and vengisto@firemail.cc email addresses. They also offer to provide the 50% discount for the ransom if they are contacted within 24 hours. However, do NOT believe these people as they are notorious scammers stealing users' money.
Grovat ransomware
Grovat is using AES-256 encryption code to make users' data useless. Additionally, the victim is required to make a special payment to a secret bitcoin wallet in exchange for the decryption code. Email addresses users are typically pointed to are called either merosa@india.com or merosa@firemail.cc. These addresses should be used to contact cybercriminals and get the bitcoin address for the payment. However, we do NOT recommend making any contact with these people.
To generate a unique identifier along with the decryption code assigned for each user, malware contacts its C&C server. The ransom note is called like any other used by other malware versions – _readme.txt. You should remove all files that belong to this malware instead of contacting cybercriminals. To recover your files, you can try using STOPDecrypter.
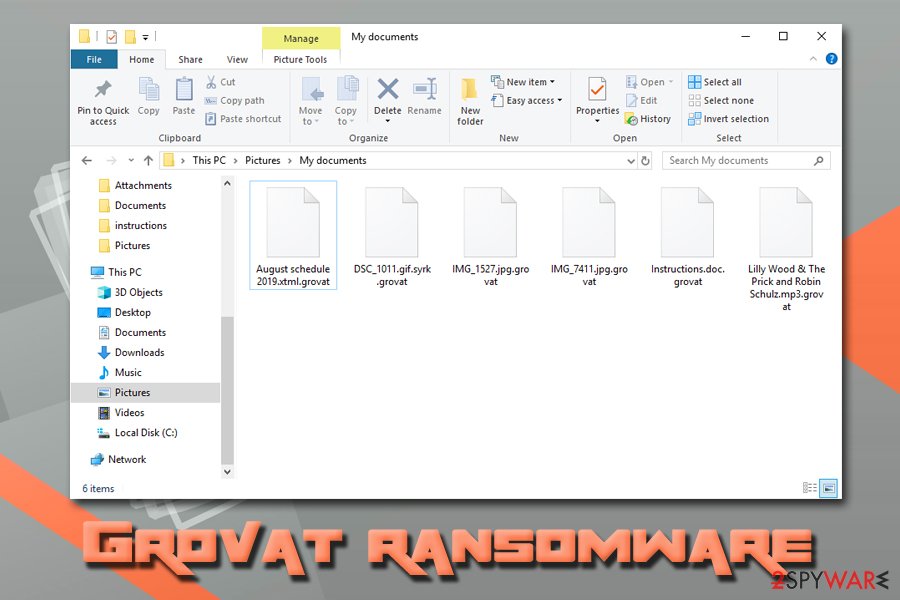
Verasto ransomware
Verasto was first spotted at the end of April 2019 and, since its release, it has been infecting hundreds of users all over the world, remains one of the most prevalent Djvu virus variants to date.
Just as its predecessors, Verasto ransomware uses various propagation techniques, including:
- Spam emails;
- Exploits;
- Software cracks or keygens;
- Fake updates;
- Backdoor,[7] etc.
After its infiltration, the malware scans the device looking for a variety of most popular file types, such as .jpg, .mpeg, .xlsx, .html, .zip, .php, and others, and appends .verasto markings. Nevertheless, the virus avoids encrypting the most crucial system files (although it does modify certain OS files and settings), along with executables as they are not considered to be valuable.
Unfortunately, data locked in such a way requires a unique key that is secured on a remote server controlled by hackers. They offer a decryption tool for a $980/$490 payment in Bitcoins. Experts recommend avoiding paying criminals, however, as the chance of getting scammed remains quite high. Instead, remove Verasto ransomware and use alternative data recovery methods as per the instructions below.
Hrosas ransomware
One of many versions in the family that came out in April 2019, Hrosas ransomware still includes the same emails as previous versions. vengisto@india.com, vengisto@firemail.cc remains the primary method to contact people behind this virus, and criminals provide another method – Telegram account.
Also, as typical for this family, ransom note comes in the text file _readme.txt and politely asks to pay up with the discount offer. Besides this version, on the same day, researchers discovered a file-locker virus that marks data using .kiratos extension, but not many samples got revealed and it may not be that widely spread as other ones.
Todarius ransomware
As known for a while, the STOP decryption tool worked for many versions, including the previous to this Todarius ransomware variant. However, many user reports and sample analysis revealed that there is a patch in the version, so decryption is not possible, unfortunately.
It seems that once the STOP decrypter is run, the extension changes to .kiratos, and 0 files are decrypted. it happens with a few updated versions of this tool, so it is allowed to say that .todarius file extension marked files are not decryptable. This and new email added to the mix – gorentos@bitmessage.ch, are the only unique features for the variant.
Hofos ransomware
Hofos ransomware came soon after the Todarius version, at the same time like .dutan and .roldat versions that remained not that active. However, the Hofos files virus was yet again unique than other ones, as user samples showed, marking the 74th version of the ransomware. It comes with the same already known ransom note file _readme.txt and recently renewed email addresses – vengisto@firemail.cc, gorentos@bitmessage.ch.
The distribution of the malware includes packs of software spread around in public torrent sites. Multiple users reported that particular subtitle packs and Sony Vegas 16 plugin delivered an executable with a malicious payload. This version probably started a tendency for malware creators because, since .hofos, the main attack vector, remained cracks and other pirated data.
Sarut ransomware
The first version of the month of May, Sarut ransomware came alongside other variants like .fedasot, .berost, .forasom, .fordan. The few added another email to the mix – mosteros@firemail.cc that got used in latter versions from time to time, but not as the primary contact email.
As given from the name, this version encrypts files with a .sarut file marker, and developers still use offline keys for the file locking, so many victims can get their files back with STOP decrypter. Malware developers seemed to sleep on their money gotten from victims and focusing on these continuous releases without making any crucial changes to the coding.
Ferosas ransomware
At the same time as not so unique versions .codnat, .codnat1, .bufas, .dotmap, .radman and .rectot came out Ferosas ransomware that is yet another version that cannot be easily decrypted with the STOP decryption tool or other programs offered by programmers or researchers.
These versions included a mix of contact emails with more uncommon bufalo@firemail.cc, gorentos@bitmessage.ch. However, the same ransom note, ransom amount, and encryption methods, so offline keys still help to decrypt files or at least some of them. The distribution remains focusing around software cracks and torrent files. Particular versions were reportedly included in packs with Sony Vegas application cracks and other software.
Skymap ransomware
Skymap ransomware came out in the summer alongside .mogera, .rezuc, .stone, .redmat, .lanset, .davda, .poret. A few of them got more active than others ad can be identified from a new contact email stoneland@firemail.cc. However, .skymap was the one that got more attention from researchers due to user samples and reports.
Nevertheless, these all versions can be decrypted because developers use offline keys for encryption mainly. Still, the main vector remains serial numbers, cracks and other illegal files delivered via torrent sites.
Heroset ransomware
July was not the biggest month for this ransomware strain because Heroset ransomware and .pidon, .boston, .muslat, .gerosan, .vesad, .horon, .neras, .truke variants that came out this month all were almost identical. gorentos@bitmessage.ch, ferast@firemail.cc emails, _readme.txt ransom note ant the same discount offer to lower $980 to $490 remained unchanged.
Although the versions seem to be more persistent and making all the changes in the system folders, STOP Decrypter with needed updates works perfectly for files locked using offline keys. However, during this time it was revealed that besides encryption processes, Djvu delivers AZORult malware as a secondary payload.
Litar ransomware
The summer of 2019 was big for the virus, which is uncommon in the ransomware world because developers mainly rest during the holidays. However, Litar ransomware and .dalle, .lotep, .nusar, .besub, .cezor, .lokas, .godes, .budak, .vusad, .herad, .berosuce, .gehad, .gusau all got released in a span of three weeks.
Although some of them got more popular than others, all can be decrypted with a proper version of the decryption tool. Developers still trying to calm people by stating “don't worry” but scaring them with a claim that there are no other options besides paying the ransom. At this point, decryption is possible for files locked using offline keys and there is no need to panic or pay the demanded amount.
Madek ransomware
Starting with Madek ransomware, creators released a new version a day up until the very end of August. Not developing anything new, criminals wanted to infect as many systems as possible due to positive results with the decryption tool developed by Michael Gillespie. Not many things get to be changed, as usual. Gorentos@bitmessage.ch, varasto@firemail.cc still remain default contact emails for many versions of file markers.
| .tocue .darus .lapoi .todar .dodoc .bopador .novasof .ntuseg .prandel .pedro .nuksus .vesrato |
.ndarod .access .format .nelasod .mogranos .cosakos .nvetud .lotej .kovasoh .masodas .stare .carote |
.zatrov .masok .brusaf .londec .krusop .mtogas .nasoh .coharos .nacro .shariz |
Gero ransomware
Although those last few weeks were extremely active for developers, versions were decryptable yet again. However, Gero ransomware release changed everything. Encryption method and coding were changed, and developers started to use the proper asymmetric file-locking algorithm. This fact made STOP virus decrypter useless, in most cases because offline keys cannot be used. During this time, gorentos@bitmessage.ch, gerentoshelp@firemail.cc started to be used as main, and the only contact emails, ransom note unchanged and the file remains _readme.txt.
Kvag ransomware
Kvag ransomware came out after all those changes and become extremely active, based on user reports on our site. However, previous versions .hese, .seto, .peta, .moka, and .meds also encrypted peoples' computer at the same time. Thanks to all those samples and reports, we and other researchers could investigate the newest changes made by cybercriminals.
Yet again, people are not careful with their files and illegal habits, so ransomware quietly spreads via torrent files. Some of you stated that cracks and Russian file-sharing sites led to the ransom note appears on the screen. Since there is a long period of waiting until the proper decryption tool gets developed, you should store all virus-related files on an external device and wait for the possibility to restore your data.
Karl ransomware
Karl ransomware came with .domn virus version and more options from researchers. The changed method of file-locking left no options but to disable STOP-Decrypter and end service of file recovery. However, other researchers made their analysis and now can offer other services.
In some rare cases when offline keys still get used you can try to use the decryptor, or rely on other services that are offered by researchers:
- For people that have data encrypted using offline keys, there is a decryption option here.
- Dr.Web also offers a tool named Rescue Pack that costs 150 euro per user.
Nesa ransomware
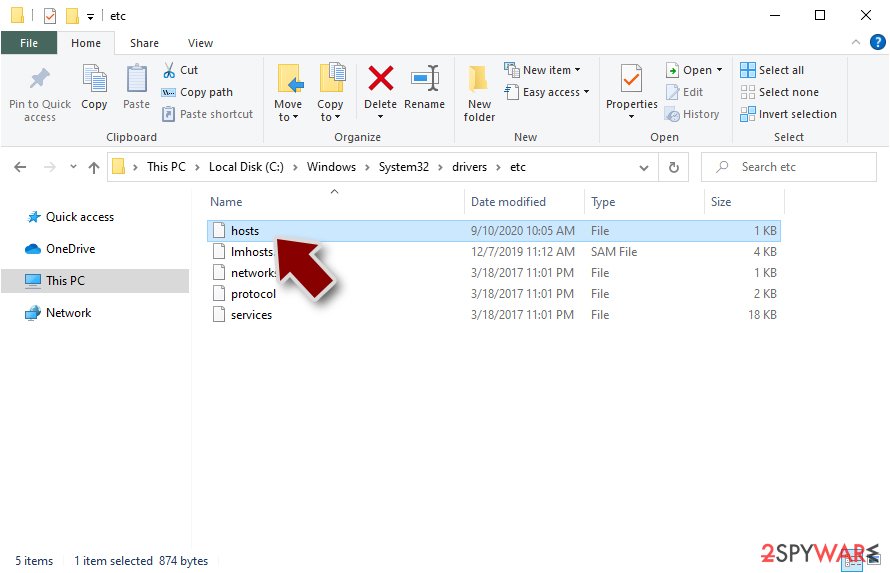
Nesa ransomware is still delivering AZORult malware and making all the changes in the system like dropping modules set to steal stored data and information from web browsers. However, the threat leaves hosts file on the system that keeps you from accessing sites like ours and search other methods to recover from the attack. For that, go to this location and find “hosts” file: C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc. Delete it completely by using admin permissions.
Upper-mentioned services can work for this variant, and you can additionally search these sites for decryption tool:
- https://www.nomoreransom.org/en/decryption-tools.html
- https://www.emsisoft.com/ransomware-decryption-tools/
- https://noransom.kaspersky.com/
- https://www.avast.com/ransomware-decryption-tools
- https://www.quickheal.com/free-ransomware-decryption-tool/
- https://www.mcafee.com/enterprise/en-us/downloads/free-tools/ransomware-decryption.html
- https://success.trendmicro.com/solution/1114221-downloading-and-using-the-trend-micro-ransomware-file-decryptor
Meka ransomware
Meka ransomware is the 178th version in this ever-changing cryptovirus family that came out in 2019, at the start of November alongside the other three versions that were spotted in the span of one week: .toec, .mosk, .nakw. This is the typical ransomware version that uses a random combination of four letters for the file marker and loads the encryption process at the start of an infection. When data gets locked, _readme.txt appears in various folders and on the desktop, so the victim is informed on further actions.
This text file as typical includes contact emails salesrestoresoftware@firemail.cc, salesrestoresoftware@gmail.com and ransom amount indication, particular ID for the victim, and suggestions where to get Bitcoins that is preferred cryptocurrency for the payment. 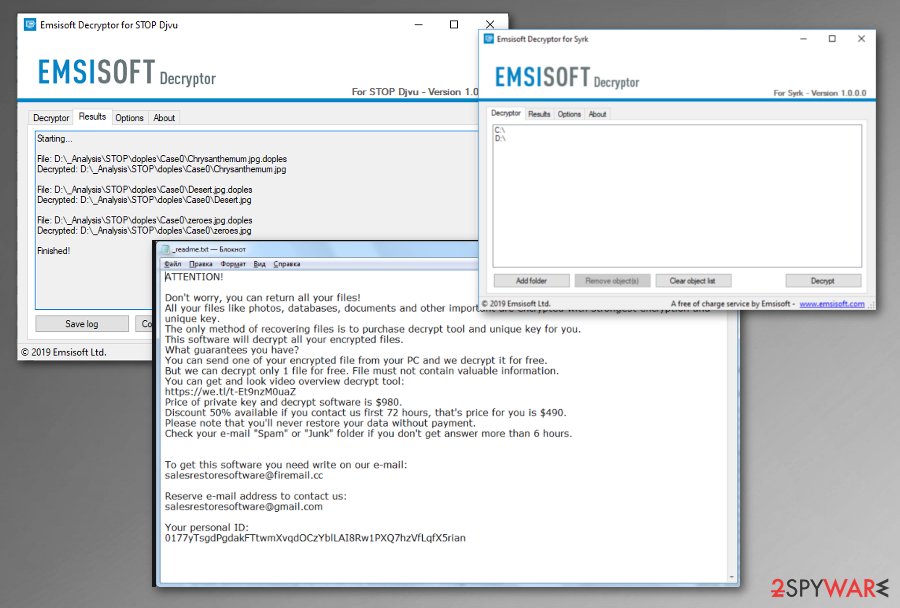
Lokf ransomware
Lokf ransomware came right after the previous version, in the first week of November 2019, but this version used different emails as contact preferences than other known variants. restoredatahelp@firemail.cc, gorentos@bitmessage.ch – the preferred method of contacting virus developers. .peet, .grod, .mbed, .kodg and .zomb came out after Lokf with the same reason note as before – _readme.txt and slight alterations in coding.
However, the usage of online IDs stopped way before these variants to released. So people haven't been decrypting their files using any third-party tools. .lokf marked data cannot get covered without proper data backups or programs designed to restore data.
Remk ransomware
Remk ransomware was one of the first versions that started to use helpdatarestore@firemail.cc, helpmanager@mail.ch email addresses as the main preferred contact methods.
These emails are exceptionally used by other later versions too. .remk extension came after a not-so-active period for ransomware creators. December was not the most active month for the criminals because, during the time of Holidays, malware actors released only five new variants.
January and February together have around ten new extensions in total, including .reha, .topi, .repp, .alka, .bboo, .mmnn, .ooss, and .nppp. Hackers became more active in March and April of 2020, releasing new variants every week. However, changes remaining very slight because the same emails, ransom notes, and ransom amount go for at least 20 or 30 versions.
Mado ransomware
Mado ransomware comes right after .npsk and .opqz versions that all came up to the researchers' attention in few days from each other. This is one of the many variants that have all the common and typical features of this ransomware family:
- helpdatarestore@firemail.cc, helpmanager@mail.ch contact emails;
- _readme.txt – ransom note;
- online keys as the primary method of generating victims' IDs;
- AES and RSA encryption algorithms;
- discount offer int he ransom note;
- distributed via pirated software files mainly;
- $980 final ransom amount.
Jope ransomware
Jope ransomware is also one of these similar versions that came out in Spring 2020 when helpdatarestore@firemail.cc, helpmanager@mail.ch get used as primary email addresses and _readme.txt still contains the same message:
ATTENTION!
Don't worry, you can return all your files!
All your files like photos, databases, documents and other important are encrypted with strongest encryption and unique key.
The only method of recovering files is to purchase decrypt tool and unique key for you.
This software will decrypt all your encrypted files.
What guarantees you have?
You can send one of your encrypted file from your PC and we decrypt it for free.
But we can decrypt only 1 file for free. File must not contain valuable information.
You can get and look video overview decrypt tool:
hxxps://we.tl/t-y7G4t6cSO4
Price of private key and decrypt software is $980.
Discount 50% available if you contact us first 72 hours, that's price for you is $490.
Please note that you'll never restore your data without payment.
Check your e-mail “Spam” or “Junk” folder if you don't get answer more than 6 hours.To get this software you need write on our e-mail:
helpdatarestore@firemail.ccReserve e-mail address to contact us:
helpmanager@mail.chYour personal ID:
Unfortunately, malware creators are not planning to change encryption methods or rely on online keys for the ID generation, so decryption options remain limited and only those people who get versions using offline IDs can use the existing decryption tool and restore their data. For others, paying still shouldn't be an option. Anti-malware tools can detect most of these versions,[8] so you have methods for the virus removal at least.

Sqpc ransomware
Sqpc ransomware variant has been attributed to the big family in May 2020. Since this meets new family members every few weeks, this variant is not a surprise. People on Reddit started reporting about their personal files being compromised by ransomware that adds .sqpc file extension to the locked files and creates a ransom note _readme.txt.
The _readme.txt note is typical to most of this ransomware variants. It reports the attack and demands the victim to contact the criminals behind the ransomware within 72 hours if he or she wants to get 50% off the decryption software's price.
The main contact of the criminals was not changed, i.e. helpmanager@mail.ch is still used as the main e-mail contact like in most of the variants of this ransomware family. However, a never-seen-before e-mail addressrestoremanager@firemail.cc has been added making a slight, thus making the ransomware slightly deviated from its ancestors.
Unfortunately, the virus cannot be decrypted, at least not yet. Its developers rely on online key leaving a limited room for experts to create a decryption software that worlds for all victims. Nevertheless, we do not recommend paying the ransom. At best, remove sqpc ransomware from the system ASAP and try to recover data with STOPdecryper or alternative software.
Mzlq ransomware
Mzlq ransomware is a version that showed up in the middle of May 2020. Just as its predecessors, the malware uses the RSA encryption algorithm to encrypt pictures, videos, music, documents, and other files, and then appends a four-letter file extension (in this case, .mzlq). After that, the malware drops a ransom note _readme.txt, which explains to users what happened to their machines.
Unfortunately, they are told that all of their files have been locked, and only Mzlq ransomware authors are capable of restoring data. While this is partially true (files can be restored through backups, if such were prepared), criminals are correct about only them possessing the unique key for the decryption process. Security experts recommend avoiding contacting cybercriminals, as they might not deliver the required Mzlq ransomware decryptor even after the bitcoins are transferred.
Currently, Mzlq file virus installer has a relatively low detection rate – the following names are used for the sample:[9]
- Win32.Trojan-Ransom.STOP.XQ922Z
- Trojan.Ransom.Stop
- Win/malicious_confidence_100% (W)
- Ransom:Win32/STOP.BS!MTB
- Mal/Generic-S
- Ransom.STOP!8.10810 (CLOUD), etc.
Koti ransomware
Koti ransomware emerged on the surface as a 226th family member of the infamous ransomware. Since this ransomware family is infamous for its regular releases of new variants, Koti has been expected in the Middle of May 2020 and here it is.
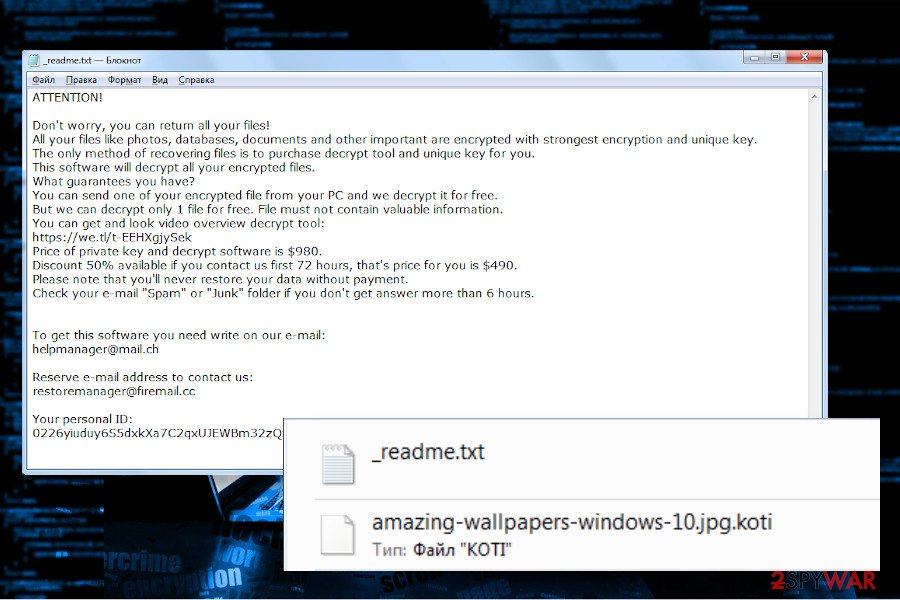
In fact, it's similar to its predecessors, except one thing – a new file extension used as a marker of the encrypted files. All photos, documents, archived files, and other system unrelated data get a .koti file extension. Upon encryption, it drops a ransom note named _readme.txt, which contains the following information:
- The fact that the system has been attacked by ransomware due to multiple vulnerabilities;
- Warning about the consequences if the victim attempts to remove the ransomware or uses third-party data recovery programs;
- Email addresses of the ransomware managers, i.e. helpmanager@mail.ch and restoremanager@firemail.ch;
- The size of the redemption ($490 if the victim pays within 72 hours or $980 if the payment is delayed);
- Bitcoin wallet number[10].
At the moment of writing, this ransomware is not the most proliferate. However, it may gather momentum at any time, so be careful with email attachments, make sure to install all available Windows updates, keep anti-virus programs activated all the time, and be very attentive when browsing the Internet. In case of an attack, do not postpone Koti removal since it may not only encrypt files, but also try to download trojan or another malware as a secondary payload.
Zipe ransomware
Zipe ransomware, also known as .zipe file extension virus is a copy-paste version of the earlier malware family members, so there's no need to expatriate on its traits. Likewise its predecessor, it renders AES encryption algorithm and protects the password with the RSA encryption algorithm, making itself impossible to crack.
When the cipher does its job, the ransomware marks its territory by adding a .zipe file extension to every locked file. It may skip some of the personal files unlocked; however, it will definitely attack pictures, photos, documents, compressed files, archives, etc.
Aside from altered suffixes of files, people will find the _readme.txt file on the desktop and other random folders. This text file informs about the ransomware attack, explains how to purchase Bitcoins, and asks to pay $480 (or $980 if the time of 72 hours is exceeded) in Bitcoins.
Victims of this virus should not pay redemption. Although the decryption software hasn't yet been developed, it's only a matter of time when Emsisoft's decryptor will be updated. Therefore, it's advisable to remove Zipe ransomware from the machine and make the backups of the locked files. After that, either try alternative decryption methods listed below or wait until cybersecurity experts create a software that can decrypt Djvu versions that have been launched after August 2019.
Nlah ransomware
Questions on how to decrypt files encrypted by .nlah file extension virus have emerged on the 2nd of June, 2020 on Reddit[11]. That was the first signal that ransomware developers are strengthening their forces and rescheduling the weekly releases of the new strains. The previous 228th version dubbed as Zipe has occurred a day before the emergence of Nlah ransomware.
Thus, cybersecurity experts have a presumption that the summer of 2020 may exhibit increased activity of ransomware. The Nlah virus seems to be fully functional since it has already started attacking individual PC users via spam emails and unprotected RDPs.
During the phases of the attack, the ransomware enables encryption engine (AES and RSA) and locks files in exchange of almost $1000 ransom in Bitcoins. If you have been attacked by this threat, do not write emails to helpdatarestore@firemail.cc or helpmanager@mail.ch because these emails are managed by criminals. Instead of that, eliminate Nlah ransomware with a proper security tool and try to decrypt files using third-party recovery tools.
Zwer ransomware
Zwer ransomware is another member of an ever-expanding ransomware family. First picked up by a security researcher Michael Gillespie,[12] this variant does not differ much from previous versions.
The malware typically spreads via infectious pirated program installers or software cracks that can typically be downloaded from third-party websites (mainly torrent sites). The main executable can be named as anything, although one sample of Zwer file virus was found as b71d.tmp.exe and is detected by many anti-malware programs.
The malware uses the RSA encryption algorithm to lock files and then appends .zwer extension to pictures, videos, documents, databases, and other files, preventing user access. To unlock data, victims are asked to email the perpetrators via helpmanager@mail.ch or restoremanager@airmail.cc in order to retrieve a decryption tool.
Additionally, the _readme.txt note also informs users that they are eligible for a 50% price discount if they send an email within 72 hours of the infection. As usual, security researchers do not recommend paying for the Zwer ransomware decryptor and rather rely on Emsisoft's decryptor or third-party tools to recover data.
Newest Djvu ransomware versions
Djvu ransomware is the biggest malware family that attacks regular consumers, accounting for approximately 70% cases reported to Ransomware-ID, according to Emsisoft report.[13]
The malware family is constantly growing, and, while there are minimal differences from one variant to the next, there are little chances of victims retrieving their files for free if they were locked using an online key. Here are the most recent ransomware versions:
Ransomware is distributed via spam messages, software cracks, and adware bundles
According to cybersecurity specialists from LosVirus.es,[14] ransomware infections can appear on the computer because of an opened spam letter or its attachment. Some email messages, that are dropped by the crooks, might contain a hazardous link inserted inside the letter itself, or a dubious attachment that comes clipped to the email. Be aware of all questionable emails, do not open, and if they look malicious or suspicious in some certain way.
Furthermore, you can detect that something is wrong if the email message contains various grammar mistakes, and if it comes from an unrecognizable sender. However, not all of them look this way. Some crooks pretend to be from worldwide organizations. So, if you were not expecting to receive anything important recently, you better not access any messages. What you should do is contact the company directly if necessary.
Additionally, in some cases, ransomware viruses can distribute through third-party networks. All pages that come from secondary sources often lack required protection and do not fit the security requirements. This leads to a high risk of getting infected by dangerous malware, e.g. ransomware. We suggest avoiding all non-original pages and suspicious hyperlinks that you might encounter while browsing the web.
With the .tro file extension, ransomware was spotted being distributed with the help of so-called “cracks” and “keygens.” These files are used to crack the original software to make it perform as a licensed version. Such activity is highly illegal, and users could face fines and legal actions if they get caught. Besides, the risk of infecting the PC with ransomware should diminish the urge to crack programs.
Finally, researchers said that the virus is also being spread bundled with adware programs. To stop unwanted apps from entering the machine, never skip the installation steps, and read through the installation instructions. Always pick Advanced/Custom installation mode instead of Recommended/Quick one and remove all the optional components that are offered.
Many users recently reported that the ransom note stating about encryption and ransom demand appeared on their screen after cracked software installation. Such programs like Adobe Photoshop, Illustrator or video games like NBA package, serial numbers or license keys of legitimate applications, security tools contain much more in the installation setup.
Public pirated content pages deliver such ransomware payload as installer file and once the executable gets loaded on the machine malicious script is triggered and encryption starts. The file-locking process happens in a matter of minutes, so you cannot do anything about it, even though you noticed that something is off.
Remove malware with sophisticated AV software
To remove Djvu virus, use only reputable computer software. Furthermore, you can detect all malware-laden content by scanning the computer system with the proper security or anti-malware tool like:
Such software is created to lengthen the removal process for all users. Even though the detection process might take a while, please, be patient as you will find it incredibly useful later on. You should also look for detection rates and sample analysis to see if the threat you encounter can be detected and removed with other tools that worked for previous virus versions.
Performing ransomware removal requires a lot of attention. This is the main reason why you should leave the process for automatic computer tools. Furthermore, after you proceed with the elimination, make sure that you perform some system backups. All ransomware-related components need to be removed permanently for the computer to work normally again. Also, files that get corrupted during these malicious processes need to get repaired using FortectIntego or different PC tools.
Getting rid of Djvu virus. Follow these steps
Important steps to take before you begin malware removal
File encryption and ransomware infection are two independent processes (although the latter would not be possible without the former). However, it is important to understand that malware performs various changes within a Windows operating system, fundamentally changing the way it works.
IMPORTANT for those without backups! →
If you attempt to use security or recovery software immediately, you might permanently damage your files, and even a working decryptor then would not be able to save them.
Before you proceed with the removal instructions below, you should copy the encrypted files onto a separate medium, such as USB flash drive or SSD, and then disconnect them from your computer. Encrypted data does not hold any malicious code, so it is safe to transfer to other devices.
The instructions below might initially seem overwhelming and complicated, but they are not difficult to understand as long as you follow each step in the appropriate order. This comprehensive free guide will help you to handle the malware removal and data recovery process correctly.
If you have any questions, comments, or are having troubles with following the instructions, please do not hesitate to contact us via the Ask Us section.
IMPORTANT! →
It is vital to eliminate malware infection from the computer fully before starting the data recovery process, otherwise ransomware might re-encrypt retrieved files from backups repeatedly.
Isolate the infected computer
Some ransomware strains aim to infect not only one computer but hijack the entire network. As soon as one of the machines is infected, malware can spread via network and encrypt files everywhere else, including Network Attached Storage (NAS) devices. If your computer is connected to a network, it is important to isolate it to prevent re-infection after ransomware removal is complete.
The easiest way to disconnect a PC from everything is simply to plug out the ethernet cable. However, in the corporate environment, this might be extremely difficult to do (also would take a long time). The method below will disconnect from all the networks, including local and the internet, isolating each of the machines involved.
- Type in Control Panel in Windows search and press Enter
- Go to Network and Internet
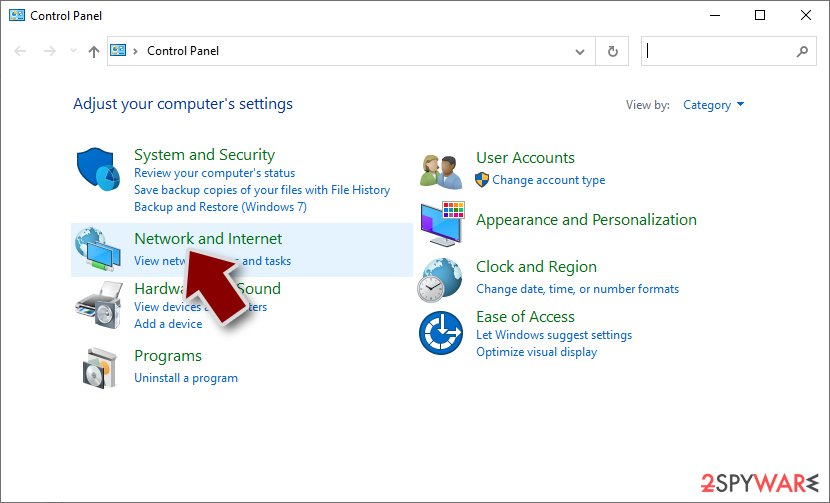
- Click Network and Sharing Center
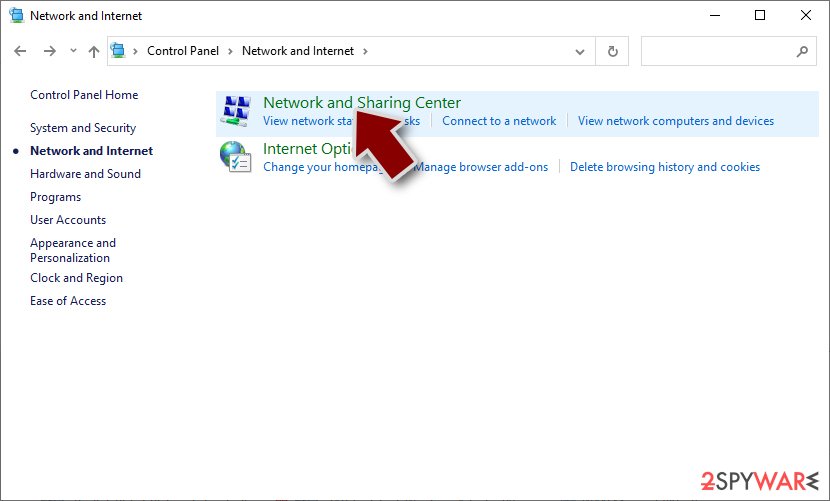
- On the left, pick Change adapter settings
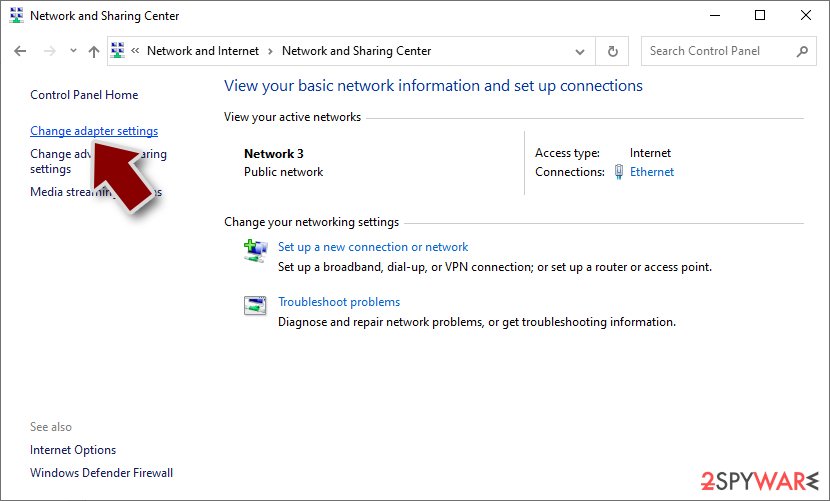
- Right-click on your connection (for example, Ethernet), and select Disable
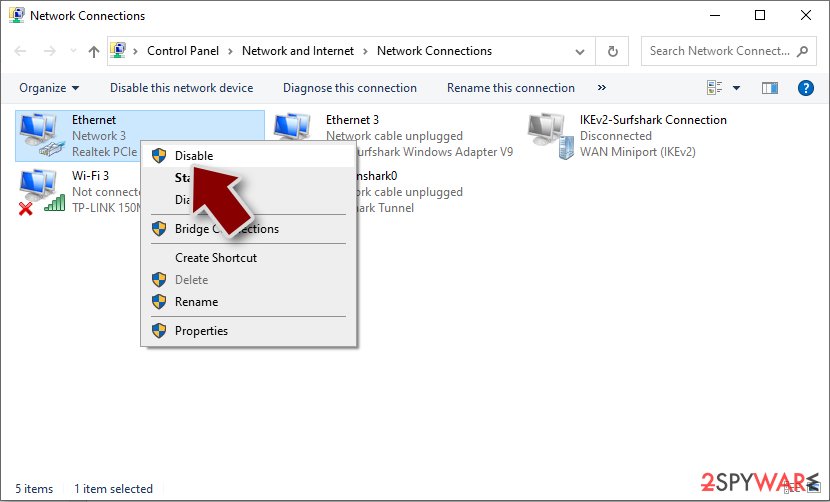
- Confirm with Yes.
If you are using some type of cloud storage you are connected to, you should disconnect from it immediately. It is also advisable to disconnect all the external devices, such as USB flash sticks, external HDDs, etc. Once the malware elimination process is finished, you can connect your computers to the network and internet, as explained above, but by pressing Enable instead.
Scan your system with anti-malware
If you are a victim of ransomware, you should employ anti-malware software for its removal. Some ransomware can self-destruct after the file encryption process is finished. Even in such cases, malware might leave various data-stealing modules or could operate in conjunction with other malicious programs on your device.
SpyHunter 5Combo Cleaner or Malwarebytes can detect and eliminate all ransomware-related files, additional modules, along with other viruses that could be hiding on your system. The security software is really easy to use and does not require any prior IT knowledge to succeed in the malware removal process.
Repair damaged system components
Once a computer is infected with malware, its system is changed to operate differently. For example, an infection can alter the Windows registry database, damage vital bootup and other sections, delete or corrupt DLL files, etc. Once a system file is damaged by malware, antivirus software is not capable of doing anything about it, leaving it just the way it is. Consequently, users might experience performance, stability, and usability issues, to the point where a full Windows reinstall is required.
Therefore, we highly recommend using a one-of-a-kind, patented technology of FortectIntego repair. Not only can it fix virus damage after the infection, but it is also capable of removing malware that has already broken into the system thanks to several engines used by the program. Besides, the application is also capable of fixing various Windows-related issues that are not caused by malware infections, for example, Blue Screen errors, freezes, registry errors, damaged DLLs, etc.
- Download the application by clicking on the link above
- Click on the ReimageRepair.exe

- If User Account Control (UAC) shows up, select Yes
- Press Install and wait till the program finishes the installation process
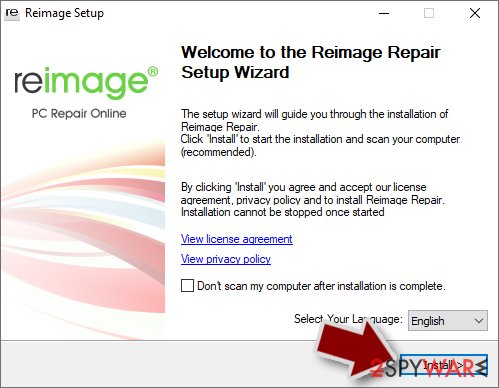
- The analysis of your machine will begin immediately
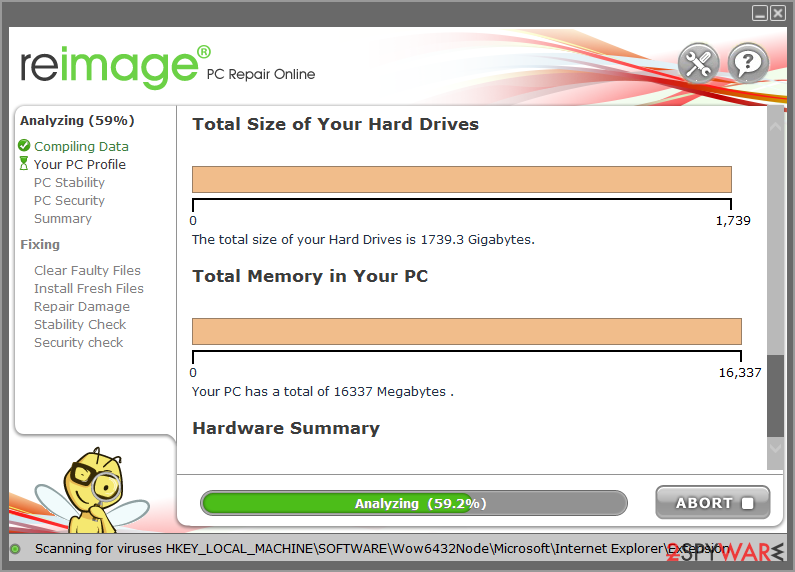
- Once complete, check the results – they will be listed in the Summary
- You can now click on each of the issues and fix them manually
- If you see many problems that you find difficult to fix, we recommend you purchase the license and fix them automatically.
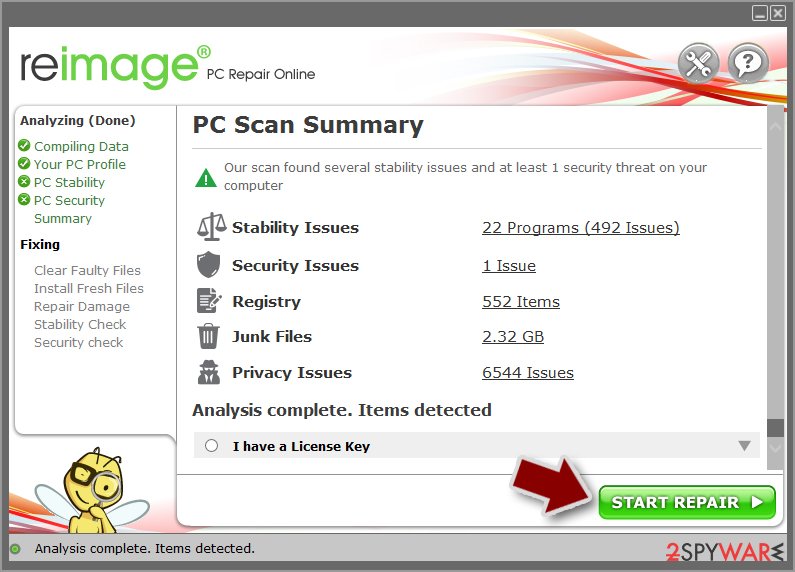
By employing FortectIntego, you would not have to worry about future computer issues, as most of them could be fixed quickly by performing a full system scan at any time. Most importantly, you could avoid the tedious process of Windows reinstallation in case things go very wrong due to one reason or another.
Restore Windows "hosts" file to its original state
You can find yourself blocked while trying to download anti-virus software or visit a legitimate security site. For that, go to this location and find the “hosts” file: C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc. Delete it completely by using admin permissions.
Some ransomware might modify Windows hosts file in order to prevent users from accessing certain websites online. For example, Djvu ransomware variants add dozens of entries containing URLs of security-related websites, such as 2-spyware.com. Each of the entries means that users will not be able to access the listed web addresses and will receive an error instead.
Here's an example of “hosts” file entries that were injected by ransomware:
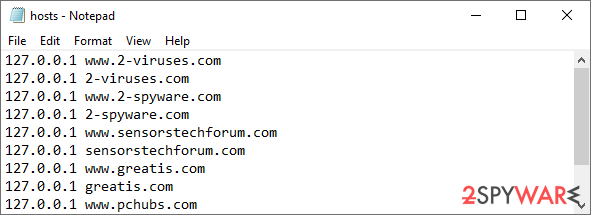
In order to restore your ability to access all websites without restrictions, you should either delete the file (Windows will automatically recreate it) or remove all the malware-created entries. If you have never touched the “hosts” file before, you should simply delete it by marking it and pressing Shift + Del on your keyboard. For that, navigate to the following location:
C:\\Windows\\System32\\drivers\\etc\\
Restore files using data recovery software
Since many users do not prepare proper data backups prior to being attacked by ransomware, they might often lose access to their files permanently. Paying criminals is also very risky, as they might not fulfill the promises and never send back the required decryption tool.
While this might sound terrible, not all is lost – data recovery software might be able to help you in some situations (it highly depends on the encryption algorithm used, whether ransomware managed to complete the programmed tasks, etc.). Since there are thousands of different ransomware strains, it is immediately impossible to tell whether third-party software will work for you.
Therefore, we suggest trying regardless of which ransomware attacked your computer. Before you begin, several pointers are important while dealing with this situation:
- Since the encrypted data on your computer might permanently be damaged by security or data recovery software, you should first make backups of it – use a USB flash drive or another storage.
- Only attempt to recover your files using this method after you perform a scan with anti-malware software.
Install data recovery software
- Download Data Recovery Pro.
- Double-click the installer to launch it.
- Follow on-screen instructions to install the software.
- As soon as you press Finish, you can use the app.
- Select Everything or pick individual folders where you want the files to be recovered from.
- Press Next.
- At the bottom, enable Deep scan and pick which Disks you want to be scanned.
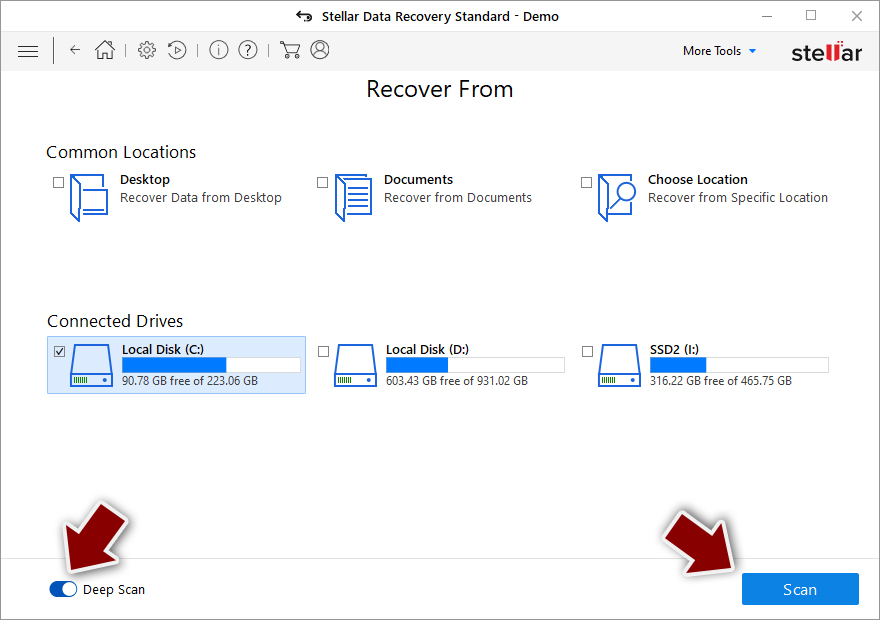
- Press Scan and wait till it is complete.
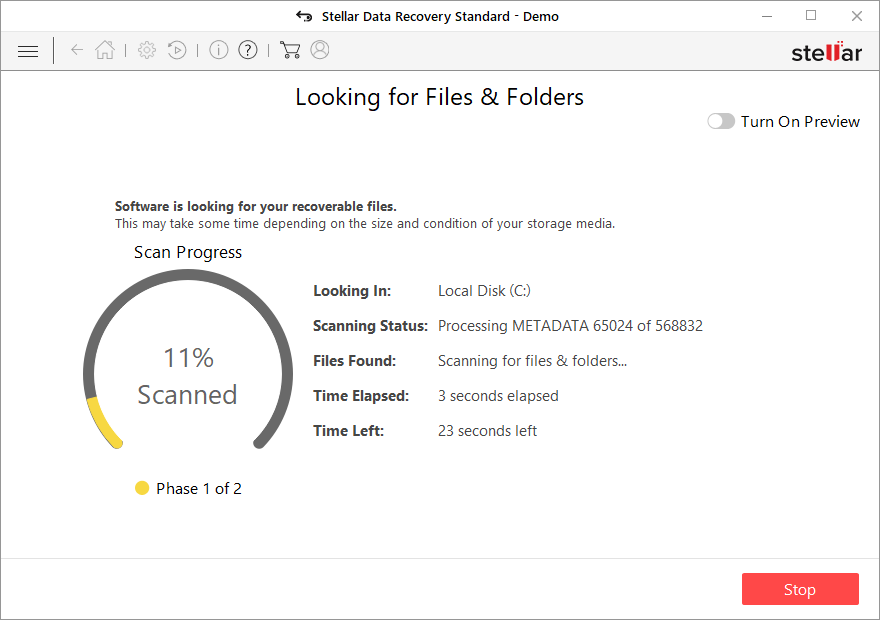
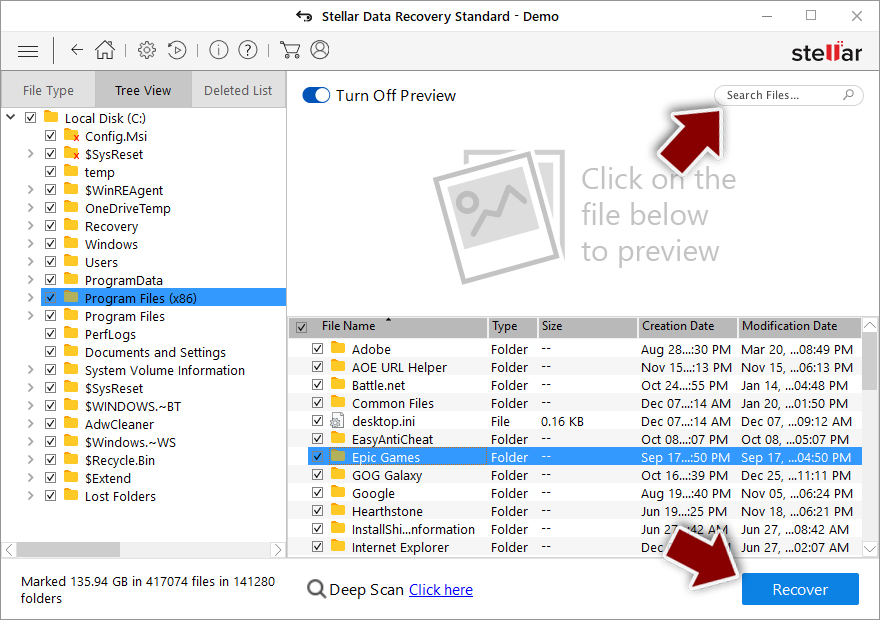
- You can now pick which folders/files to recover – don't forget you also have the option to search by the file name!
- Press Recover to retrieve your files.
Find a working decryptor for your files
File encryption is a process that is similar to applying a password to a particular file or folder. However, from a technical point of view, encryption is fundamentally different due to its complexity. By using encryption, threat actors use a unique set of alphanumeric characters as a password that can not easily be deciphered if the process is performed correctly.
There are several algorithms that can be used to lock data (whether for good or bad reasons); for example, AES uses the symmetric method of encryption, meaning that the key used to lock and unlock files is the same. Unfortunately, it is only accessible to the attackers who hold it on a remote server – they ask for a payment in exchange for it. This simple principle is what allows ransomware authors to prosper in this illegal business.
While many high-profile ransomware strains such as Djvu or Dharma use immaculate encryption methods, there are plenty of failures that can be observed within the code of some novice malware developers. For example, the keys could be stored locally, which would allow users to regain access to their files without paying. In some cases, ransomware does not even encrypt files due to bugs, although victims might believe the opposite due to the ransom note that shows up right after the infection and data encryption is completed.
Therefore, regardless of which crypto-malware affects your files, you should try to find the relevant decryptor if such exists. Security researchers are in a constant battle against cybercriminals. In some cases, they manage to create a working decryption tool that would allow victims to recover files for free.
Once you have identified which ransomware you are affected by, you should check the following links for a decryptor:
- No More Ransom Project
- Free Ransomware Decryptors by Kaspersky
- Free Ransomware Decryption Tools from Emsisoft
- Avast decryptors
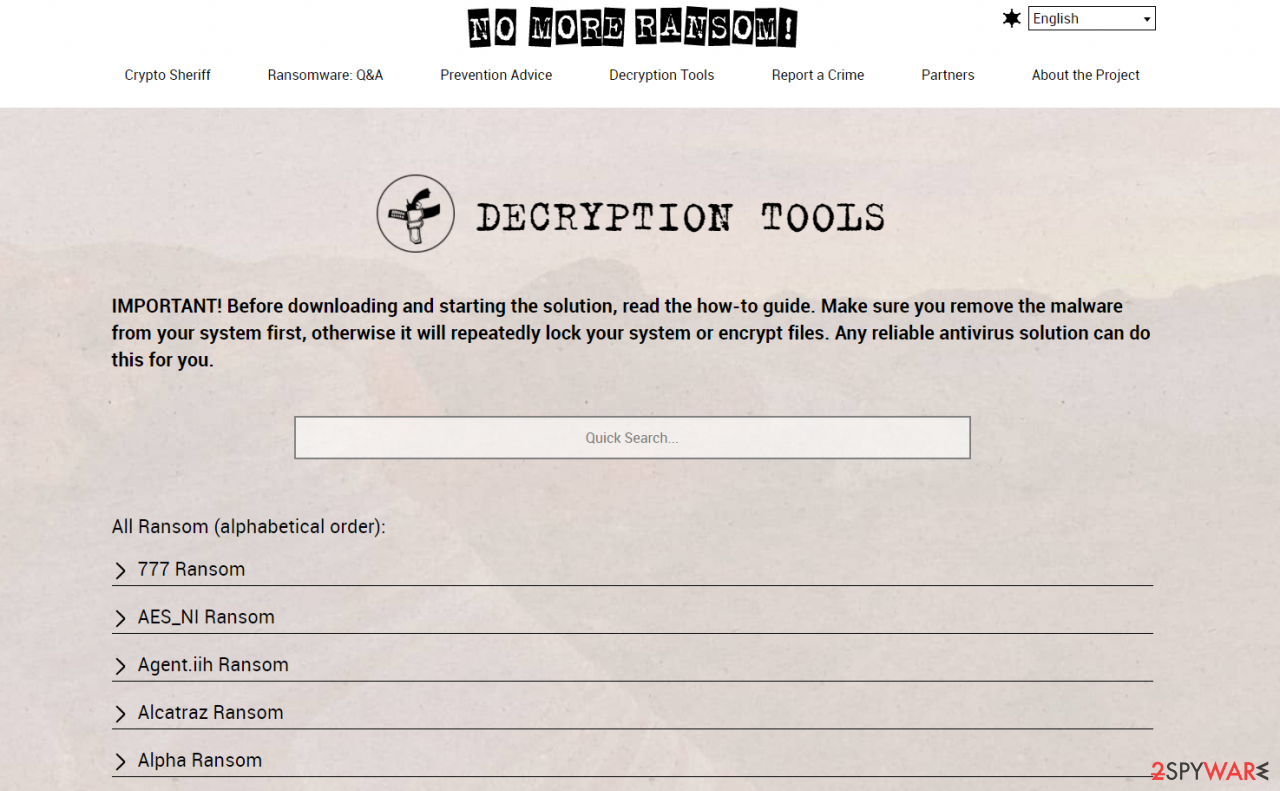
If you can't find a decryptor that works for you, you should try the alternative methods we list below. Additionally, it is worth mentioning that it sometimes takes years for a working decryption tool to be developed, so there are always hopes for the future.
Use Emsisoft decrytor for Djvu/STOP
If your computer got infected with one of the Djvu variants, you should try using Emsisoft decryptor for Djvu/STOP. It is important to mention that this tool will not work for everyone – it only works if data was locked with an offline ID due to malware failing to communicate with its remote servers.
Even if your case meets this condition, somebody from the victims has to pay criminals, retrieve an offline key, and then share it with security researchers at Emsisoft. As a result, you might not be able to restore the encrypted files immediately. Thus, if the decryptor says your data was locked with an offline ID but cannot be recovered currently, you should try later. You also need to upload a set of files – one encrypted and a healthy one to the company's servers before you proceed.
- Download the app from the official Emsisoft website.
- After pressing Download button, a small pop-up at the bottom, titled decrypt_STOPDjvu.exe should show up – click it.

- If User Account Control (UAC) message shows up, press Yes.
- Agree to License Terms by pressing Yes.
- After Disclaimer shows up, press OK.
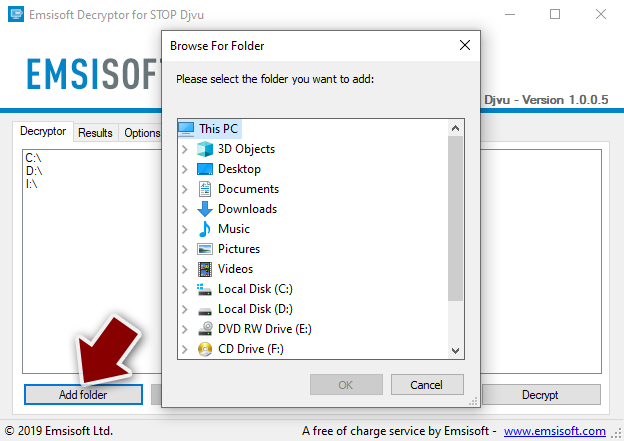
- The tool should automatically populate the affected folders, although you can also do it by pressing Add folder at the bottom.
- Press Decrypt.
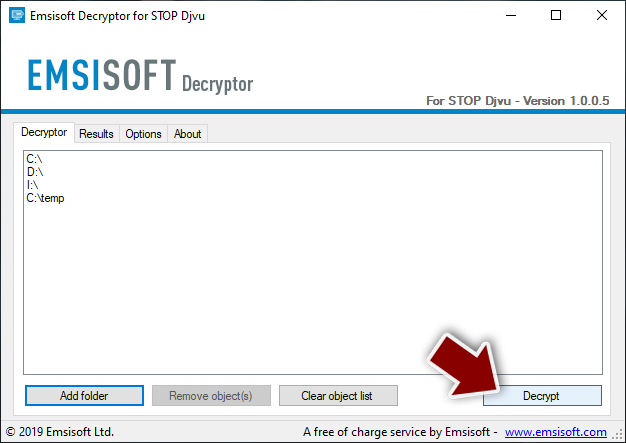
From here, there are three available outcomes:
- “Decrypted!” will be shown under files that were decrypted successfully – they are now usable again.
- “Error: Unable to decrypt file with ID:” means that the keys for this version of the virus have not yet been retrieved, so you should try later.
- “This ID appears to be an online ID, decryption is impossible” – you are unable to decrypt files with this tool.
Create data backups to avoid file loss in the future
One of the many countermeasures for home users against ransomware is data backups. Even if your Windows get corrupted, you can reinstall everything from scratch and retrieve files from backups with minimal losses overall. Most importantly, you would not have to pay cybercriminals and risk your money as well.
Therefore, if you have already dealt with a ransomware attack, we strongly advise you to prepare backups for future use. There are two options available to you:
- Backup on a physical external drive, such as a USB flash drive or external HDD.
- Use cloud storage services.
The first method is not that convenient, however, as backups need to constantly be updated manually – although it is very reliable. Therefore, we highly advise choosing cloud storage instead – it is easy to set up and efficient to sustain. The problem with it is that storage space is limited unless you want to pay for the subscription.
Using Microsoft OneDrive
OneDrive is a built-in tool that comes with every modern Windows version. By default, you get 5 GB of storage that you can use for free. You can increase that storage space, but for a price. Here's how to setup backups for OneDrive:
- Click on the OneDrive icon within your system tray.
- Select Help & Settings > Settings.
- If you don't see your email under the Account tab, you should click Add an account and proceed with the on-screen instructions to set yourself up.
- Once done, move to the Backup tab and click Manage backup.
- Select Desktop, Documents, and Pictures, or a combination of whichever folders you want to backup.
- Press Start backup.
After this, all the files that are imported into the above-mentioned folders will be automatically backed for you. If you want to add other folders or files, you have to do that manually. For that, open File Explorer by pressing Win + E on your keyboard, and then click on the OneDrive icon. You should drag and drop folders you want to backup (or you can use Copy/Paste as well).
Using Google Drive
Google Drive is another great solution for free backups. The good news is that you get as much as 15GB for free by choosing this storage. There are also paid versions available, with significantly more storage to choose from.
You can access Google Drive via the web browser or use a desktop app you can download on the official website. If you want your files to be synced automatically, you will have to download the app, however.
- Download the Google Drive app installer and click on it.
- Wait a few seconds for it to be installed.

- Now click the arrow within your system tray – you should see Google Drive icon there, click it once.
- Click Get Started.
- Enter all the required information – your email/phone, and password.
- Now pick what you want to sync and backup. You can click on Choose Folder to add additional folders to the list.
- Once done, pick Next.
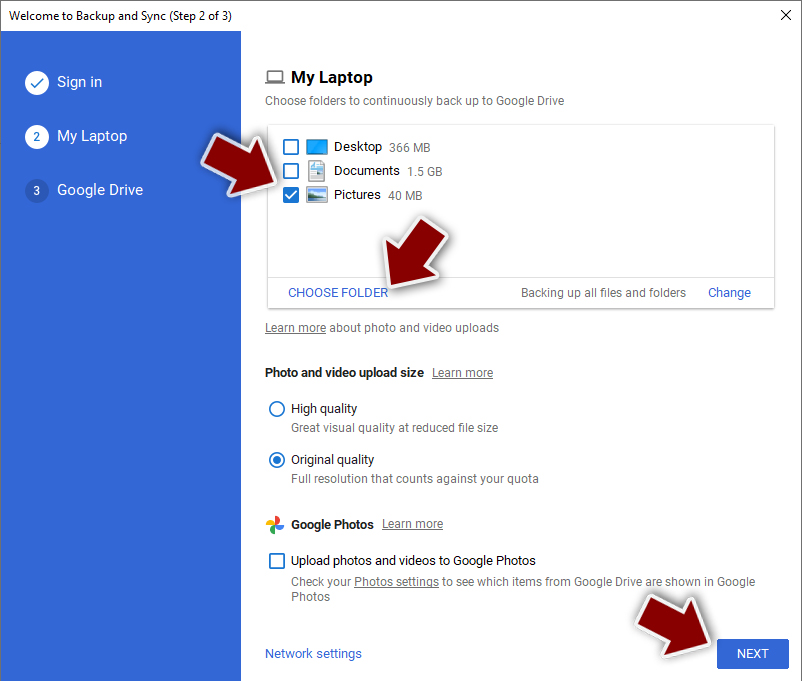
- Now you can select to sync items to be visible on your computer.
- Finally, press Start and wait till the sync is complete. Your files are now being backed up.
Report the incident to your local authorities
Ransomware is a huge business that is highly illegal, and authorities are very involved in catching malware operators. To have increased chances of identifying the culprits, the agencies need information. Therefore, by reporting the crime, you could help with stopping the cybercriminal activities and catching the threat actors. Make sure you include all the possible details, including how did you notice the attack, when it happened, etc. Additionally, providing documents such as ransom notes, examples of encrypted files, or malware executables would also be beneficial.
Law enforcement agencies typically deal with online fraud and cybercrime, although it depends on where you live. Here is the list of local authority groups that handle incidents like ransomware attacks, sorted by country:
- USA – Internet Crime Complaint Center IC3
- United Kingdom – ActionFraud
- Canada – Canadian Anti-Fraud Centre
- Australia – ScamWatch
- New Zealand – ConsumerProtection
- Germany – Polizei
- France – Ministère de l'Intérieur
If your country is not listed above, you should contact the local police department or communications center.
Manual removal using Safe Mode
Important! →
Manual removal guide might be too complicated for regular computer users. It requires advanced IT knowledge to be performed correctly (if vital system files are removed or damaged, it might result in full Windows compromise), and it also might take hours to complete. Therefore, we highly advise using the automatic method provided above instead.
Step 1. Access Safe Mode with Networking
Manual malware removal should be best performed in the Safe Mode environment.
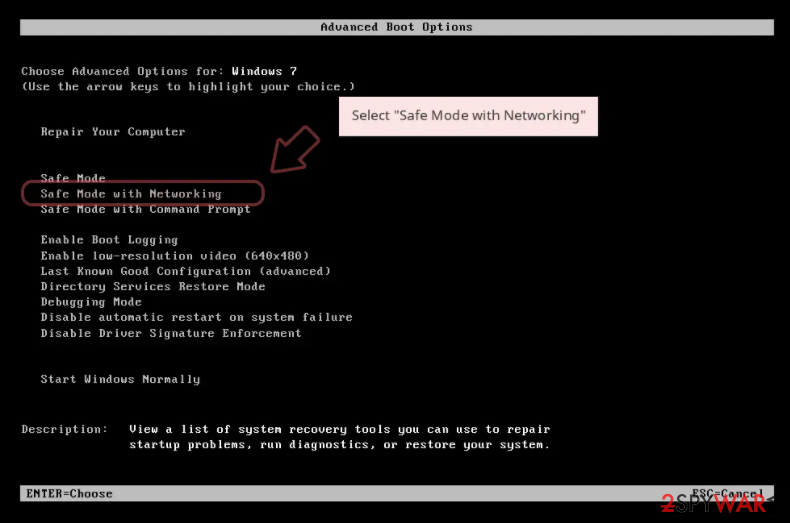
Windows 7 / Vista / XP
- Click Start > Shutdown > Restart > OK.
- When your computer becomes active, start pressing F8 button (if that does not work, try F2, F12, Del, etc. – it all depends on your motherboard model) multiple times until you see the Advanced Boot Options window.
- Select Safe Mode with Networking from the list.
Windows 10 / Windows 8
- Right-click on Start button and select Settings.
- Scroll down to pick Update & Security.
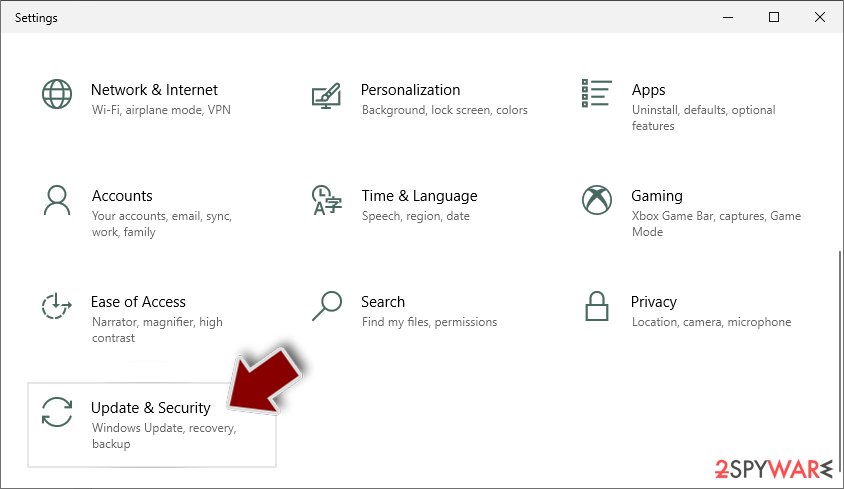
- On the left side of the window, pick Recovery.
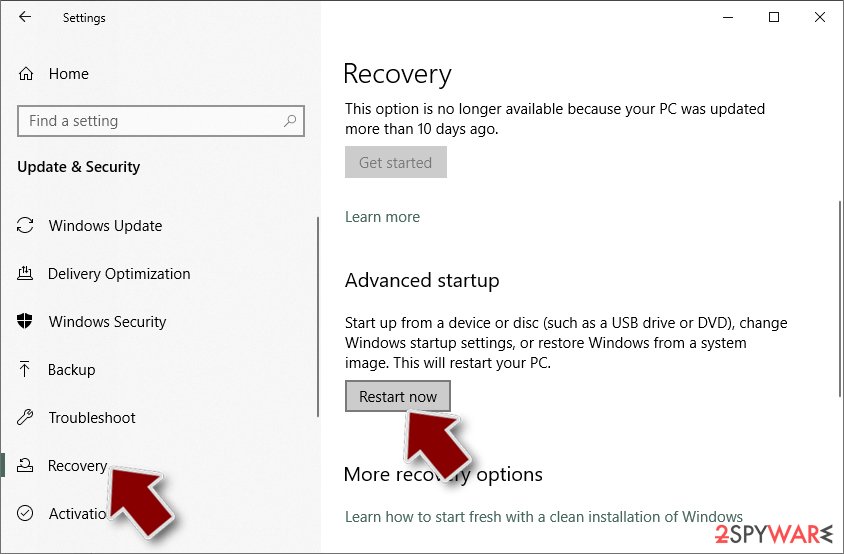
- Now scroll down to find Advanced Startup section.
- Click Restart now.
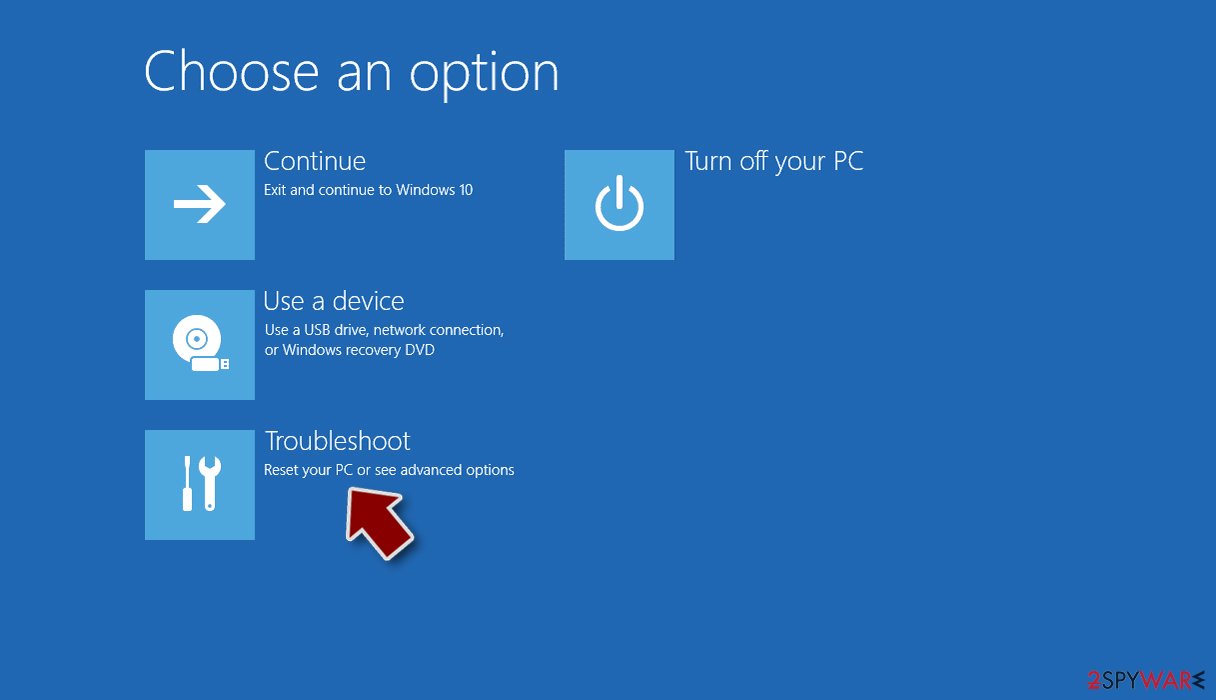
- Select Troubleshoot.
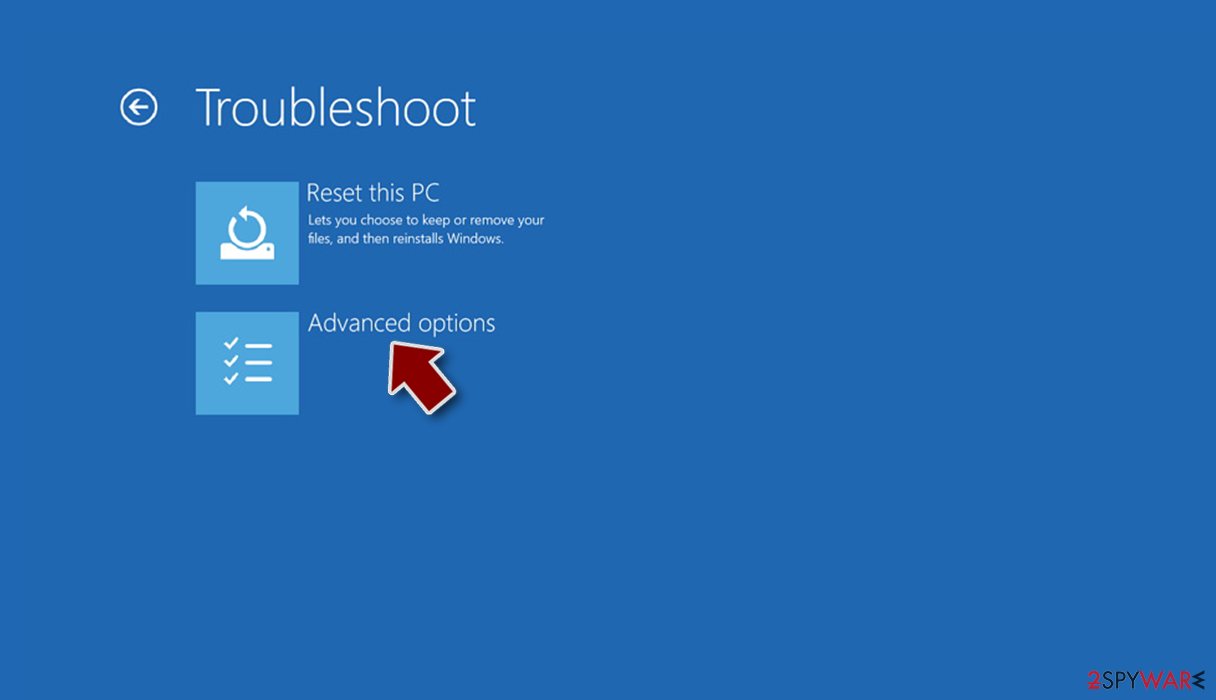
- Go to Advanced options.
- Select Startup Settings.

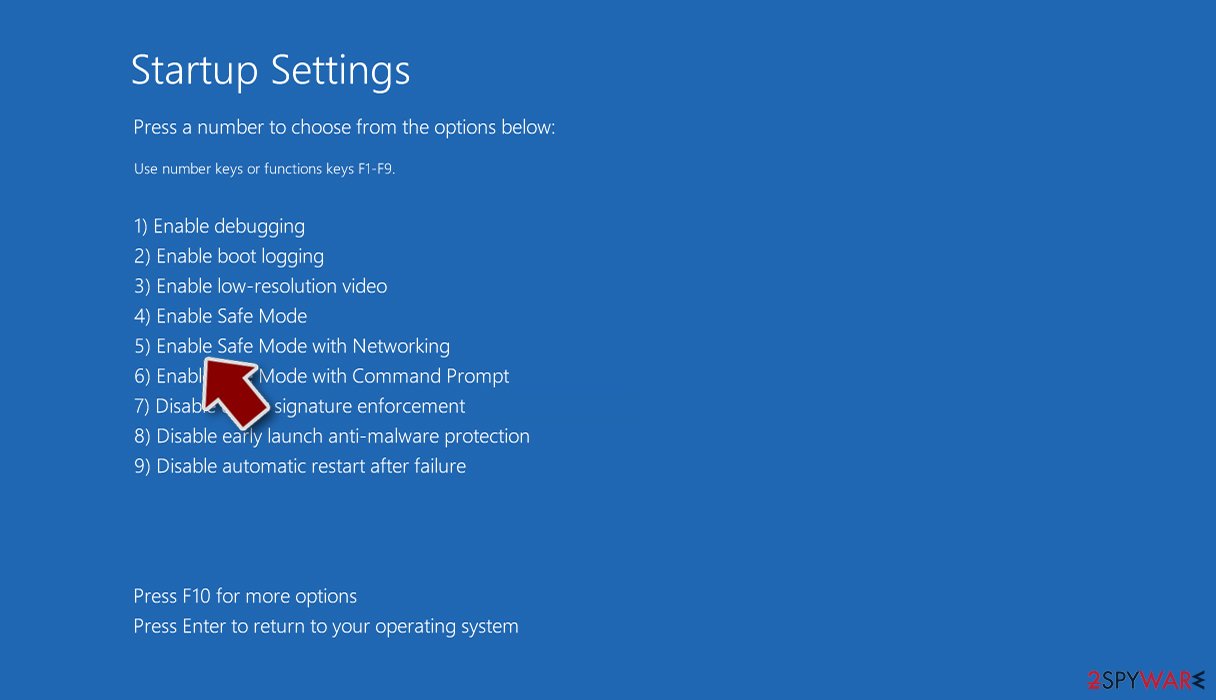
- Press Restart.
- Now press 5 or click 5) Enable Safe Mode with Networking.
Step 2. Shut down suspicious processes
Windows Task Manager is a useful tool that shows all the processes running in the background. If malware is running a process, you need to shut it down:
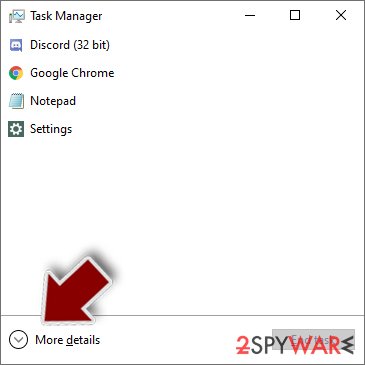
- Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc on your keyboard to open Windows Task Manager.
- Click on More details.
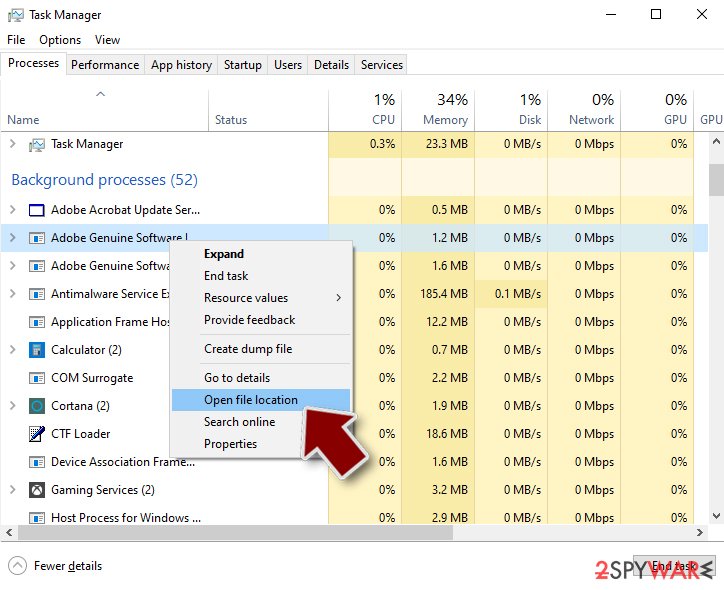
- Scroll down to Background processes section, and look for anything suspicious.
- Right-click and select Open file location.
- Go back to the process, right-click and pick End Task.
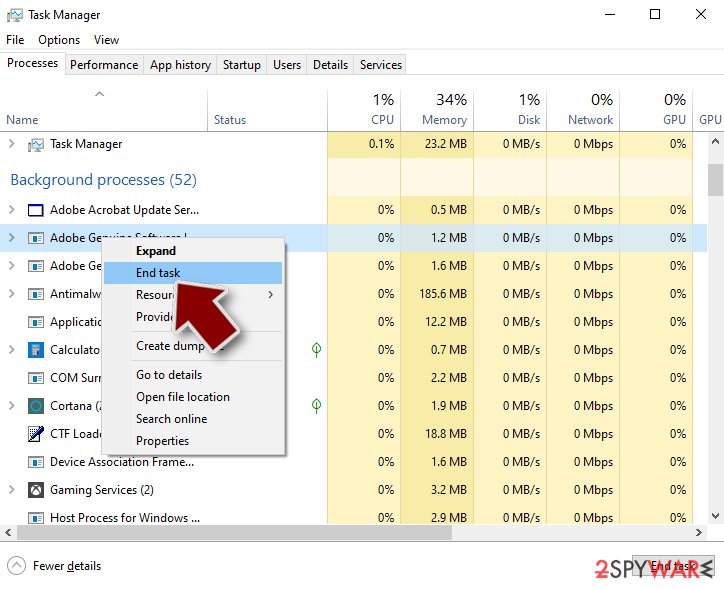
- Delete the contents of the malicious folder.
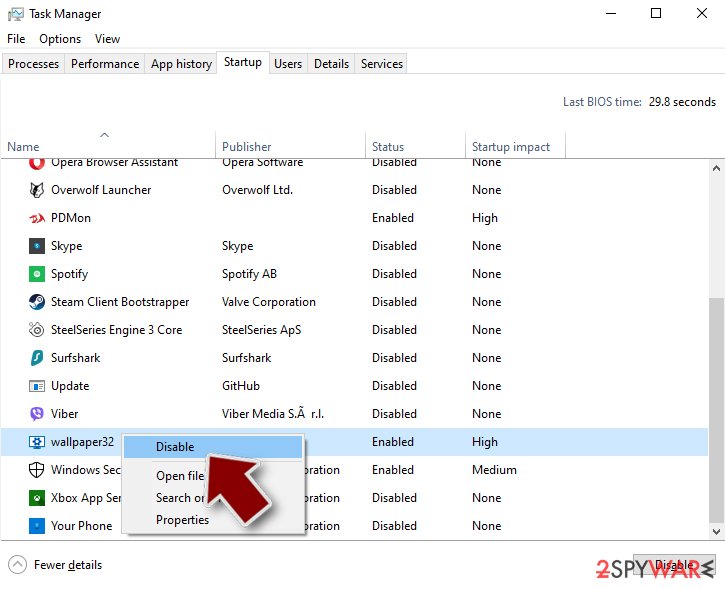
Step 3. Check program Startup
- Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc on your keyboard to open Windows Task Manager.
- Go to Startup tab.
- Right-click on the suspicious program and pick Disable.
Step 4. Delete virus files
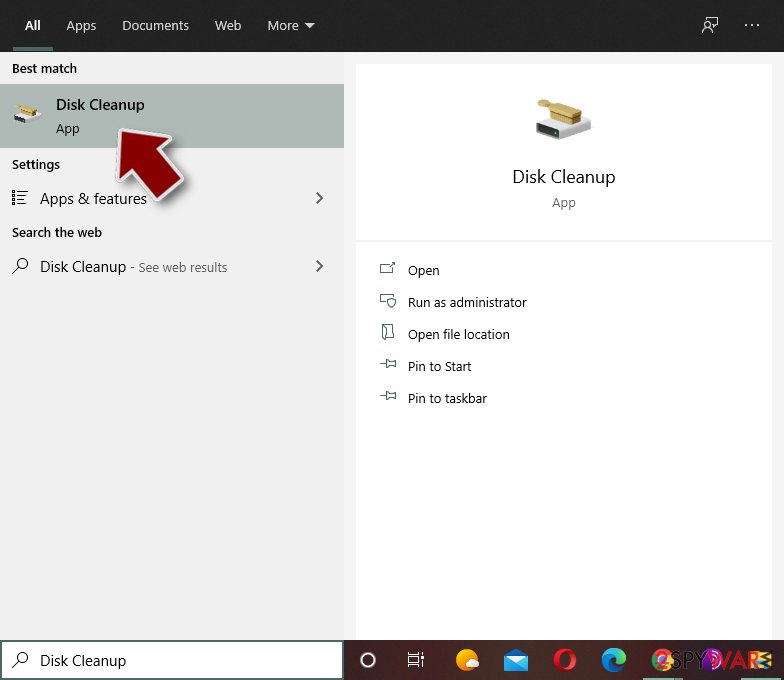
Malware-related files can be found in various places within your computer. Here are instructions that could help you find them:
- Type in Disk Cleanup in Windows search and press Enter.
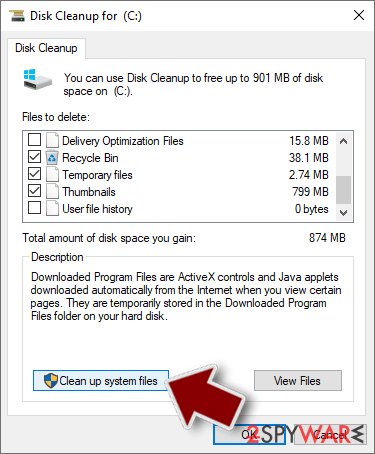
- Select the drive you want to clean (C: is your main drive by default and is likely to be the one that has malicious files in).
- Scroll through the Files to delete list and select the following:
Temporary Internet Files
Downloads
Recycle Bin
Temporary files - Pick Clean up system files.
- You can also look for other malicious files hidden in the following folders (type these entries in Windows Search and press Enter):
%AppData%
%LocalAppData%
%ProgramData%
%WinDir%
After you are finished, reboot the PC in normal mode.
Finally, you should always think about the protection of crypto-ransomwares. In order to protect your computer from Djvu and other ransomwares, use a reputable anti-spyware, such as FortectIntego, SpyHunter 5Combo Cleaner or Malwarebytes
How to prevent from getting ransomware
Do not let government spy on you
The government has many issues in regards to tracking users' data and spying on citizens, so you should take this into consideration and learn more about shady information gathering practices. Avoid any unwanted government tracking or spying by going totally anonymous on the internet.
You can choose a different location when you go online and access any material you want without particular content restrictions. You can easily enjoy internet connection without any risks of being hacked by using Private Internet Access VPN.
Control the information that can be accessed by government any other unwanted party and surf online without being spied on. Even if you are not involved in illegal activities or trust your selection of services, platforms, be suspicious for your own security and take precautionary measures by using the VPN service.
Backup files for the later use, in case of the malware attack
Computer users can suffer from data losses due to cyber infections or their own faulty doings. Ransomware can encrypt and hold files hostage, while unforeseen power cuts might cause a loss of important documents. If you have proper up-to-date backups, you can easily recover after such an incident and get back to work. It is also equally important to update backups on a regular basis so that the newest information remains intact – you can set this process to be performed automatically.
When you have the previous version of every important document or project you can avoid frustration and breakdowns. It comes in handy when malware strikes out of nowhere. Use Data Recovery Pro for the data restoration process.
- ^ Margaret Rouse. Advanced Encryption Standard (AES). SearchSecurity. Information Security information, news and tips.
- ^ Margaret Rouse. Encryption. Search Security. Tech Target.
- ^ Bitcoin. Wikipedia. The free encyclopedia.
- ^ Registry. Computer hope. Free computer help since 1998.
- ^ Chris Hoffman. What Is the AppData Folder in Windows?. How-to Geek. Site that explains technology.
- ^ MAC address. Wikipedia. The free encyclopedia.
- ^ Kim Zetter. Hacker Lexicon: what is a backdoor?. Wired. Monthly American magazine.
- ^ mado ransomware file detection. VirusTotal. Online malware scanner.
- ^ fafa82e7a61c1a516bb83c19d0e5ffce99eac17d34bb9280da34c515e1279653. Virus Total. File and URL analysis.
- ^ Is ransomware driving up the price of Bitcoin?. Emsisoft Blog. Cybersecurity researchers.
- ^ ".nlah" Ransomware infected some files, any news or decryptors for these?. Reddit. The biggest collection of forums.
- ^ Michael Gillespie. #STOP #Djvu #Ransomware w/ extension ".zwer". Twitter. Social Network.
- ^ Ransomware statistics for 2020: Q3 report. Emsisoft. Blog.
- ^ LosVirus.es. LosVirus. Malware news worldwide.
